7 Types of BGA (Ball Grid Array) Packages
BGAs offer efficient, reliable IC connections with superior performance, comprising seven types ideal for high-performance electronics, optimizing space and thermal efficiency.
Among the fast-changing world of electronics, one of the important technologies in integrated circuit assembly is the Ball Grid Array package. BGAs are a reliable and efficient way of connecting sensitive components, offering superior electrical performance, heat dissipation, and space management compared to traditional surface-mount packages. This article examines what BGAs are, their advantages, and the seven primary types taking over the face of electronics.
The BGA is a surface-mount package technology that has an array of small solder balls on the bottom of the package. This sets it apart from the older technologies like QFP with its pins along the edges. BGAs take advantage of the whole surface area beneath the package to gain much higher connection densities and better performance, thus becoming ideal for the high-performance computation machines of today.
Why BGA?
BGA packages solve the problem of interconnecting complex ICs to printed circuit boards. Other interconnect approaches, such as peripherally connecting a chip using pins, are bound to have severe limitations in terms of connection density and reliability. BGAs eliminate these limitations by allowing connections to be made across the entire footprint of the package, dramatically reducing connection density and easing PCB layout.
Besides, although the BGAs are difficult to solder and their inspection visually is not possible due to unreachable joints, this is mostly solved in modern manufacturing of PCBs. The result is enhanced reliability and performance, which become very critical in complicated electronic systems.
Advantages of BGA
There are several advantages associated with the use of BGA packages:
Saving in PCB Space: In BGAs, there can be many more connections under the package and not just on the edges.
Better Thermal and Electrical Performance: BGAs feature added low-inductance power planes and heat-dissipation paths to improve operational reliability for electronic packages.
Enhanced Soldering and Yields: In BGAs, because of widely spaced and larger-sized pads, soldering is easier and offers better production results.
Compatibility and Versatility: BGA packages come in a lot of configurations with regard to application need and production cost to value optimization.
7 Types of BGA Packages
Plastic Ball Grid Array (PBGA)
Because of the cost and performance reliability, the most common type of BGA is the PBGA. The PBGA package has a plastic encasement and offers a very good balance between thermal performance and cost. Hence, it finds a wide application in consumer electronics and telecommunications equipment. The plastic substrate aids in heat management with structural integrity.
Tape Ball Grid Array (TBGA)
The tape substrate in TBGA packages is less rigid than in others, allowing good heat dissipation and great electrical performance. This package solution would be a great fit for data centers or networking equipment applications where high performance is expected. As compared to PBGAs, TBGAs can be more expensive; however, TBGAs are efficiently capable of withstanding thermal loads in high demanding situations, making them justifiably worth the investment.
Ceramic Ball Grid Array (CBGA)
The ceramic material encapsulates CBGAs, offering excellent thermal stability and robustness in extreme environments for both aerospace and military applications where reliability is critical. The material utilized for ceramic can bear high temperature, hence preserving the integrity and life of the electronic components.
Flip Chip Ball Grid Array
The FCBGA technology mounts the chip face-down to minimize distance to the PCB, hence improving electrical performance and signal integrity. This package is very suitable for applications that require high-frequency operations, such as advanced microprocessors and RF modules. FCBGAs offer ultra-fast signal transmission with minimal electrical path lengths, which is critical in high-speed devices.
Micro Ball Grid Array (MBGA)
MBGA plays an important role in miniaturization; the major differences include small ball pitch and compact package size. Package type application typically consists of a small-sized smartphone, smartwatch, wearables, or similar. There is no compromise on the functionality factor but at small factor size. MBGAs help modern gadgets boast sleek designs with typical portability without sacrificing their functionality.
Thin Ball Grid Array
Thin BGAs are designed for low-profile applications, enabling the manufacture of slim and lightweight devices such as ultrathin laptops and tablets. While performance is maintained, TBGAs also support manufacturers in producing cutting-edge designs that appeal to the consumer's desire for portability in electronics.
Wafer-Level Ball Grid Array
WLBGA packages achieve compactness by redistributing I/O paths at the wafer level. Because of that, it offers very highly integrated solutions to mobile and wireless applications like IoT devices. This will further enhance connectivity within a smaller form factor to help drive the trend toward intelligent, interconnected devices.
Ball Grid Array packages have become indispensable in modern electronics, providing enhanced connectivity, thermal management, and utilizing space more effectively. As the technology keeps developing, understanding the nuances of different BGA package varieties, from PBGA to WLBGA, will be critical for engineers and manufacturers looking to maximize performance and reliability. At PCBX, we are dedicated to utilizing our expertise in PCB and BGA technology in helping our partners innovate and compete effectively in today's market landscape.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Compared to THT, SMT offers better miniaturization and weight reduction in any electronic application. With the use of BGA packages, high-assembly density, reliability, and improved performance are achieved; on the other hand, this requires a rework and inspection that is not really common. PCBX specializes in the area of advanced SMT and BGA assembly to help drive modern requirements of compact electronic devices.
Ball Grid Array (BGA) components, such as PBGA, CBGA, CCGA, TBGA, and CSP, provide high I/O density, improved reliability, and high-quality electrical and thermal performance. Quality assembly and functionality are assured since advanced soldering and inspection methods are required, like AXI and AOI. Proper storage and handling shall guarantee the performance of the devices.
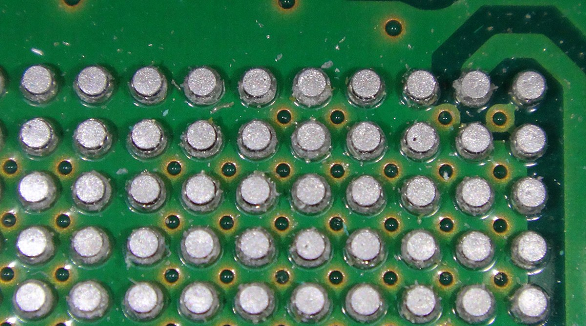
In the late 1980s, when electronics began to shrink, BGA packaging was developed to integrate more connections within a given area. Today, BGA is widely used with high-connection chips—processors being a good example. BGA uses solder balls at the bottom of the chip to connect it to the circuit board. It provides high density along with good heat dissipation and fast signal transmission, one of the main reasons it is ideal for modern electronics. However, it requires precise techniques of soldering in BGA manufacturing.