Aluminum PCB vs. Copper Base PCB
Aluminum PCBs offer cost-effective thermal management for moderate applications, while copper PCBs excel in high-performance electrical and thermal tasks.
Printed Circuit Boards are basically the backbones of modern electronics, providing the necessary framework for electrical connections and supporting components. Among the many types of PCBs, there are two that are pretty distinguished for their characteristic features and applications: A proper differentiation between these two classes of PCBs is essential in the selection of materials in electronic projects, especially in domains that necessitate particular thermal and electrical performance parameters.
Aluminum PCB
Material Composition and Design
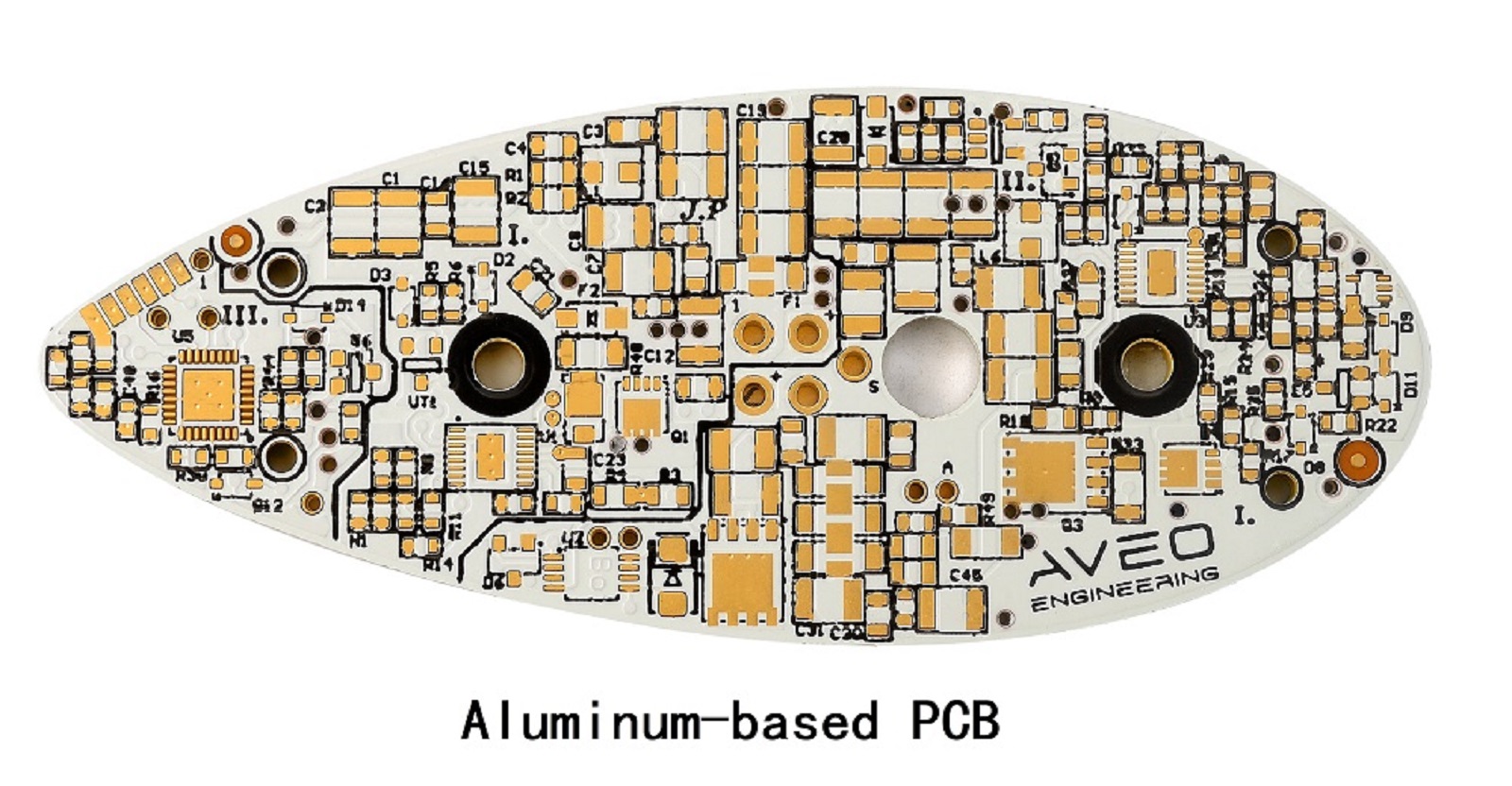
Aluminum PCBs, as generally referred to, also carry the name of Metal Core PCBs or MCPCBs for short. The base layer is laminated with a thin thermally conductive dielectric layer and a thin copper foil, forming a light but highly thermally conductive structure. The peculiar construction of the aluminum PCB makes it perfect for those applications that require thermal management.
Thermal Conductivity
Among the greatest benefits of the aluminum-based PCB is its workmanship regarding the dissipating performance of the temperature. While not as highly thermally conductive, adding thermally conductive dielectric materials further improves thermal performance. Performance for running systems at moderate powers and heat applies in nature to these PCB types, thus being mainly applied in different constructions concerning light-emitting diode lightings and converters of power. Effective heat dissipation reduces the breakdown voltage risk, making these PCBs ideal for low-voltage applications.
Electrical Insulation and Flexibility
In aluminum PCBs, the dielectric layer provides very good electrical insulation. The insulation layer generally contains ceramic or other thermally conductive materials to handle thermal issues along with the electrical separation of conductive layers. In addition, an aluminum PCB has flexible character and can bend in some cases during installation, which is highly desired in cases where area limitations exist, and also for replacing awkward wirings.
Applications
Owing to their excellent heat dissipation and mechanical strength, aluminum PCBs find applications in automotive lighting, audio equipment, and high-power LEDs. The heat and moisture resistance of the material increases the lifespan of the product, hence being favorable in harsh environments.
Copper Base PCB
Material Composition and Design
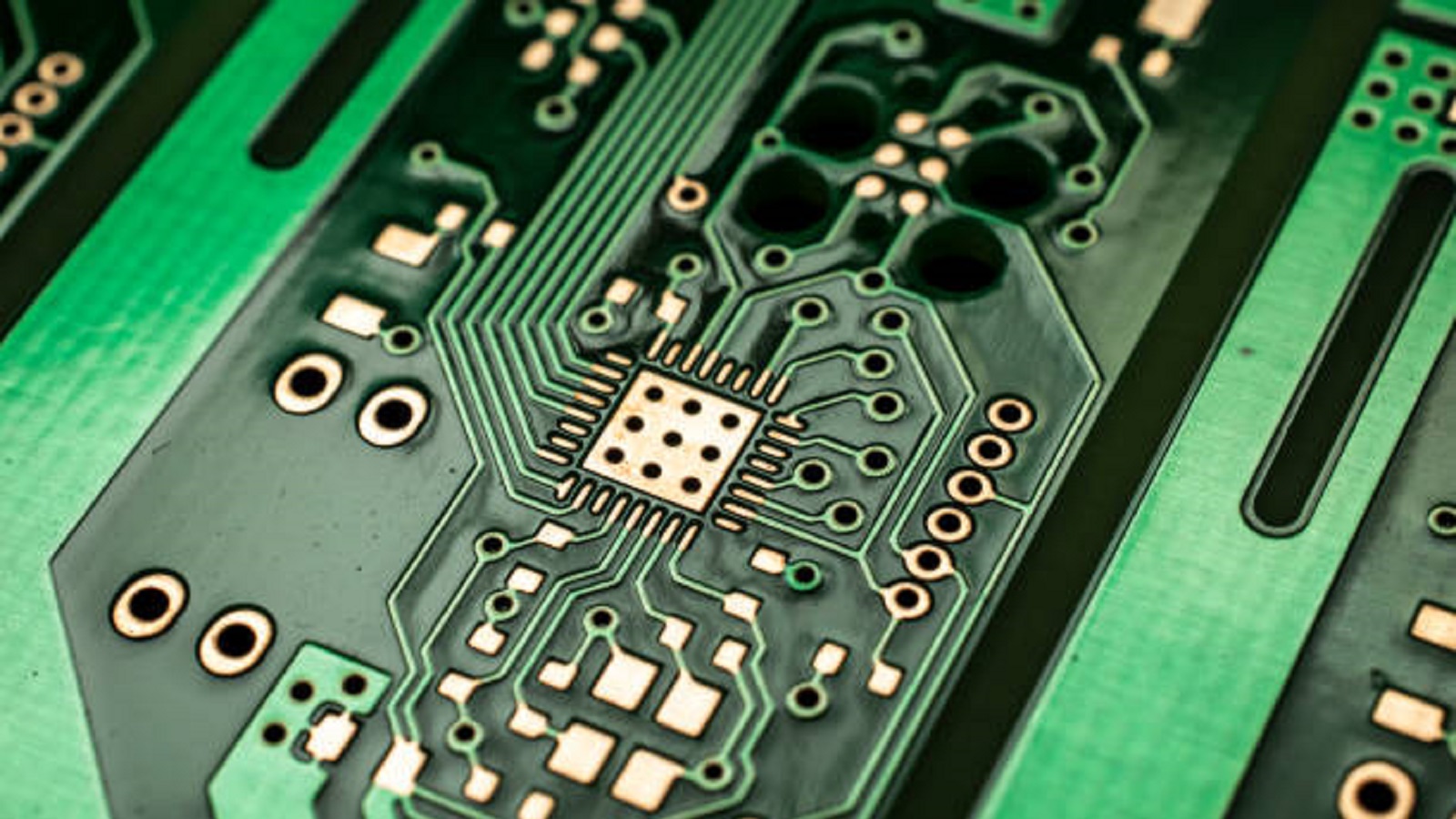
Copper Base PCBs are made with a thick copper layer, providing higher electric conductivity and can bear a higher electric load. Generally, they share the same metal core with the ones in the Aluminum PCBs, but with the addition of thicker dielectric layer and copper foil that contributes to increased mechanical strength and enhances heat dissipation.
Thermal Conductivity and Electrical Performance
Copper has the highest electrical conductivity; hence, copper base PCBs are highly efficient. In general, copper base PCBs are preferred for high-frequency circuit designs, radio frequency applications, and thermally demanding environments due to their high thermal and electrical conductivity. Although heavier and more expensive than their aluminum counterparts, copper base PCBs are capable of withstanding high-performance applications by efficiently conducting and dissipating heat.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Copper base PCBs are sturdy, with high mechanical strength compared to the general FR4. This makes them quite suitable for industrial applications in harsh environments and also for applications where mechanical stress is an issue. Their resistance to mechanical and thermal stress enables them to bear up under severe conditions without loss of functional integrity.
Applications
Copper base PCBs are widely used in industries such as power electronics, RF/microwave circuits, and high-precision communication equipment. Their superior conductive properties enable high-heat-dissipation circuits for high-demanding industrial settings and advanced electronic applications. Copper base PCBs are widely used in applications where precision in electrical performance is the main priority.
Aluminum vs. Copper Base PCBs
Thermal Management
In applications that require thermal advantages, both aluminum and copper base PCBs do so, but in different capacities: the former are good in applications where the weight is an important issue and the temperature rise can be moderate, while for high temperatures, copper-based PCBs can bear extreme temperature because of their high heat conductivity. Therefore, choice between them is highly application-based concerning thermal requirements.
Cost and Weight Considerations
Generally, aluminum is less expensive and lighter compared to copper; hence, PCBs made of aluminum are cost-effective in many applications. The cost efficiency, along with easy handling and installation, makes them advantageous in projects at places where budget and weight are considerable concerns. Copper base PCBs are costlier but offer better electrical performance and, hence, are justified where reliability and longevity are the main issues.
Electrical Performance
In terms of electrical performance, copper base PCBs are far superior to aluminum-based PCBs. This is due to the higher electrical conductivity of copper that makes these PCBs good for applications that require electrical efficiency and minimum transmission loss. For high-frequency and high-power applications or where precision is crucial, copper base PCBs can be used more appropriately.
Application Areas
The choice between an aluminum or copper base PCB mostly boils down to the specific application. Some applications, such as LED lighting, power supplies, and automotive electronics, widely use aluminum PCBs because they ensure optimal thermal management with an economic advantage. Applications such as power electronics, RF circuits, industrial applications, and complex communication systems need better electrical and thermal properties; thus, copper base PCBs have found their place in these areas.
In summary, base PCBs for aluminum and copper have clear advantages that serve different markets based on thermal management, cost, weight, electrical performance, and requirements of the applications. For moderate applications requiring lightweight cost-effectiveness, heat can be dissipated efficiently in aluminum PCBs. Application fields that involve high electrical and thermal conductivities, particularly for high performance, require a copper base; hence, copper base PCBs are ideal.
Understanding such differences allows designers and engineers to choose the most appropriate type of PCB for their projects to offer better performance and efficiency. The choice must be determined by the application in question, in relation to factors such as cost, weight, and thermal and electrical demands. With this, informed decisions can be made to increase reliability, efficiency, and the lifespan of the end product.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Select aluminum PCBs for excellent heat management or FR4 PCBs for cost-effective versatility in diverse electronic applications.

Heavy copper PCBs enhance current capacity and thermal performance, essential for high-power applications in military, automotive, and energy sectors, offering strength and heat dissipation.

Aluminum PCBs are widely used electronic boards with comparatively better heat dissipation properties. The aluminum core cools down the components of the product, thereby improving its performance. These are eco-friendly, light, and strong PCBs and hence appropriate to be used in audio equipment, power supplies, and lighting products such as LED lighting.