Box Build Assembly
Box build assembly integrates components into complete systems, including PCBs, cables, and enclosures, requiring careful planning and quality testing.
Box build assembly is the stage where, in the high-tech world of electronic manufacturing, a collection of components becomes integrated and functional. Sometimes called "systems integration," it involves complete electronic system assembly; this goes beyond the limits of building PCBs with tasks such as cable routing to the installation of sub-assemblies. The article provides a general understanding of box build assembly: the process, main elements of the process, and recommendations on how to provide efficiency and quality.
Box build assembly, variously called systems integration, describes the process of completely assembling an entire electronic or electromechanical product. For example, besides assembly of PCBs, there is installation of sub-assemblies, cable routing or harnessing, and enclosure fabrication. Box build assembly can be very simple, placing a PCB in an enclosure, or complex, such as integrating PCBs with user interface displays.
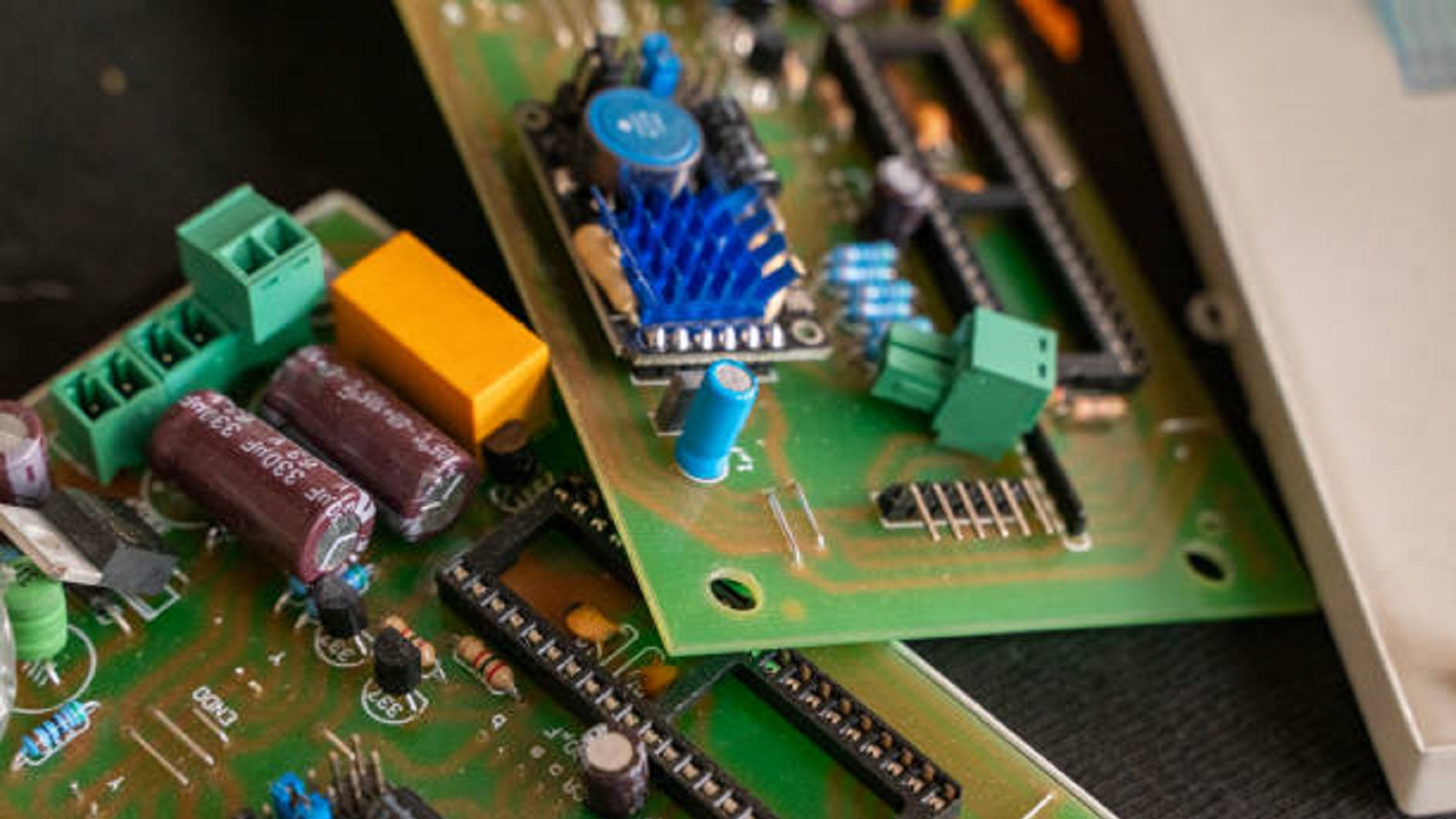
Core Components of Box Build Assembly
Enclosures and Housings: Enclosures protect internal components and can be fabricated from plastic or other metals. They have to consider environmental protection and aesthetics.
Cables and Wire Harnesses: The proper arrangement of cables is an indispensable aspect in guaranteeing that the electronic system will work as expected. It means providing custom cable assemblies that will serve in a particular product.
Sub-Assemblies: Include pre-assembled elements, such as battery packs or motor assemblies, integrated into the final product to ease the work of assembling.
Printed Circuit Boards: While fabricated independently, the PCBs are at the heart of any box build assembly.
Fasteners and Hardware: The proper choice in screw selection, bolts, and various types of fasteners are integral components that keep the parts to assure many years of reliability.
Labeling and Marking: Useful for identification, labeling includes serial numbers, barcodes, and instructions regarding safety.
Key Steps in the Box Build Assembly Process
Design and Planning
With adequate design and planning, effective box build assembly can be realized. This entails creating assembly drawings, material selection, and liaison with design engineers to ensure manufacturability. A collaborative approach aids in identifying potential design improvements that reduce issues during assembly.
Component Procurement
Obtaining the right components. The EMS shall plan and deliver all the required materials on time considering quality, price, and compatibility issues.
Assembly
Enclosure Preparation: Putting up the enclosure for receiving the interior components.
Component Integration: Installing the PCBs, sub-assemblies, and all other components and accordingly doing the proper cable dressing to route the cables nicely.
Securing Fastening: Screwing all components in their respective places using appropriate hardware.
Testing
This includes a number of rigorous tests, such as electrical, functional, and stress testing, to ensure the assembly has met all the functional and safety standards.
Quality Control
The whole quality control process finds defects in each product to ensure that it meets the standard of the industry. It is important to ensure that the integrity and reliability of the final product are maintained.
Packaging and Shipping
Effective packaging strategies are crucial for protecting the product during shipping and ensuring it reaches the customer in pristine condition.
Streamlining the Box Build Assembly Process
To efficiently manage the box build assembly process, several key elements should be considered:
Product Dimensions: Detailed information about the size and weight of the product helps in planning handling, storage, and shipping strategies.
3D CAD Models: The use of computer-aided design models helps in the visualization of the final product and conversion of designs into clear assembly instructions, reducing possible errors.
Bill of Materials (BOM): A detailed BOM helps in identifying all the materials required, which assists in efficient procurement and anticipating production challenges.
Prototype/Sample Unit: Providing a prototype aids in refining the assembly process, especially when documentation or other resources are limited.
Testing Use Cases: Identifying the necessary tests, including functional and stress tests, assures functionality and safety.
Shipping and Packaging Details: Preplanning packaging and shipping saves any after-sales time wasting and maximizes the assembling process in logistics for added overall efficiency.
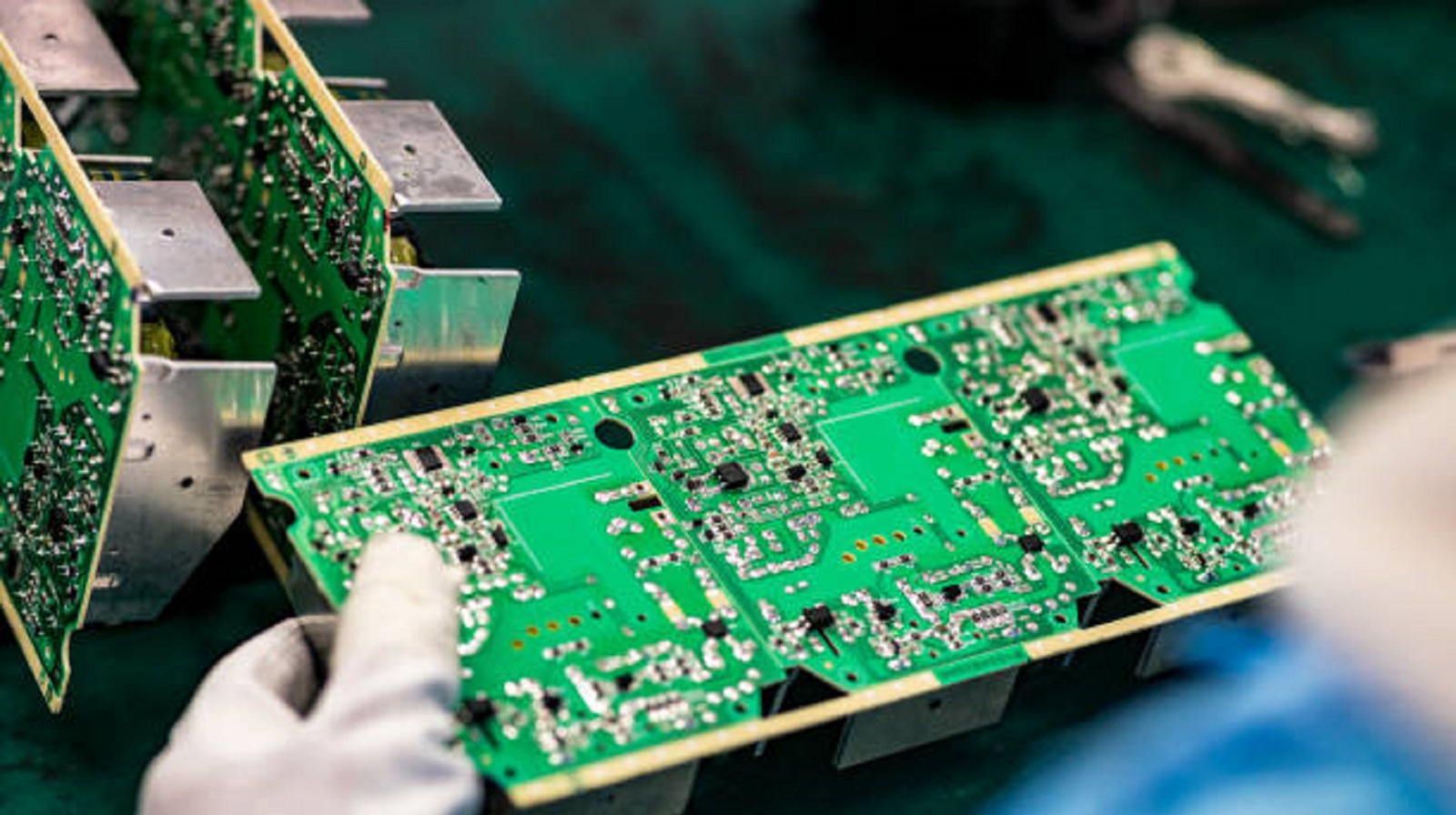
Box build assembly covers an important area in electronic manufacturing that includes more than just building a PCB into a fully integrated system. With careful planning, good documentation, and effective process management, manufacturers can get high-quality electronic systems produced efficiently for meeting exacting standards. As technology continues to evolve, precision and adaptability during box build assembly will be the keys to success in electronic products from many diverse industries. The reason companies must address these core principles is so that their systems will meet customer expectations and be the driver of innovation in the electronics market.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
PCBs are crucial in electronics, providing a platform for component interconnection. Mastering component identification ensures effective design, troubleshooting, and maintenance, vital for device reliability and performance.
Through-Hole Technology (THT) mounts electronic components by inserting their leads through pre-drilled PCB holes and soldering them. While durable and ideal for harsh conditions, THT is less space-efficient than SMT.
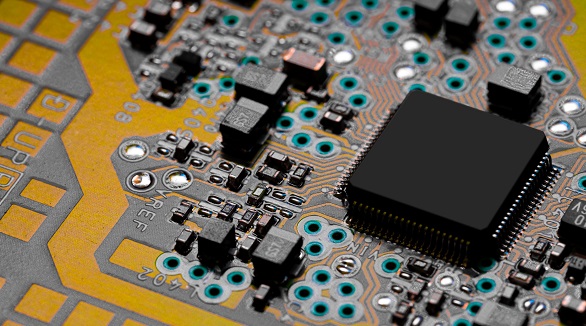
The article introduces the SMT (Surface Mount Technology) assembly process and future trends. Key steps include solder paste printing, chip mounting, reflow soldering, cleaning, inspection, and rework. Future trends highlight fast, flexible systems, green practices, and high-efficiency, intelligent systems. SMT's potential revolutionizes electronics manufacturing with wide industrial applications.
