Carrier PCBs
Carrier PCBs are crucial for data modulation, multiplexing, and network integration, supporting efficient and robust telecom infrastructures globally.
In today's connected world, the need for rapid and dependable communication infrastructures is always in demand. Complex systems like these have their heart in the form of Carrier PCBs, which are important components managing the transmission of data over huge networks. Carrier PCBs form the structural basis of telecommunication, allowing the smooth passage of information and making the digital services we use daily possible. The article explores the important function of Carrier PCBs, from what they are and how they are used in technology, to design considerations and their future, in the light of modern telecommunications.
Carrier PCBs are special types of circuit boards, which are specifically designed to handle large data volumes. They form the backbone of telecommunications networks because they modulate, route, and support data signals that will enable communication. From using the internet to exchange data to managing voice calls or facilitating video broadcasts, Carrier PCBs are part of the infrastructure on which local and global information depends.
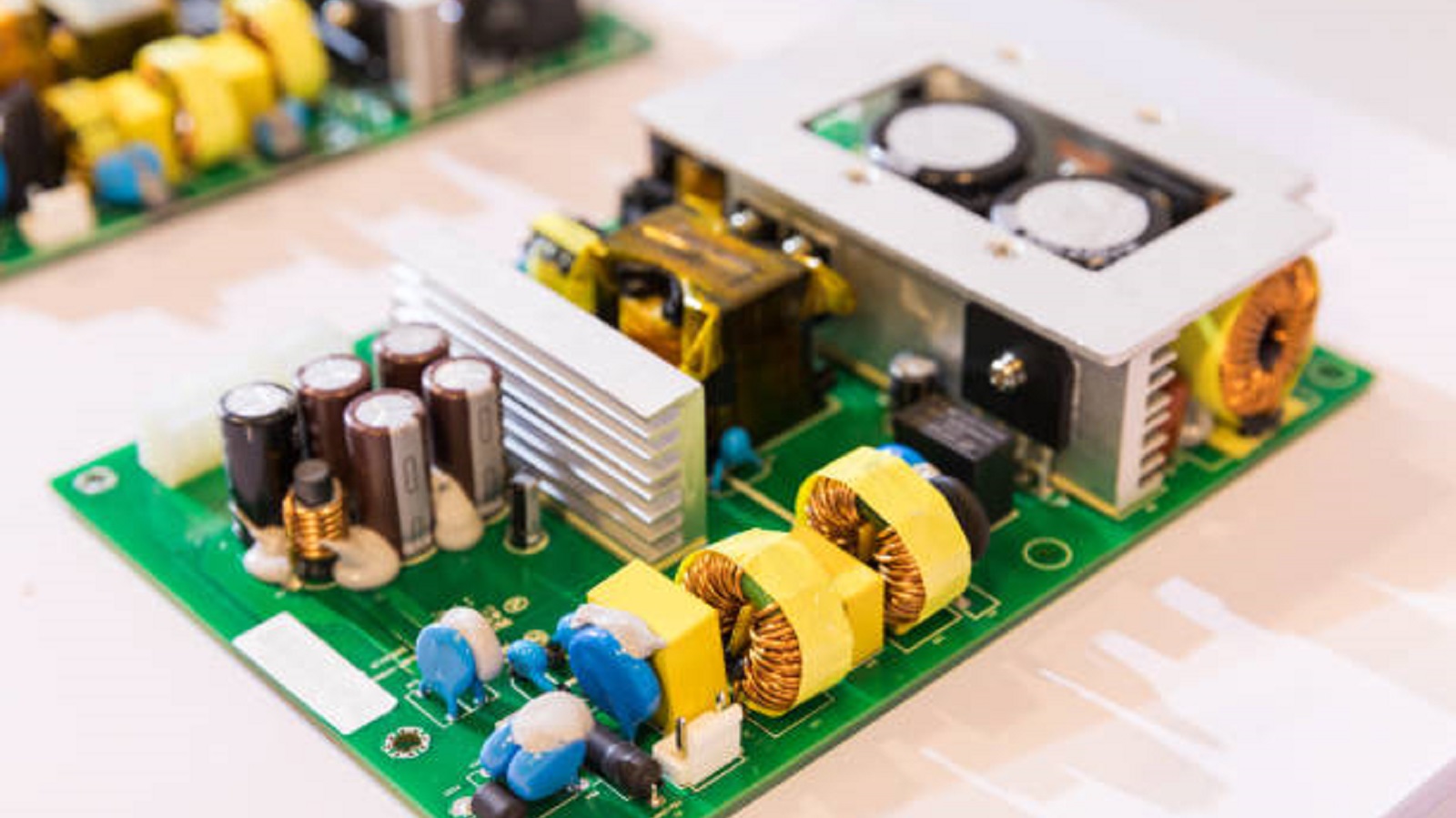
Key Functions of Carrier PCBs
Data Modulation and Routing: Carrier PCBs handle the modulation of signals at different frequencies so that the data, whether voice, video, or other forms, is effectively transmitted over the telecommunications network. These boards change the signals into suitable frequencies for the transmission of data.
Multiplexing Capabilities: The most important feature of Carrier PCBs is their capability to employ multiplexing techniques. These techniques, including TDM and FDM, allow multiple communication channels to be transmitted over a single medium simultaneously. This enables the best use of bandwidth and enhances network efficiency.
Systems with Mechanical Support and Stability: Carriers beyond the role in the modulation and routing of signals provide physical support and stability to electronic components within a system. This structural integrity ensures reliability and robustness of the telecommunication hardware.
Integration into Carrier Networks: Carrier printed circuit boards are fixed within large network systems that couple different elements and work harmoniously in coordination. They easily integrate devices of various service providers into a unified integration of regional and international communications. Thereafter,
Carrier PCB Applications
The Carrier PCB finds fundamental usage in the following:
Telecommunication Infrastructures: They support key functions in public-switched telephone networks and private branch exchanges, thus ensuring the reliable routing of voice and data signals.
Internet Services: These Carrier PCBs are important parts of infrastructures of internet service providers, aiding in effective management and controlling data-traffic quantity.
Broadcast Systems: In broadcasting, these PCBs enable the transmission of television and radio signals, which provide as the foundation for frameworks that distribute material to viewers all over the world.
Mobile Communication: Carrier PCBs play an important role in maintaining cellular network capabilities, such as signal routing and managing the complex infrastructure necessary for smooth mobile connection.
Design Considerations for Carrier PCBs
To achieve the optimum performance and dependability in telecommunications systems, many critical design elements must be considered while creating carrier PCBs:
Material Selection: Robust materials, such as FR4, are commonly employed because to their longevity and ability to withstand high-frequency demands seen in telecommunications jobs. The proper selection of material is always important for the integrity and functional aspects of circuit boards across a wide range of conditions.
Efficient Designing of Multiplex Capabilities: Efficient design to carry out multiplexing capabilities, enabling carrier PCBs to handle various streams of data simultaneously and optimize their communication channels.
Circuit Diversity and Redundancy: Circuit diversity and redundancy need to be planned. Carrier PCBs enable the overall network to resist services from being interrupted due to any disruption or system failure by creating multiple data pathways. Network engineers will have to be very interactive with service providers to comprehend routing complexities and ensure diverse circuit paths.
Managing Temperature: Since the operations that are involved in data modulation and routing are high-power, sufficient thermal management is required. There needs to be effective heat dissipation mechanisms that will prevent overheating for consistent performance.
The Importance of Carrier Networks
Carrier networks are the infrastructure with hardware that support the transfer of data over distances and act as communication service providers. They are a backbone of modern communication, which connects different networks together to provide data, voice, and video services to end-users. Much like multi-channel logistics companies that help facilitate the process of delivery for goods, carrier networks govern the smooth flow of information.
Future Directions and Trends in Carrier PCB Technology
With the advent of technologies like 5G and others, the demand for data transmission is only going to increase, which in turn will increase the role of Carrier PCBs. Some key future directions include:
Advanced Materials and Designs: New materials and innovative designs will result in more efficient and high-capacity Carrier PCBs. Enhanced performance in thermal management and dielectric will enable these boards to bear an increase in data load and more speed.
Increased Automation and AI Integration: Automation and artificial intelligence in the management and optimization of carrier networks will be done on a larger scale. Carrier PCBs will have to integrate seamlessly with smart systems that can dynamically reroute and manage data flow efficiently.
Improved Network Resilience: The more interconnected the whole world is in communication, the more urgent it becomes to handle failures on the network. Achieving this will significantly depend on carrier PCBs that create back-up pathways or systems needed to minimize possible service dislocation.
In summary, carrier PCBs form the primary technology on which the building of various telecommunications is based; they facilitate communication over reliable, efficient, and wide-reaching networks. From making the facilitation of data transmission smooth to supporting complex multiplexing, these PCBs ensure the robust operations of innumerable communication systems around the world. As the world of telecommunications continues to get an uptick, Carrier PCBs are going to contribute hugely in meeting the demand that arises out of this and further advancement for the future of the communication infrastructure across the globe. They will continue at the center of innovation in improving modern telecommunication network capabilities through further innovation.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
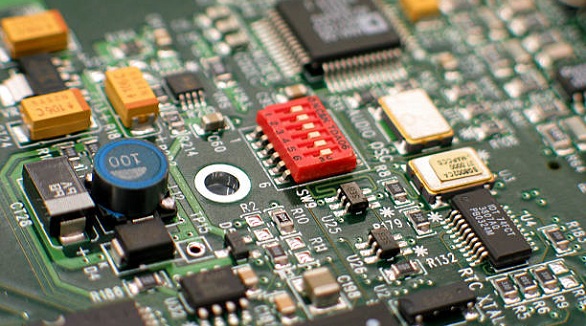
DIP switches, cost-effective and manual, enable easy configuration of device modes, offering flexibility and simplicity for various electronic applications.
High-frequency PCBs are crucial for fast, reliable tech, enhancing performance in telecoms, aerospace, and more with advanced materials and precise designs.
Amplifier PCBs enhance audio signals in devices like headphones and theater systems using components like transistors and capacitors for clear sound.