Current Limit Control Circuits
Current limit control circuits safeguard electronics by regulating excess current, ensuring device safety and reliability across various applications and industries.
In today's fastpaced technological world, safety and the reliability of electronic devices remain a topmost priority. At the heart of such a premise lies a very critical current limit control circuit. A current limiting circuit is vital whenever there is potential damage due to excessive current draw, which is one of the common problems associated with power supplies, battery chargers, motor drives, and a host of other applications. Such circuits, while acting to regulate current flow, help protect devices from potential damage, enabling them to have a longer and more efficient life. In this paper, the internal structure, methods, design considerations, and wide application of a current limit control circuit are presented.
The current limiter control circuit is designed to limit the current through an electronic system to some predetermined value. The protection provided by regulation avoids over-current conditions that may cause component failure or give rise to dangerous situations. Monitoring in current actively intervenes before too much current is drawn to keep such circuits functioning and safe for electronic devices.
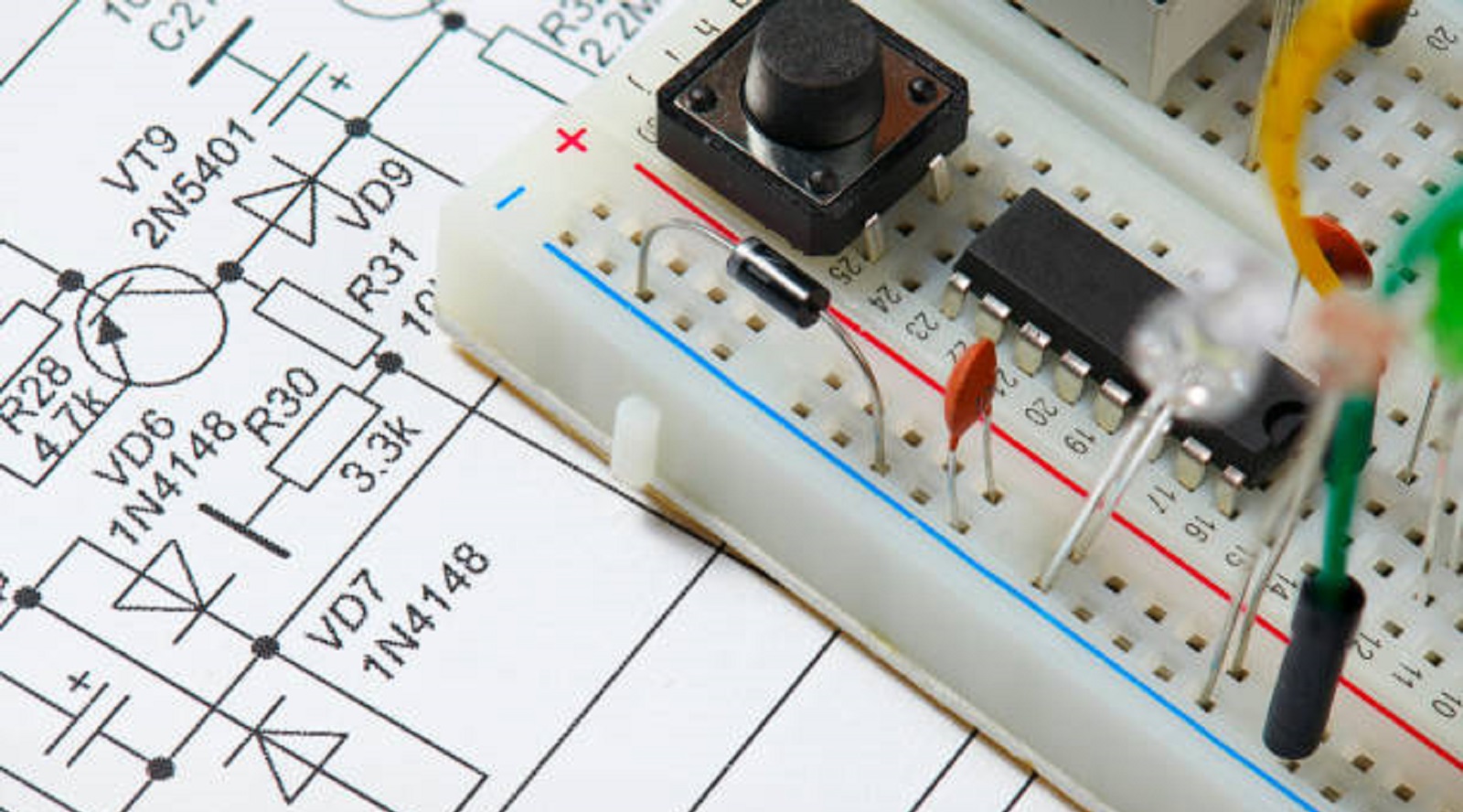
The Role of Current Limiting
Current limiting is useful for a number of reasons:
Overcurrent Protection: Against short circuits, fault conditions, and inrush current that may cause damage to the circuit.
Safety Enhancement: Ensuring current within a safe boundary reduces the chances of overheating, fire, or explosion.
Operational Continuity: The ability to keep systems functional when there is an overload condition below full capacity.
System Reliability: This will help the electronics function in a well-mannered fashion without quirky behaviors based on unstable levels of current.
Current Limiting Approaches
Some of the following methods can ensure effective current limiting, along with a few advantages and applications, as follows:
Power Supply Current Limiting
Basic protection: It provides an internal current-sensing resistor to monitor output current.
A feedback loop reduces output when current exceeds set thresholds, preventing excess current flow.
Current Sensing with Pass Element
Utilizes a pass element, normally a transistor, for the regulation of current flow.
A sense resistor measures current, and a feedback circuit adjusts the pass element to stay within limits.
Foldback Current Limiting
The output voltage is reduced with an increase in the load to maintain a constant current to avoid thermal overload.
Electronic Current Limiting
This uses fast-acting solid-state devices such as op-amps, MOSFETs, and comparators for accurate and quick-acting regulation.
Allows for complex limiting profiles and multiple threshold levels.
Design Considerations for Current Limit Circuits
In designing a current limit control circuit, a number of parameters are to be taken into consideration: setting of current limit levels for maximum allowable current in normal operations and minimum sustaining level during overload; load characteristics include steady-state, inrush, and transient currents; response time must be fast to avoid damage but should not cause false trips; and power dissipation includes thermal management for heat generated by sense elements.
Protection Coordination: Combine with other protection devices such as fuses or circuit breakers for complete protection.
Monitoring and Status: Provide diagnostic indicators to monitor the system in real time.
Component Tolerances: Choose components that have tolerances suitable for the application to ensure accuracy.
Environmental Factors: Design to be insensitive to temperature variations, humidity, and noise.
Example Current Limit Control Circuits
Simple DC Power Supply Current Limiting
Uses a low-side pass transistor as a variable resistor.
The voltage across a sense resistor is proportional to the load current, and this signal drives the transistor in order to keep the current within limits.
Dual-Threshold Limiting
Power and fault current limits offer flexibility.
Allows higher inrush current at power-up and enforces stricter limits during normal operation.
Precision Programmable Limiting
Uses a microcontroller to program a DAC in order to set the reference levels.
It provides the capability of an adjustable current limit using a closed-loop feedback system.
Setting and Implementing Adjustable Current Limiting
Making current limits adjustable adds versatility to the design:
Sense Resistor Tuning: Change the resistance to alter the voltage drop for setting current limits.
Reference Voltage Adjustment: Use potentiometers or other digital means to change the comparator or amplifier reference inputs.
PWM/Duty Cycle Control: In switch mode power supplies, change the PWM duty cycles to control peak current levels.
User Interface: Provide knobs or digital controls for easy changes in threshold settings.
Improvements to Current Limiting Accuracy
Some ways to obtain an accurate current limiting include:
Precision sense resistors.
Filtering on the inputs to the sense voltage to reject noise.
Amplifiers are made using chopper stabilization.
Trim circuitry that electronically trims off the offset voltage and thus increases accuracy.
The current mirror eliminates the current-setting resistor-related error.
Feedforward compensation methods will immediately compensate the real voltage drop when load changes, making it feasible in such load-sensitive applications like switching-mode converters.
Applications of Current Limit Control Circuitry
Nowadays, current limiting control circuits find their vital role in many applications to protect and enhance performance in the following fields:
Switch Mode Power Supplies: Which limit peak inductor current to assure stability.
Battery Chargers: Regulating charging currents to prevent overcharge.
LED Drivers: Managing current through LEDs to maintain consistent lighting while managing thermal performance.
DC Motor Drives: Preventing damage from high current during rotor stall.
Automotive Electronics: Ensuring safety across electronic control units.
Audio Amplifiers: Protection against short circuits in speaker lines.
Industrial Equipment: Provide customized protection in laboratory and industrial power supplies.
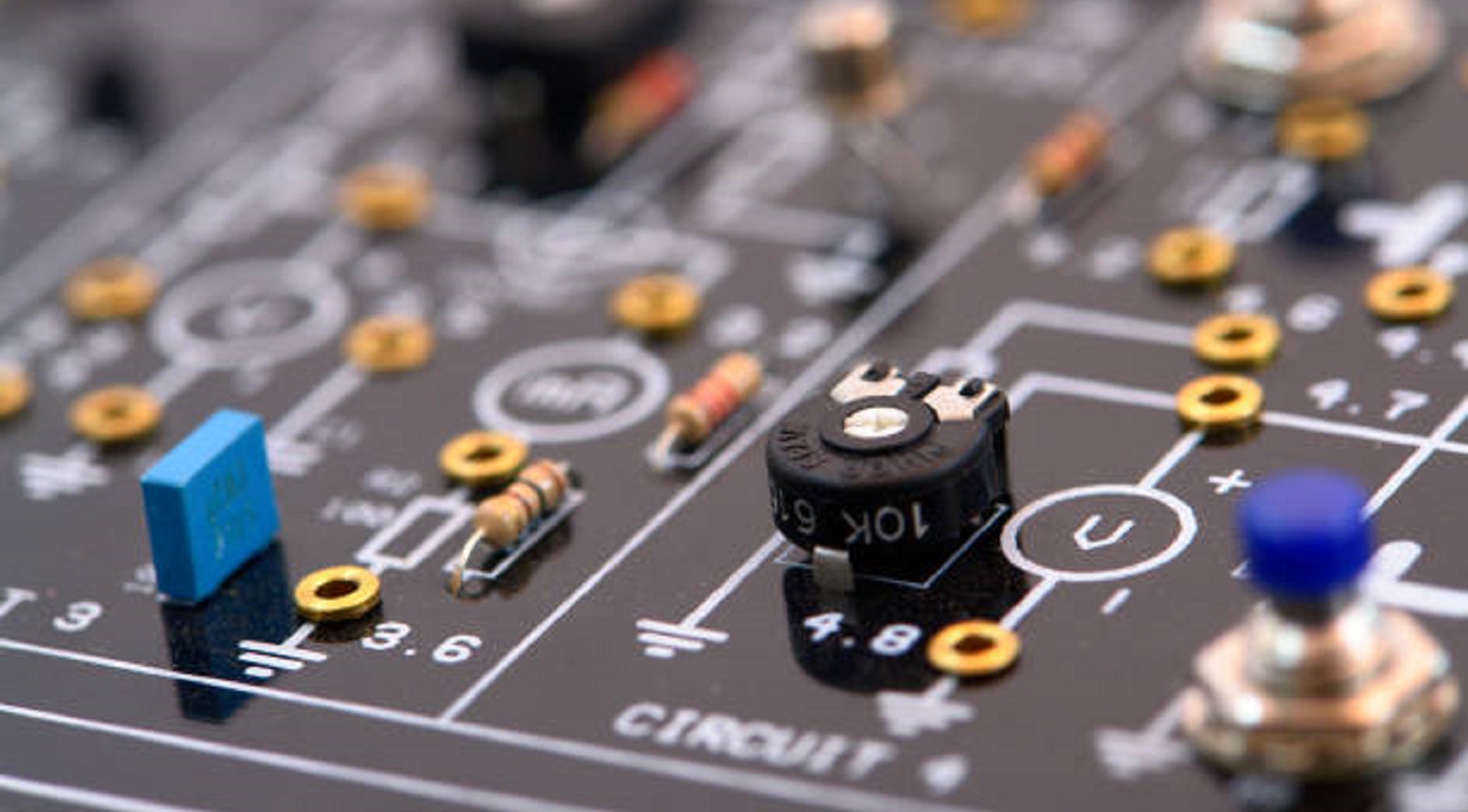
Current limit control circuits are the backbone of the safety and efficiency of modern electronics; thus, they are invaluable to the furtherance of technology along many fields by making devices durable enough to operate under multiple conditions safely. Effective design of a current limit solution must balance response speed, precision, cost, and adherence to regulations; it is variously implemented with classic linear and modern digitally-controlled circuits. At PCBX, we remain committed to supporting designers in their effort to create safe and reliable electronic systems, well into the future of technology.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
CTI measures PCB material's resistance to electrical tracking, ensuring safety and reliability in electronic circuits, crucial for design and manufacturing.

Capacitive circuits store and release energy, stabilize voltage, filter signals, and manage power flow, making them vital for modern electronic systems.
High-speed PCBs (>1GHz) are crucial for advanced electronics like 5G and data processors. Key practices include ensuring signal integrity, controlling EMI, and maintaining power integrity for reliable performance.