DIP Switch PCB
DIP switches, cost-effective and manual, enable easy configuration of device modes, offering flexibility and simplicity for various electronic applications.
In the dynamic field of electronics design, versatile and customizable are the necessities. Among components, the DIP (Dual In-line Package) switch provides a manual and sure method of configuring the various operational modes for electronic devices. DIP switches practically solve the main problems in device functionality adjustments while retaining simplicity and a low-cost approach.
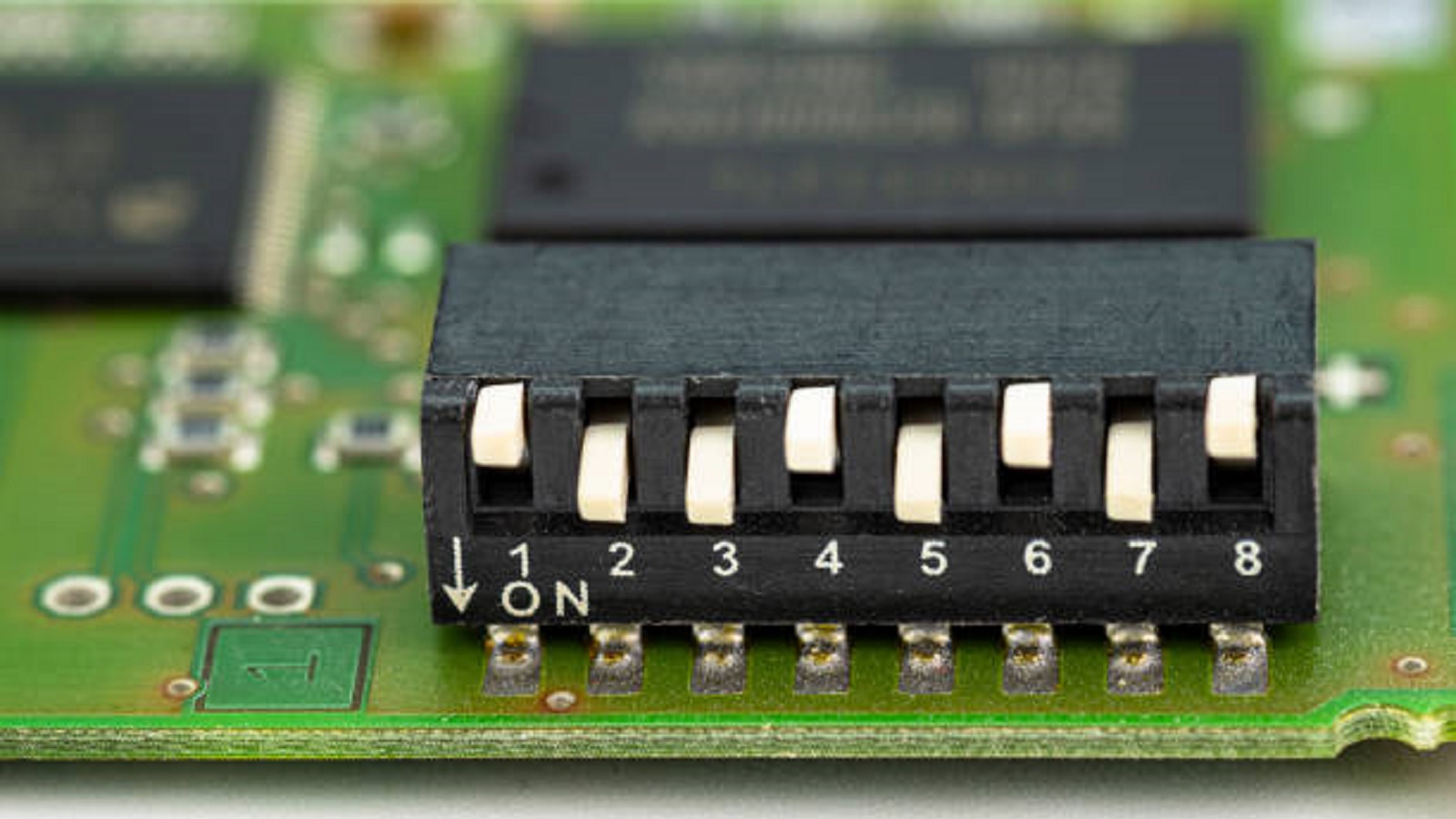
A DIP switch is a variety of electronic component in which a number of small, manually operated switches are enclosed in a dual in-line package type configuration. Each switch in the series may be enabled or disabled independent of the other to alter the flow of electrical current across a PCB, enabling different modes of operation. Enclosed in a compact thermoplastic polymer housing, a DIP switch resembles a series of miniature toggle switches, small light switches lined up.
How Does a DIP Switch Work?
DIP switches work by manually opening or closing electrical contacts. This is done with the help of simple two-terminal (on/off) switches within the DIP housing. Each switch has contact pins arranged in two parallel lines (hence "dual in-line") that connect directly to the PCB. Users can toggle these switches manually in order to set device functions or modes.
Within one DIP switch unit, toggles can range from one to 32 or more. Each toggle can be set differently, thus enabling a great number of combinations and operation modes. The movement of switching actuates a flexible suspension, which opens or closes a passive contact inside the module. In this way, a very simple but effective way of changing device settings is provided.
Advantages of Using DIP Switches
Cost-Effectiveness: They are generally inexpensive compared with their alternatives, like programmable chips or control panels, making them practical for applications that have tight budgets.
Simplicity and Visibility: They provide an immediate visual indication of settings and require no software to adjust, ensuring ease of use.
Durability: Options for robust gold contacts enhance durability and efficiency, extending the lifespan of switches in demanding environments.
Flexibility: It is available in configurations from single to multiple poles, and thus DIP switches are very versatile for different design needs. Replaceability: They are convenient upgrades for older jumper systems and easily adjustable, saving time in busy production workflows.
Applications of DIP Switch PCB
Even with the presence of more sophisticated ones, the DIP switch remains a significant option for several scenarios because it is rather simple and fairly inexpensive. They offer an easy way to configure PCBs across many different applications:
Computer Hardware and Accessories: DIP switches are commonly used for expansion modules, motherboards, and peripherals like modems and video cards. They allow easy setup of device parameters for compatibility and functionality.
Universal Remote Controllers: Used to avoid electrical interference, ensuring the selection of the correct frequency in the operation of devices.
Industrial and Testing Environments: Ideal for test circuits, prototypes, and industrial applications where quick changes in configurations are needed.
Design Considerations
When using a DIP switch in a PCB design, the available space on the board, the current ratings of the switch, and physical access that will be required to manipulate it should all be important considerations. The designer needs to consider whether the switches support the necessary electrical load and electrical specifications for the operation of the device.
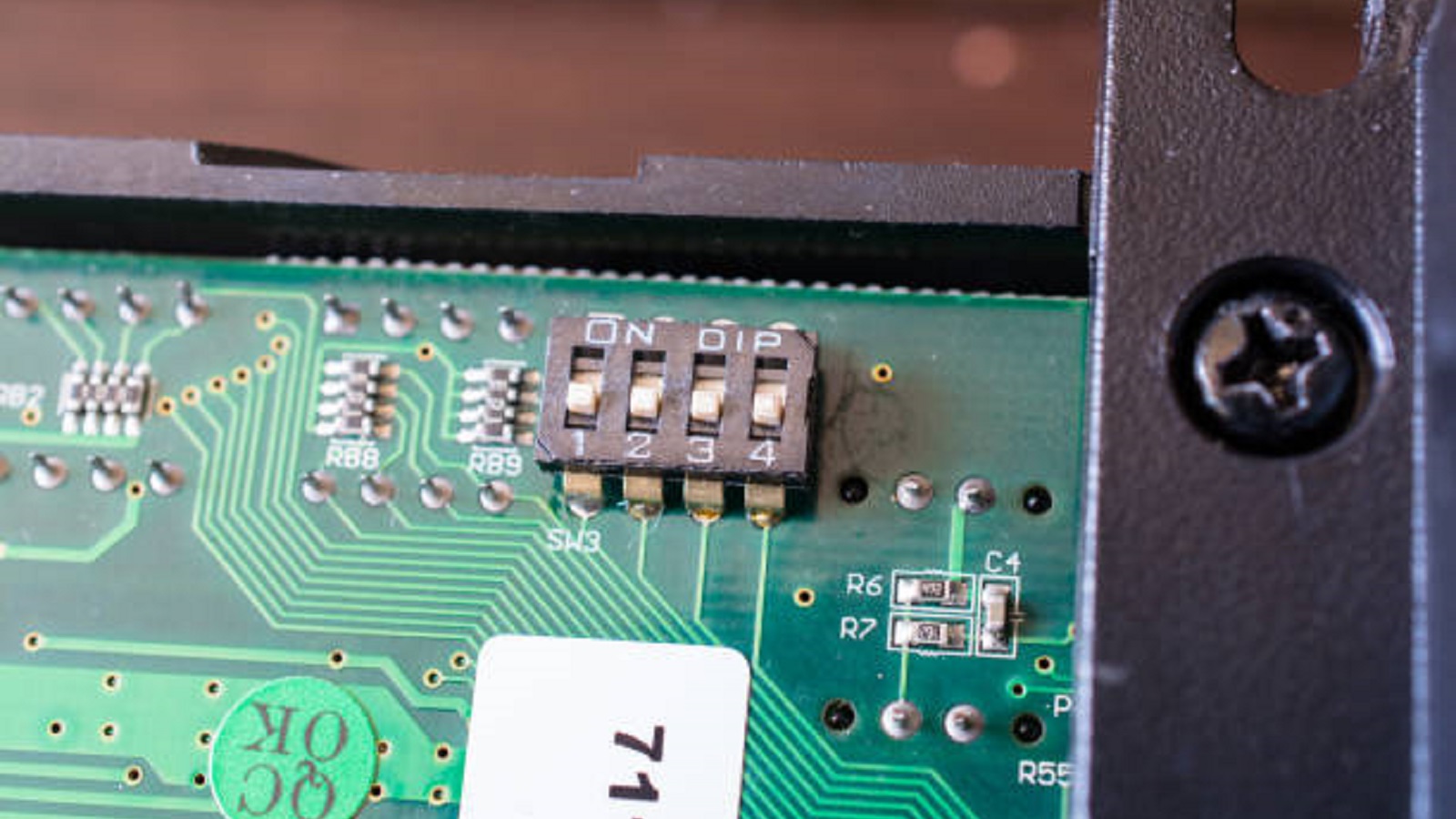
While digital solutions have increasingly replaced some of the traditional applications of DIP switches, their role in providing a user-friendly, reliable, and cost-effective means for configuring electronics endures. In design, testing, or industrial settings, understanding and leveraging the full capabilities of DIP switches can greatly extend the functionality and flexibility of electronic devices and systems. It is important to recognize these components to ensure that designs meet the demands of modern electronic applications.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Black FR4 PCBs offer aesthetic and functional benefits, including light blocking, heat dissipation, and enhanced signal performance, suitable for electronics.
SMD soldering mounts small components on the PCB surface for compact, automated designs but has high setup costs and repair challenges. DIP soldering uses through-hole components for robust, easily repairable, lower-volume applications.
PCBX offers fast, high-quality turn-key PCB prototype assembly services, including fabrication, component sourcing, and testing, all at competitive prices, to accelerate product development.
