Differences Between Flexible Solder Masks and Coverlay FPC
Flexible solder masks offer cost-effective flexibility, while coverlays provide durable protection for FPCs, catering to different application needs.
In the dynamic realm of electronics, flexible printed circuits (FPCs) are the solution for creating multi-use and reliable electronic devices. Since consumers demand more compact, light, and power-efficient devices, the need for sophisticated materials and processes to cater to these parameters increases proportionately. It is here that coverlays and flexible solder masks become the savior. Both are employed to shield and improve the performance of FPCs but in different manners, suitable for different applications.
Flexible Solder Masks
Composition and Application
Flexible solder masks are usually made of liquid photoimageable (LPI) materials. They are noted for their ability to create a thin, conformal coating capable of adhering to the flexible circuit surface. The solder mask is applied via a photolithographic process that involves coating the circuit, exposing it to ultraviolet light through a photomask, and developing the mask to expose soldering pads and vias needed.
Advantages
Cost-Effectiveness: Flexible solder masks rank among the most significant cost advantages. They are less expensive than coverlays and therefore suitable for projects where the budget is not high.
Thin Profile: They add negligible thickness to the FPC, which is particularly useful for applications with lightweight and low-profile requirements.
Accuracy of Application: The photolithographic procedure allows for high accuracy, which is required in the case of closely packed circuit layouts. The accuracy allows for smaller solder pads and trace spacing, which is optimal in terms of space use in the circuit. Limitations
Flexible solder masks have their limitations even though they have their benefits. They are not as physically protective as coverlays and are not as effective in tightly bent applications because they can crack after a while.
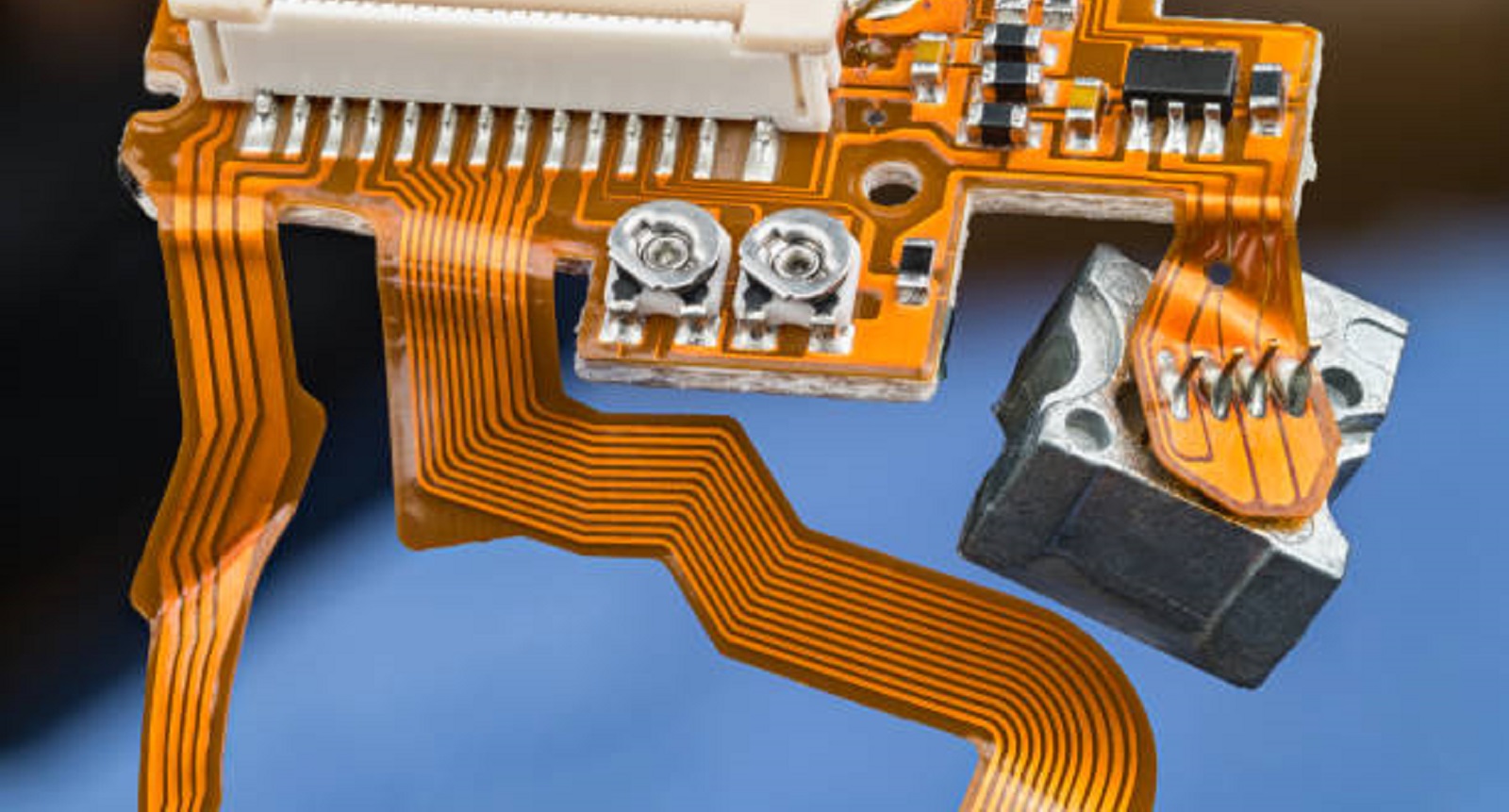
Coverlay
Composition and Application
Coverlay, often made of polyimide film held together with adhesive, provides excellent protection for flexible circuits. Unlike solder masks, coverlays are solid films that are pressed on to the circuit using heat and pressure. Pads and vias require careful cutting through—either mechanical or laser—to expose them for soldering.
Advantages
Durability and Protection: Coverlays have greater mechanical strength and durability and are thus most suitable for circuits with dynamic flexing and harsh environments. Their thermal endurance at high temperatures also makes them suitable for high-temperature applications.
Chemical Resistance: The chemical resistance of the polyimide material in coverlays is very high, providing excellent protection in harsh environments.
Thermal Management: Owing to their material properties, coverlays also aid thermal management, further ensuring reliability and durability of the circuit.
Limitations
Coverlays are more expensive than flexible solder masks owing to the complexity associated with the lamination process and the sophisticated equipment employed for making precise openings. Furthermore, application of a coverlay can cause adhesive squeeze-out, which has to be treated with utmost caution so as not to degrade the performance of the circuit.
Major Differences Between Flexible Solder Masks and Coverlay
Material Composition and Application Process
Flexible Solder Masks: Made of LPI materials, they offer a thin, precise covering through a photolithographic process. This allows cost-effective manufacturing and the capability to handle intricate circuit layouts with fine features and tight spacing.
Coverlay: Made from polyimide films, coverlays entail mechanical lamination and punching of holes, providing a high physical barrier. The extra processing steps contribute to their higher cost and thickness.
Physical Properties and Flexibility
Thickness: Solder masks contribute minimal extra thickness, maintaining FPC flexibility, whereas coverlays contribute more thickness but provide better durability and protection.
Flexibility vs. Protection: Solder masks are best suited for flexible circuits and high resolution features, while coverlays are best suited for applications needing mechanical strength and resistance to bending and environmental conditions.
Cost Considerations
Flexible solder masks are less expensive, offering an economic solution for applications where cost is a major factor. Coverlays, although costly, are well worth the expense for applications needing higher reliability and protection.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Coverlays are better for environmental and mechanical protection, which is critical in harsh or high-temperature applications. Solder masks offer basic protection suitable to less demanding conditions.
Application Considerations
Flexible solder masks vs. coverlays ultimately boils down to requirements of your specific project:
For Flexibility and Dense Circuitry: Flexible solder masks are optimal when high circuit density and flexibility are required without sacrificing budget considerations.
For Mechanical Resilience: In the event that the circuit will be exposed to physical strain or harsh environments, coverlays are a better option due to their superior protection and environmental resistance.
With its dynamism, knowing flexible solder mask vs. Coverlays is vital to optimize the performance and reliability of flexible printed circuits in the world of PCB design.
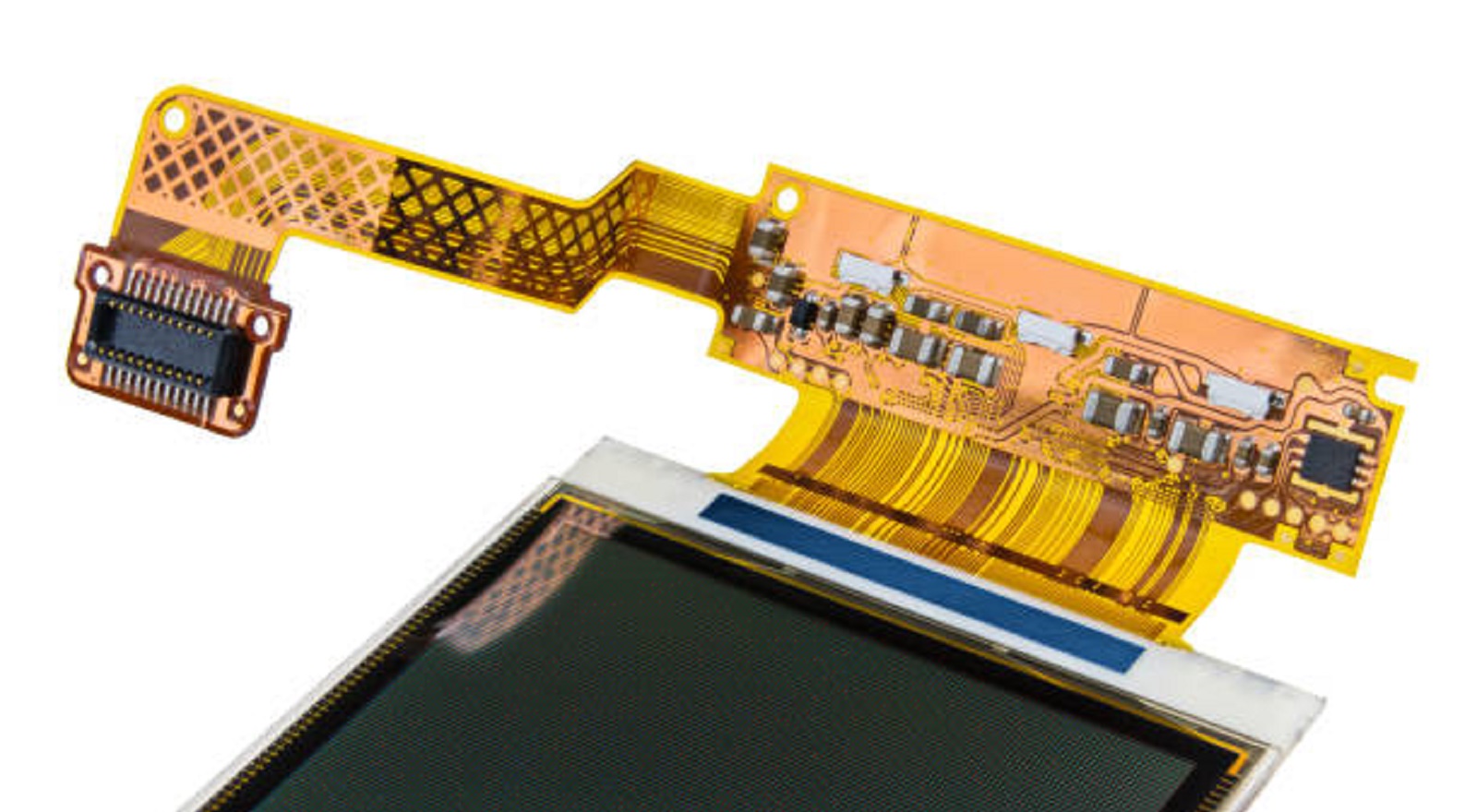
As electronics become more integrated and complex, selecting the correct material for your FPC is even more crucial. By matching the material to your specific application requirements, you can ensure that your designs meet functional requirements and cost targets, leading to successful and reliable electronic products.
At PCBX, we specialize in offering you exceptional PCB solutions that are tailored to your specific requirements. Having worked with coverlays and flexible solder masks, we can offer you unparalleled support and guidance in choosing the most suitable materials for your flexible circuits. Committed to quality and innovation, PCBX is your partner in achieving the best design and manufacturing outcomes. We invite you to receive a quote from PCBX today and see the value of doing business with industry leaders dedicated to meeting your electronic design needs.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Flex PCB thickness affects performance, offering flexibility, compact design, and durability but demands careful material selection and precise engineering.

FPC stiffeners provide rigidity to prevent deformation, protecting components and ensuring reliability in flexible circuits used in electronics and wearables.

Flex PCBs fit into devices, saving space, while Rigid-Flex PCBs combine flexible and rigid parts, ideal for varied applications. PCBX offers custom designs, rapid prototyping, and high-quality manufacturing.
