Functions and Types of PCB Plates
PCB plates enhance electronic devices' structure and function, crucial in keyboards for stability and connectivity. Materials and designs aid efficient decisions.
Printed circuit boards are the backbone of nearly every electronic device in this modern world, providing both structure and electrical interconnectivity. In the design and functionality of an electronic system, a PCB plate plays an essential role, especially in specialized applications such as mechanical keyboards.
The Role of PCB Plates
The plate is serving numerous functions concerning the electronics, both mechanically and electrically:
Mechanical Support: PCB plates provide a stable mechanical base for the attachment of components, reducing flex or deformation, which enhances durability in devices like keyboards, preventing keys from excessive flex during use.
Electrical Connectivity: Beyond physical support, PCBs provide electrical connectivity through copper traces that replace complex wiring; this feature is integral to signal integrity, reducing electromagnetic interference and maintaining clear communications between parts.
Heat Management: Good thermal management is part of many applications today. While not all plates serve this purpose, those integrated with heat-dissipating materials help maintain component performance and longevity.
Compact Design: Because components and interconnects are contained on a single board, PCBs enable more compact and efficient device design, crucial in modern technology.
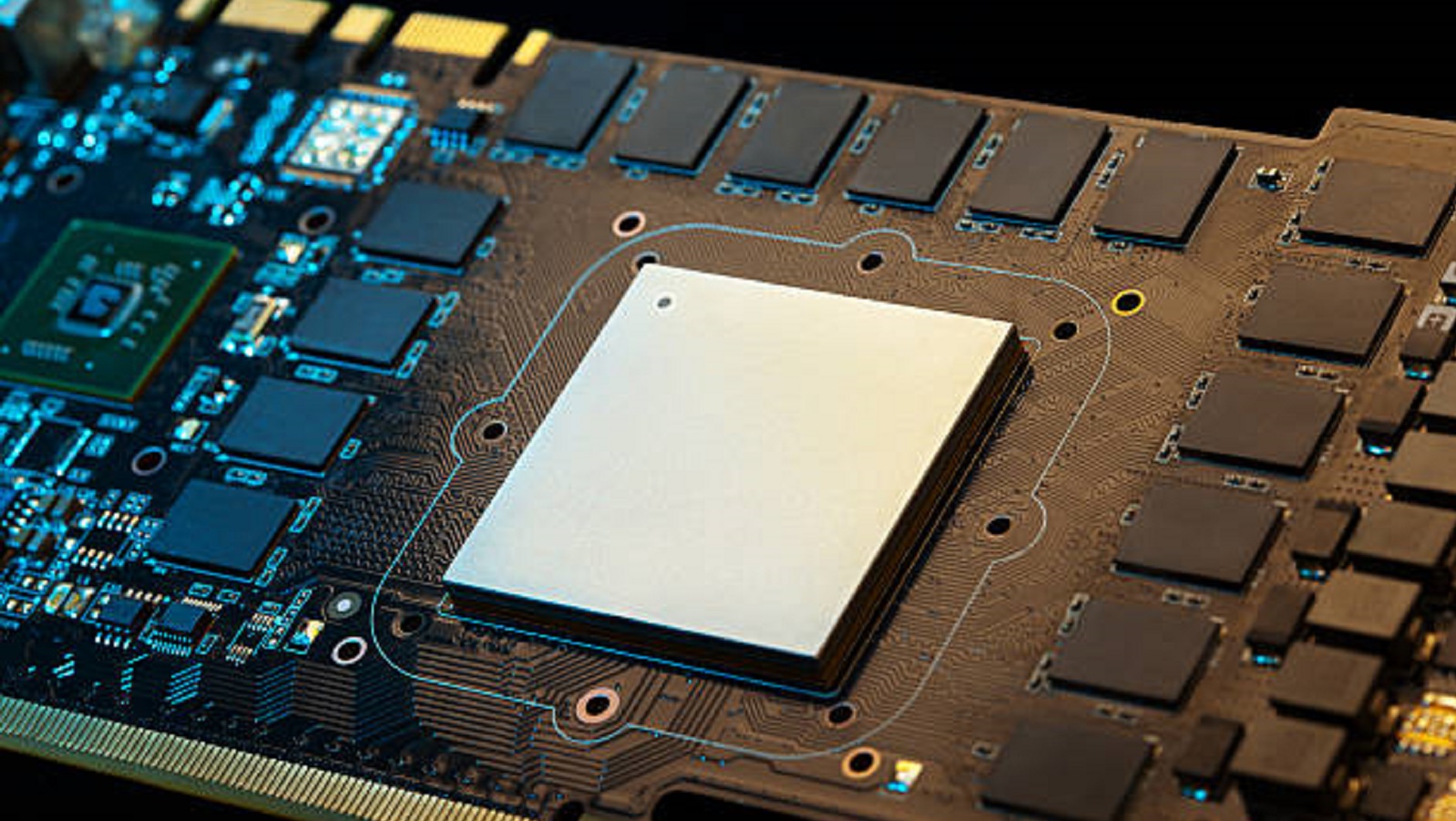
PCB Plate Applications in Keyboards
PCB plates now serve the following purposes in the context of mechanical keyboards:
Extra Assistance: A PCB plate, often known as a metal plate put over the PCB of a keyboard, supports the switches for consistent operation and gives the typing surface more structural strength.
Flex Prevention: A PCB plate provides a robust platform that does not flex, essential in larger keyboards where there is naturally more propensity for movement.
Switch Stability: Plates also stabilize the switches, fundamental in achieving consistent key presses. This usually translates to stability; the type of material applied can also have a difference in both feel and sound upon use.
PCB Plates Materials
Different materials used in the manufacture of PCB plates will provide a variety of characteristics, including the following:
Aluminum: A widely used material, aluminum is durable and easy to shape, making it ideal for both custom and prebuilt keyboard plates.
Brass: Despite its tendency to tarnish with time, brass is known for its hardness and strong feel.
Carbon Fiber: Known for its distinct mechanical qualities, carbon fiber is lightweight and robust, offering a springy tactile reaction.
Polycarbonate: For users who want a softer, more flexible feel when typing, polycarbonate is a kind of material that offers flexibility.
Types of Keyboard Mounting
The type of mounting impacts design complexity and user experience:
Plate-Mounted Keyboards: In this design, switches are mounted to a metal plate before being soldered to the PCB. This method gives way to increased durability, especially in larger keyboards, at the possible expense of additional time and resources required.
PCB-Mounted Keyboards: Switches are soldered directly to a PCB without the use of any separate mounting plate. It's cheaper and offers the possibility for customization, though it's less stable on larger keyboards.
PCB Types in Keyboards
Keyboard PCBs may vary based on the needs of the design:
Through-Hole PCB: Traditional PCBs with extra soldering of resistors are definitely best left to advanced builders.
Hot-Swappable PCBs: These are boards on which switches can be mounted without soldering, favored for easy customization by beginners.
Soldered PCBs: These are employed on custom-made keyboards, where every switch needs to be soldered in for security, and support 5-pin switches.
PCB plates are very important parts in an electronic system, especially keyboards, because they add structure and performance to them. While not every keyboard features a PCB plate, the role of them in both structural and electrical support manifests their importance. Knowing all the different types of materials and designs enables responsible decision-making in the realm of electronics design with respect to fulfilling device requirements for reliability and efficiency.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article

FR4 is a key PCB substrate with excellent electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and thermal resistance. It's valued for its balance of cost and performance, crucial for a wide range of applications.

PCB recycling is vital to reduce environmental hazards and recover valuable materials, especially copper. Effective methods include mechanical, chemical, and thermal processes, significantly benefiting sustainability.
PCB panelization consolidates multiple PCBs into a larger board, improving manufacturing efficiency and reducing waste. Techniques include V-scoring and tab-routing. Proper design enhances assembly, testing, and cost-effectiveness.
