Hex Inverter ICs
Hex inverter ICs are vital in digital electronics for signal inversion, logic functions, oscillators, and data transmission, enabling efficient circuit designs.
Logic gates are the backbone of complex circuit designs that drive modern technology in this fast world of digital electronics. Among such critical components, the hex inverter IC is a versatile and indispensable element in so many electronic applications. HEX inverter IC is known to invert signals and carry out basic logics, hence it is a significant building block in a digital system. This article covers the function, application, and subtleties of hexadecimal inverter integrated circuits to learn about their roles at the very center of electronics design.
A hex inverter IC is a package that integrates six individual inverter gates into one package and usually comes in the form of a 14-pin dual in-line package. The word "hex" designates that there are six inverter circuits within one package. Each of these gates provides the mere function of inverting an input signal, such that a change in logical '1' becomes '0', and vice versa. Such a simple yet basic operation does much when managing and manipulating digital signals in several applications.
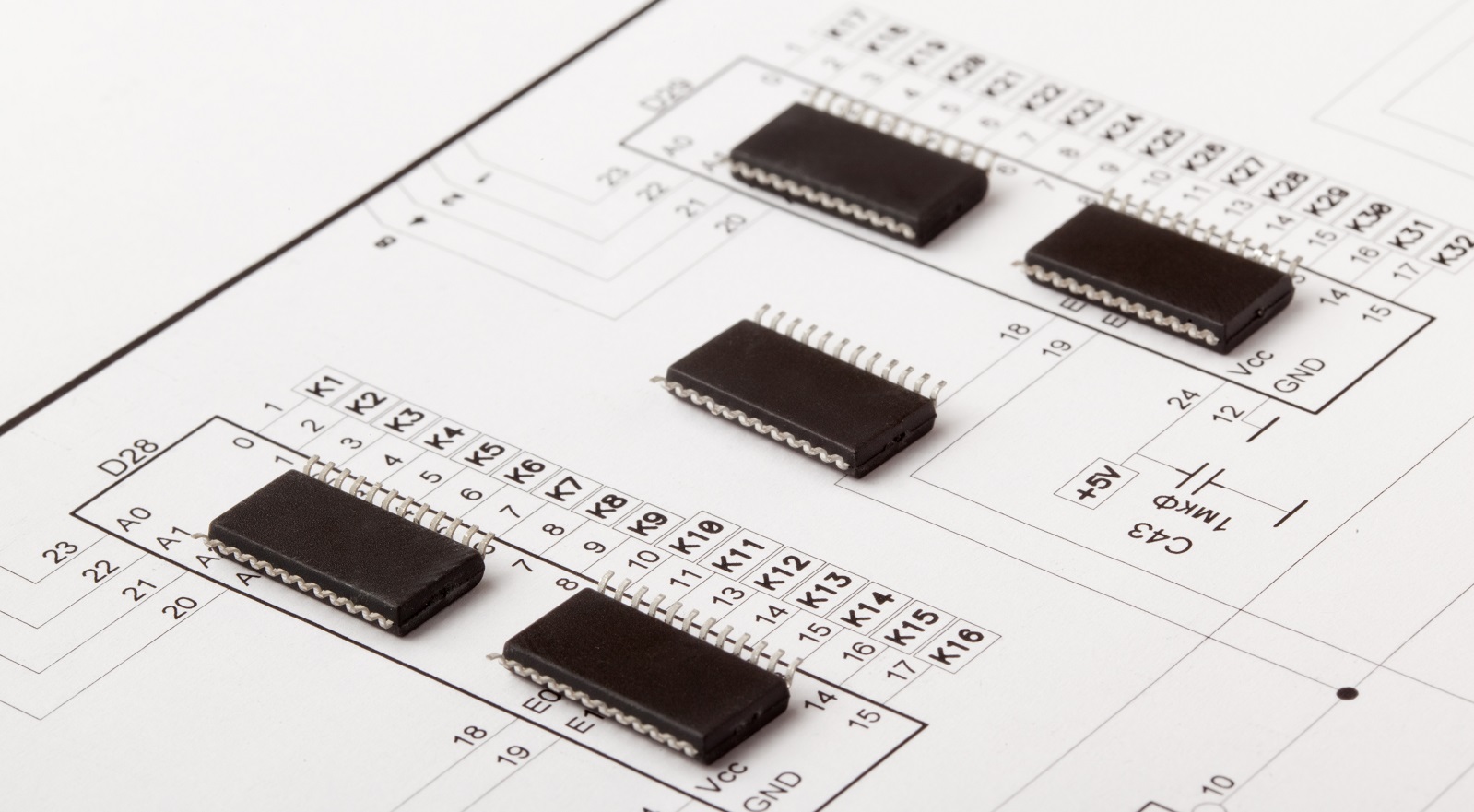
Functions and Features of Hex Inverter ICs
Hex inverter ICs have some functions that make them useful during work with digital electronics. Among such functions is:
Signal Inversion: Their main function of signal inversion creates ground on which the other logical operations or control processes act in the digital circuits.
Amplification and Delay: The hex inverter is normally used along with other components in order to amplify the signals or to introduce some necessary delays with a view to managing the timing of signals.
Level Shifting: These ICs provide logic-level shifting to allow different systems that have different voltage requirements to communicate properly.
Types of Hex Inverter Integrated Circuits
There are many kinds of hex inverter integrated circuits used to fulfill particular demands in electronics design with unique features:
IC-4069: A CMOS-based hex inverter that fits low-power applications, especially where the drive of medium-power TTL (transistor-transistor logic) is not needed.
IC-7414: This is equipped with Schmitt trigger inputs to provide fast-changing digital signals against slow transitions for operation quality improvement even in a hostile noisy environment.
IC-7404: A faithful, all-purpose package, IC 7404 with basic inverter functions, with buffering capacity at the input-may prove relevant in training practice for educational use but also industrially.
IC-7405 and IC-7407: These variants offer open collector and buffer input, respectively, for high voltage applications and noise immunity in more hazardous industrial surroundings.
Applications of Hex Inverter ICs
Hex Inverter IC finds its application over a wide area in both the Digital and Analog domains:
Digital Logic Gates: Connecting a couple of hex inverting logic circuits provides designers the power to make complex NAND, NOR, and XOR logic gates required for complex digital logics.
Oscillators: Hex inverters are part of oscillator circuits that generate square and sine waves for clock signals and timing through feedback loops made up of resistors and capacitors.
Data Transmission: Such ICs provide support in converting digital signals at different voltage levels and thereby help protocols such as RS-232 reach their respective TTL levels from high-order voltages, say, between -12V to +12V.
Signal Conditioning: Hex inverter, together with comparators, can convert analogue signals into digital output and thereby enhance clarity and efficiency of processing in signal conditioning applications.
Power Management: Hex inverters regulate voltage levels within power management systems and may provide feedback signals to maintain stability in operation across the connected components.
Specialized Hex Inverter IC Examples
IC-74HCT04: Popularly used because of its fast switching action on account of Schottky-clamped inputs; for applications requiring very accurate timing, minimum propagation delay is required.
IC-4049: This inverter buffer operates both in CMOS and TTL levels, logic-compatible, dual-in, and comes in the two most common package types: PDIP and SOIC.
CD4069: Offers high impedance inputs, immunity to noise, suitable for applications that require logic inversion and pulse framing in a noise-sensitive electronic environment.
Key Features and Design Considerations
Operating HEX inverter ICs means knowing the electrical characteristics and operational parameters of these chips. Key characteristics include:
Propagation Delay: Very significant for applications requiring timing. As an example, IC-74HCT04 has a propagation delay of approximately 29ns and is thus very suitable for clock and waveform generation.
Power Consumption: Especially in CMOS varieties, low power consumption is critical to battery-operated and portable applications, where it enables very extended usage without frequent power recharge.
Voltage and Current Ratings: Their limits in terms of voltage and current ratings shall strictly follow if ICs are crucial for the assurance of long-term performance.
Package and Pin Configuration: Knowledge of an IC package that includes DIP, SOIC, etc. in structure with pin layout shall allow for integration to any PCB design accurately.

Hex inverter ICs are still the bedrock of digital electronics, ranging from basic signal inversion, which is arguably the most significant, to a host of other functionalities that are so important in today's modern electronic apparatus. From their use in the realization of digital logic gates to oscillators, transmission of data, conditioning of signals, and power management, hex inverting finds its place to show the flexibility and efficiency of integrated circuit technology. At PCBX, we value these components and are committed to offering designers the necessary expertise and resources to help them implement hex inverters in state-of-the-art circuit designs. Be it educational tool development or commercial electronics advancement, the understanding and use of hex inverter ICs are the ways to excellence and innovation in electronic design.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
3-pin vs 5-pin: 3-pin offers simplicity in plugs and keyboard switches, ideal for residential and custom projects. 5-pin supports higher power and stability.
The 3.3K resistor is vital in electronics for current regulation, is widely available, and ideal in precision circuits, ensuring stability and cost-effectiveness.

Electronic module assembly is crucial for innovation, driven by demands for high-performance, reliable modules in fields like connectivity and electric transportation.
