How Hearing Aids Transform Lives
Hearing aids enhance lives by improving sound perception, thanks to advancing technology and compact PCBs, offering various styles and connectivity features.
Hearing is among all the senses that play a very important role in communication and social interaction. For millions of people in the world suffering from hearing loss, hearing aids are a boon. These have undergone tremendous changes in the last few decades and have improved the quality of life by allowing better perception of sound. The development of hearing aids has been closely related to the evolution of printed circuit board technology, which enables miniaturization and the addition of functionality. This article will look into the technology of hearing aids, their benefits, types, and the latest trends, including the role of PCBs in their development.
A hearing aid is a small electronic device that is designed to amplify sound for individuals with hearing impairment. Amplifying the vibrations of sound entering the ear, hearing aids improve speech perception and thereby substantially improve communication. They are usually composed of three basic components:
Microphone: Picks up sound waves and converts them into electrical signals.
Amplifier: Increases the power of electrical signals.
Speaker (Receiver): Converting the electrical signals back to sound and passing it to the ear.
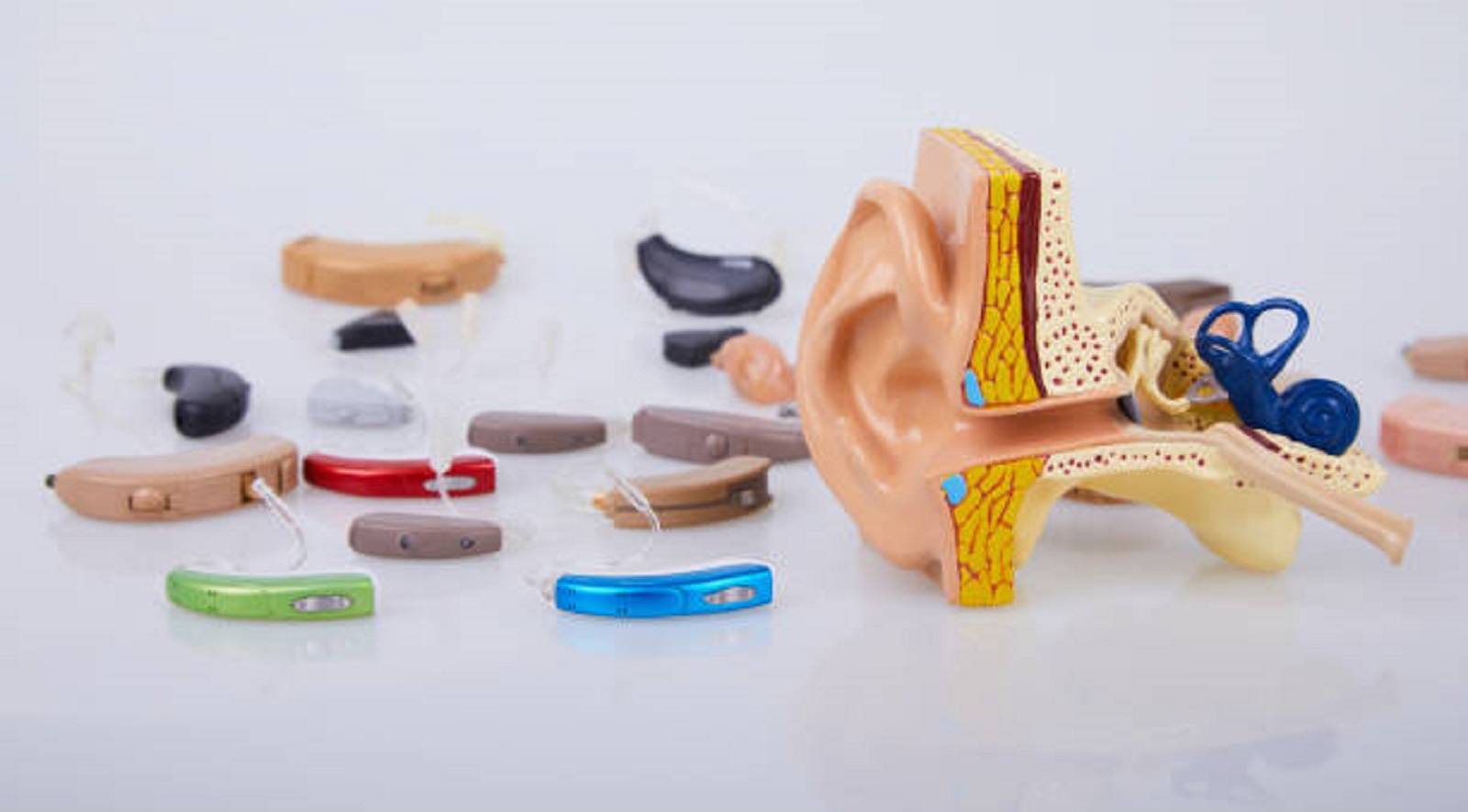
Types of Hearing Aids
Hearing aids come in a number of styles and design to suit particular levels of loss and personal preference. These include:
Behind-the-Ear: These are some of the most traditional styles that can fit almost any degree of hearing loss. BTE hearing aids have a behind-the-ear placement and are connected with an earpiece via a thin tube.
In-the-Ear: Factory-made to sit completely within the outer ear, ITE hearing aids serve as a less obvious alternative than BTE styles but are applicable for moderate to serious hearing loss.
ITC and Completely-in-the-Canal: Smaller yet are the ITC and CIC styles, which fit partly or completely within your ear canal. While cosmetically appealing, they may not be suitable for more serious hearing losses, since their smaller size limits their power.
Receiver-in-Canal: In the RIC category of hearing aids, the receiver is utilized inside the ear. This makes for a much more natural listening experience and is, hence, preferred due to its discretion.
Technological Advancements
The field of technology for hearing aids has developed significantly, which turns these devices functional, as well as user-oriented. Some major developments include:
Digital Sound Processing: Newer models are fully equipped with digital processors, which can pick up the background noise and make speech clear and as natural as possible.
Connectivity: Bluetooth-enabled devices can connect directly to smartphones, TVs, and other digital devices for seamless audio to the user.
Rechargeable Batteries: Most of the new models now offer rechargeable batteries, hence reducing ongoing costs by not having to replace batteries very often.
Directional Microphones: These are special microphones fitted in the device that concentrate the sound from one direction, thereby helping the user concentrate on a conversation even when surrounded by noisy conditions.
Tinnitus Masking: Some hearing aids are fitted with a built-in sound generator that generates pleasant, soothing sounds to mask the ringing in the ears associated with tinnitus.
Benefits of Hearing Aids
The advantages of using hearing aids are not confined to simply hearing better:
Improved Communication: Hearing aids improve communication by amplifying sounds, thus making their wearer communicate with ease and confidence.
Improved Mental Health: Untreated hearing loss has been associated with loneliness and depression, so hearing aids are very important for the psychological health of a person.
Cognitive Health: There is fair evidence that the use of hearing aids reduces the risk of cognitive decline associated with untreated hearing loss.
Social Interaction: Better hearing enables the user to participate actively in social activities, adding much to the quality of life.
The Role of PCBs in Hearing Aids
Printed circuit boards form an indispensable part in the design and functionality of modern hearing aids. During the design of these devices, they act as the backbone through which other electronic components are connected to ensure smooth and quick functioning. Advances in the technology of PCBs have greatly contributed to the miniaturization and improvement in the performance of hearing aids by providing:
Compact Design: The manufacturing of hearing aids utilizing multi-layered PCBs, along with advanced circuitry design, is essential in compacting higher functionality in very small and discreet hearing devices that provide not only aesthetics but comfort for wearers.
Increased Functionality: Advanced PCBs can deliver complicated digital processing to let hearing devices allow noise reduction, feedback cancellation, and the connecting capability with other digital devices.
Durability: High-quality material and process of PCBs make hearing aids durable and reliable for a long time in all sorts of environmental conditions.
Power Management: The PCBs contribute to effective power distribution within the hearing aid, supporting longer battery life and integration of rechargeable batteries.
Future Trends
The future of hearing aids seems bright with the continuous improvement in technology. Following are some of the possible future developments that may take place:
AI: The AI algorithms can further enhance sound processing by learning the users' preferences and automatically adjusting settings for optimum sound clarity.
Miniaturization: Advances in microelectronics and PCB design continue to make hearing aids smaller and more discreet while retaining power and effectiveness.
Health Monitoring: Future hearing aids may include sensors to monitor health metrics such as heart rate and even detect falls, providing holistic health benefits.
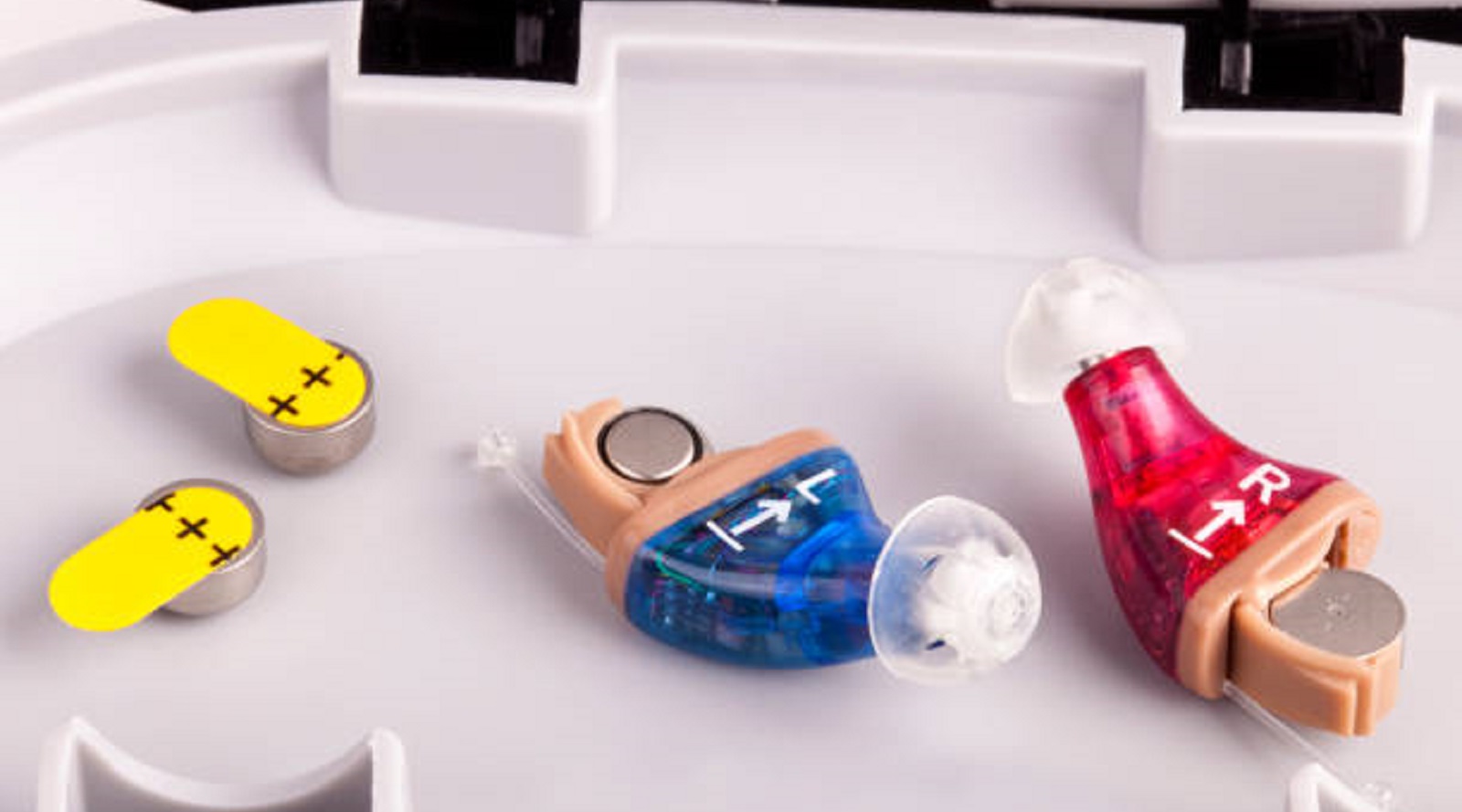

The technology of hearing aids has been invaluable to millions of people in the world, improving their ability to hear and thus changing their lives. At the core of such devices are PCBs, which are critical in ensuring functionality, reliability, and usability. As technology continues to evolve, so will hearing aids, which could offer even more power, expanded capabilities, and integrations. A consultation with an audiologist is the first step toward better hearing health and quality of life for anyone considering hearing aids. By embracing recent technological advancements, including advanced PCB design, hearing aids will continue to provide essential support to those experiencing hearing loss.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article

Color ultrasound enhances diagnostic accuracy with Doppler imaging for real-time blood flow analysis, aiding early detection and minimizing invasive procedures.
High-frequency PCBs are crucial for fast, reliable tech, enhancing performance in telecoms, aerospace, and more with advanced materials and precise designs.

Smartwatches enhance life with health, connectivity, and safety features, supported by tech advances and ecosystem integration, driving market growth.