How to Remove Gold from PCB Board
Gold recovery from circuit boards needs safety gear, precise dismantling, cleaning, etching, and filtering, crucial for safe e-waste recycling.
Gold recovery from electronic wastes, especially from gold plated circuit boards and gold circuit boards is a complicated process and requires very delicate handling and precision. Here's how to remove gold from circuit boards professionally:
Take Safety Precautions
Safety first: wear proper PPE-protective suits, gloves, goggles, and masks. Ensure the process is done in a well-ventilated area to avoid fumes from exposure. Store all chemicals safely and confirm dates of expiration, especially with dangerous chemicals like cyanide.
Prepare the Circuit Boards
Dismantle the electronics to separate the components into plastic, metal, and glass. Also, segregate combustible materials carefully so that no hazardous reaction may occur during its processing. The more elaborate the preparatory steps, the better the extraction will be.
Clean Circuit Boards
Clean the circuit boards completely, with no visible residues visible. Use acetone with caution to dissolve any stubborn shards of metal. Be very careful not to harm your skin or the more sensitive parts of the boards.
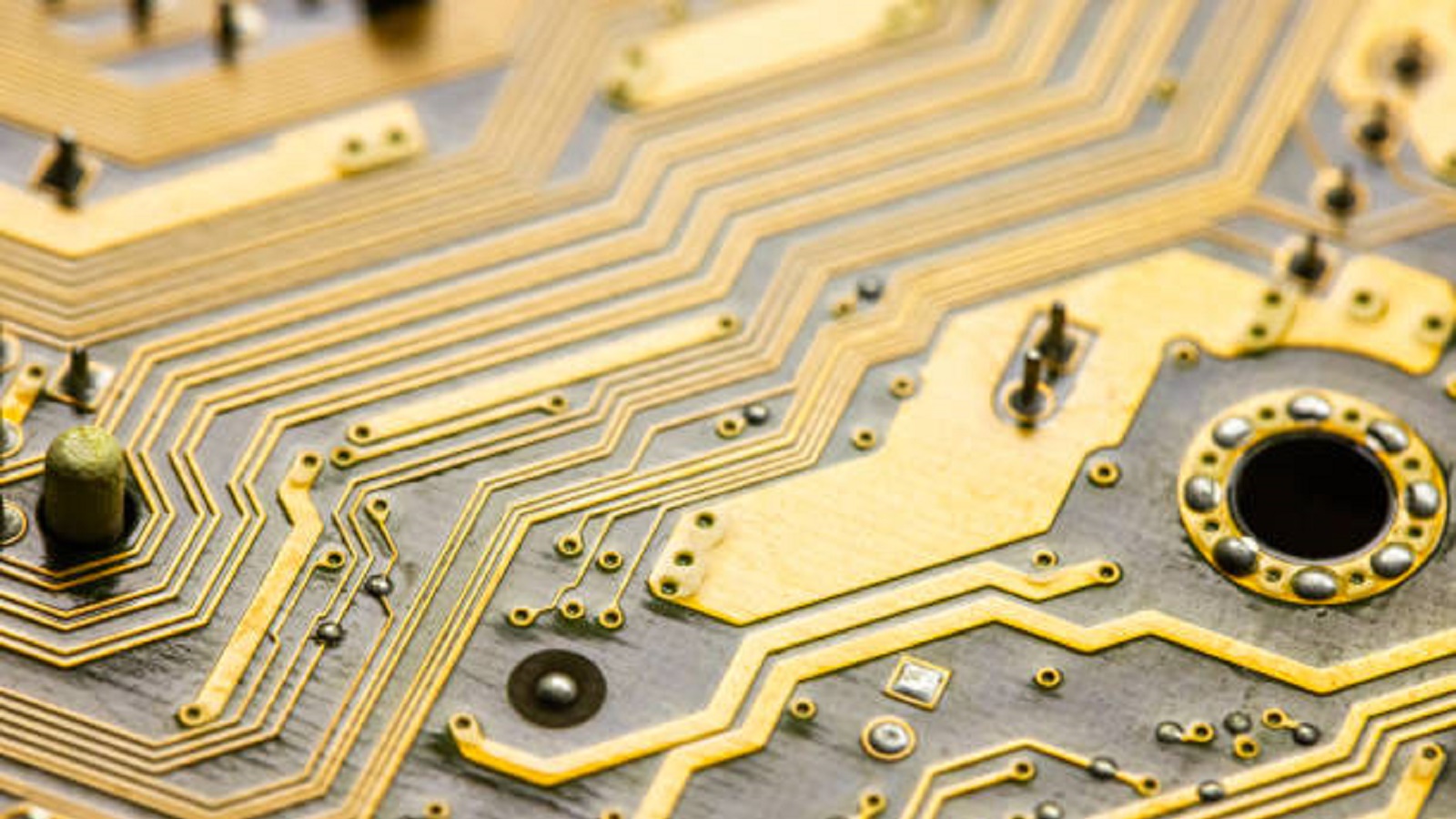
Prepare the Etching Solution
The etching solution should be prepared in order to dissolve the gold plating. The mixture of cyanide and water is effective but very dangerous; hence, utmost care should be taken. Aqua regia can also be applied hydrochloric acid, and nitric acid by expert hands. Ensure the solution concentration is controlled in order to optimize gold recovery while minimizing risks.
Execute Gold Dissolution
Immerse the PCBs in the etching solution and allow the etching to proceed until the gold dissolves. This is the most crucial stage in the process and can be accelerated with the addition of a heat source, like a Bunsen burner, while observing strict safety measures.
Extract and Precipitate Gold
After dissolution, re-precipitate the gold using a precipitant to change the dissolved gold into solid. This could be done by letting the gold particles settle down at the bottom of the reaction container for easy collection.
Filter and Collect Gold
Use a filter to extract the gold foils that have been precipitated from the solution. Rinsing the collected gold with distilled water helps in the elimination of the chemical residues. If it happens that the gold is sticking to a coffee filter, use acetone in a cautious manner to free it.
Finalize with Drying and Refining
Dry the gold particles well, then store them in a safe container until you are ready to further refine them, if that becomes necessary. On a larger scale, you could refine it by fire assay or gold leaching, but both require considerable expertise and equipment.

These systematic procedures help experts extract gold from circuit boards safely and effectively while reducing personal danger and the impact on the environment. This detailed overview, created by PCBX, is crucial for anybody working in the e-waste recycling industry. Following these comprehensive steps will help you maintain the required safety requirements while managing the gold recovery process efficiently.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article

Gold plating in PCB manufacturing increases electrical properties, durability, and corrosion resistance, ideal for high-reliability applications. Types include ENIG (common, flat, solderable) and ENG (thicker, durable).
The article insinuates the need for Organic Solderability Preservatives on printed circuit boards. OSP can adsorb onto the copper surface to prevent oxidation and moisture and can easily get washed out by soldering. It is easy to manufacture an OSP, which is environmentally friendly and not expensive, thus becoming one of the most popular surface finishes today.
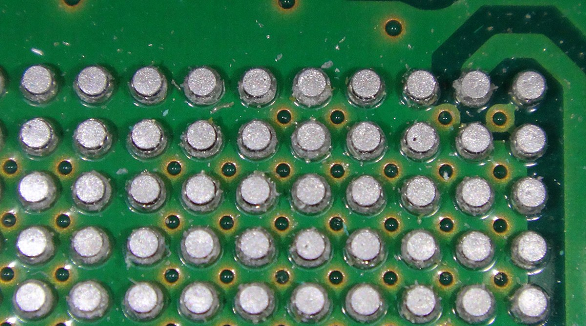
In the late 1980s, when electronics began to shrink, BGA packaging was developed to integrate more connections within a given area. Today, BGA is widely used with high-connection chips—processors being a good example. BGA uses solder balls at the bottom of the chip to connect it to the circuit board. It provides high density along with good heat dissipation and fast signal transmission, one of the main reasons it is ideal for modern electronics. However, it requires precise techniques of soldering in BGA manufacturing.