LED PCB Circuit Design
LED PCBs power modern lighting with efficiency and adaptability, ideal for diverse applications. Their design emphasizes thermal management, cost-effectiveness, and versatility, driving sustainable illumination solutions.
Among these various luminaries, LEDs have grown to become the most preferred for not only commercial but also residential lighting needs. Their efficiency, durability, and adaptability make them ideal for settings that range from automotive to outdoor. Central to elevating functionality features in LEDs is the design of the LED Printed Circuit Board or simply PCB. This article shall delve into the nuances of LED PCB circuit design through an exploration of its challenges, benefits, and varied applications.
Why Choose LED PCB Circuit Design?
LED PCBs are at the heart of modern lighting because of their many advantages:
Small in Size: The tiny size of LEDs is suitable for different purposes, including computers, cars, and mobile phones, where the space can be quite small.
Energy Efficiency: When LED bulbs use almost 80 percent less power compared to ordinary light bulbs, energy resources are saved considerably.
Longer Life: Provide a lifespan as long as 25 times longer than that of traditional bulbs; LEDs reduce maintenance and replacement costs.
Environmentally Friendly: Unlike mercury-containing traditional bulbs, LEDs pose minimal environmental hazards.
Efficient Heat: While most of the energy in LEDs is transformed into light, very little heat is produced. However, proper heat dissipation is necessary for protecting the integrity of LED circuits.
For sustaining performance, LED PCBs must address heat management keenly, hence carrying some specific design challenges and considerations.
Challenges in LED PCB Circuit Design
Thermal Management: Excessive heat generation can reduce the performance and life of LEDs. Employing materials such as aluminum substrates and heat sinks becomes necessary for efficient dissipation of heat.
Lifespan Preservation: High temperatures have the ability to deteriorate the life of LEDs, and thus good thermal regulation becomes necessary.
Color Consistency: Color shift may occur due to temperature variation, which in turn impairs the dependability of LEDs in applications where high color accuracy is desired.
These issues reflect the need for creative design strategies that support superior performance from LEDs.
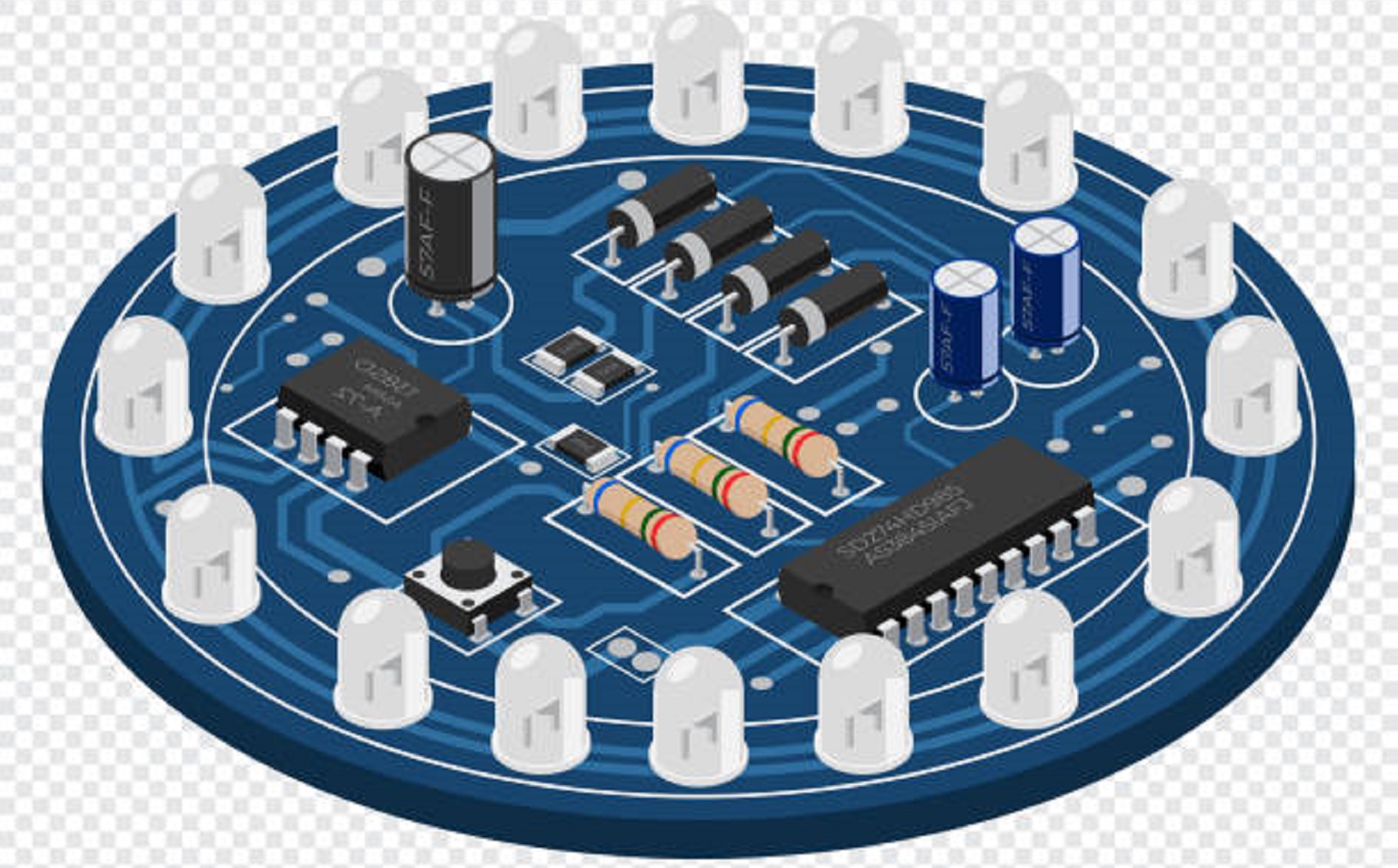
Important LED PCB Design Considerations
Cost vs. Quality: There should be a balance between cost and quality. For a superior overall performance, design considerations such as component placement, thermal management capability, and efficiency in layout play a very important role.
Layer Configuration: LED PCBs can be designed on a single, double-sided, or multi-layered depending on application needs.
Advantages of LED PCB Circuit Design
Heat Efficiency: Emits light at low heat generation, thereby promising longer life and safety.
Ease of Assembly: Involves easy product assembly since flexible design is possible.
Resistance to Environment: Has great resistance to moisture and dust, which offers durability.
Energy Efficiency: Provides low power consumption and thus helps in environmental sustainability.
Versatility: Available in a number of sizes, intensities, and colors, for various applications.
Ease of Integration: Integrates into complex assemblies with ease due to its lightweight design and enhanced stability.
Cost Efficiency: Offers an affordable solution to backlighting and signaling applications.
Applications of LED PCB Circuit Design
LED-based PCBs are used in many applications to satisfy the needs of the modern world:
LED Strip PCB Design: Suitable for a wide range of decorative and functional lighting, these PCBs take into consideration demands in water resistance and voltage.
SMD LED PCB Design: Highly used in notebooks and communication equipment, it has great heat management.
LED Street Light PCB: It is designed to light the street continuously for traffic management.
COB LED PCB: It is widely used in high energy usage because of its efficient heat dissipation and compact design.
LED Matrix PCB: These support a wide variety of display functions, ranging from simple informational displays to sophisticated animation sequences.
From telecommunications to horticulture lighting, LED PCBs, by virtue of being customizable and with state-of-the-art design, are the key to improved efficiency and reliability within systems of lighting. It will be a way to achieve energy-efficient and sustainable illumination solutions by embracing LED PCBs for a brighter future ahead.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Surface Mount Technology revolutionizes electronics, offering size, cost, and performance benefits, but poses challenges with high setup costs and handling.
The article compares Ball Grid Array (BGA) and Land Grid Array (LGA) packaging technologies for mounting microprocessors on PCBs. It details their pros and cons, applications, and factors to consider for optimal design choices.
Mixed Assembly PCBs combine Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT) for high-performance, compact, and reliable circuit boards. This integration leverages both technologies to enhance reliability, component selection, flexibility, and efficiency. Used in CPUs, IoT hardware, and more, they offer economic, efficient manufacturing for versatile applications in modern electronics.
