Mixed Assembly PCBs: Exploring the Benefits
Mixed Assembly PCBs combine Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT) for high-performance, compact, and reliable circuit boards. This integration leverages both technologies to enhance reliability, component selection, flexibility, and efficiency. Used in CPUs, IoT hardware, and more, they offer economic, efficient manufacturing for versatile applications in modern electronics.
In this ever-evolving world of electronics, the demand for high-performance, compact, and reliable circuit boards is a thing of high urgency now. To meet these requirements, Mixed Assembly PCB is one of the most versatile solutions available in the present scenario. This technology integrates both Surface Mount Technology and Through-Hole Technology into a single PCB, hence using the individual strengths of each in reducing their limitations. Below, we go through the many advantages of Mixed Assembly PCBs and their broad applications.
Overview of Mixed Assembly PCBs
Mixed Assembly PCB is a printed circuit board that applies both SMT and THT technologies in its assembly. SMT makes the components be mounted on the surface of the board, with no drilled holes needed hence making higher component density and smaller size possible. Contrarily, the THT involves passing of component leads through pre-drilled holes in the board to realize excellent mechanical stability and reliability. These techniques together yield a PCB that manages to combine the best attributes of both methodologies.
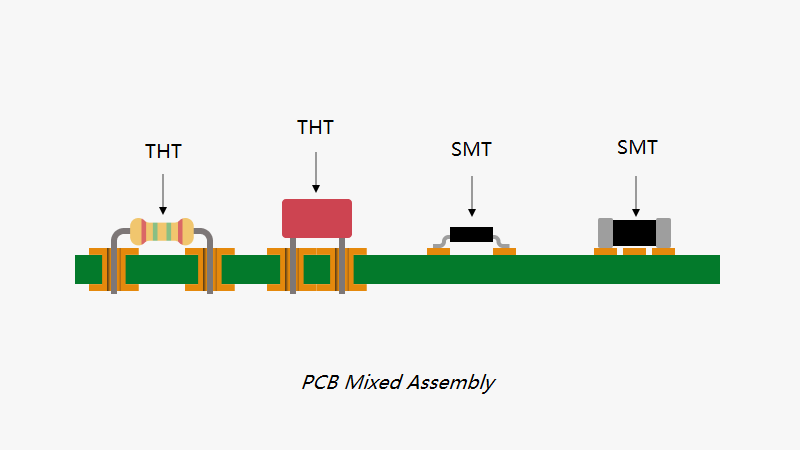
Improved Reliability
One of the major advantages associated with Mixed Assembly PCBs is enhanced reliability. High accuracy and speed in placing components characterize SMT, while strong mechanical bonds characterizing THT guarantee high resistance to stress. The result is a robust PCB assembly that will not only be very durable but also highly reliable, which would be ideal for applications requiring performance over a very long period, such as in industrial controls, automotive electronics, and medical equipment.
Greater Component Selection
Not all the components in electronics could work exclusively for either SMT or THT. In Mixed Assembly, designers can employ a technology that best fits different components; hence, there will be wider component variety. For instance, some big or high-power components would best fit the THT technology due to their mechanical robustness, but smaller and fragile parts need the finesse of the SMT. This flexibility allows more varieties of functionalities to be embedded into one single PCB design.
Increased Flexibility
Mixed Assembly PCBs are much more flexible in design compared to others. That means they can adapt easily according to different requirements and can work just about anywhere, with complex and multifaceted applications. For instance, high-speed signal processing and power electronics. It is important because industries thrive on customized and innovative solutions, which further will increase the application of Mixed Assembly PCBs in a number of technological fields.
Higher Performance
By integrating both SMT and THT on one unit, the Mixed Assembly PCBs can perform better overall. The greater component density, as realized in SMT, allows for compact and efficient designs; at the same time, the mechanical strength made available by THT ensures stability under strenuous conditions. This duality in benefits then translates into better performance, especially in areas like RF communication, where precision and reliability are key.
Production Efficiency and Cost Savings
That is why Mixed Assembly PCB manufacturing can be heavily automated; furthering production efficiency by reducing costs. Smaller SMT components are placed automatically, both quicker and more accurately, hence it is cost-effective for high-volume batches. While THT components might require more manual intervention, a mixed assembly can be organized in a manner that would ensure an overall efficient process. Companies therefore can enjoy speedy production cycles and decreased assembly costs; hence, making Mixed Assembly PCBs in most cases a very economical option.
DFA - Design for Assembly and DFM - Design for Manufacturing
Mixed-assembly PCBs guarantee a fine end product, right from the design stage, particularly in relation to practices such as DFA and DFM. DFA is about the identification of possible assembling problems before their emergence, while DFM concerns the fabricating process. Component type consideration, placement methods, and even design rules in advance by the manufacturers exclude the obstacles during the assembling phase and hence make this process effective and reliable.
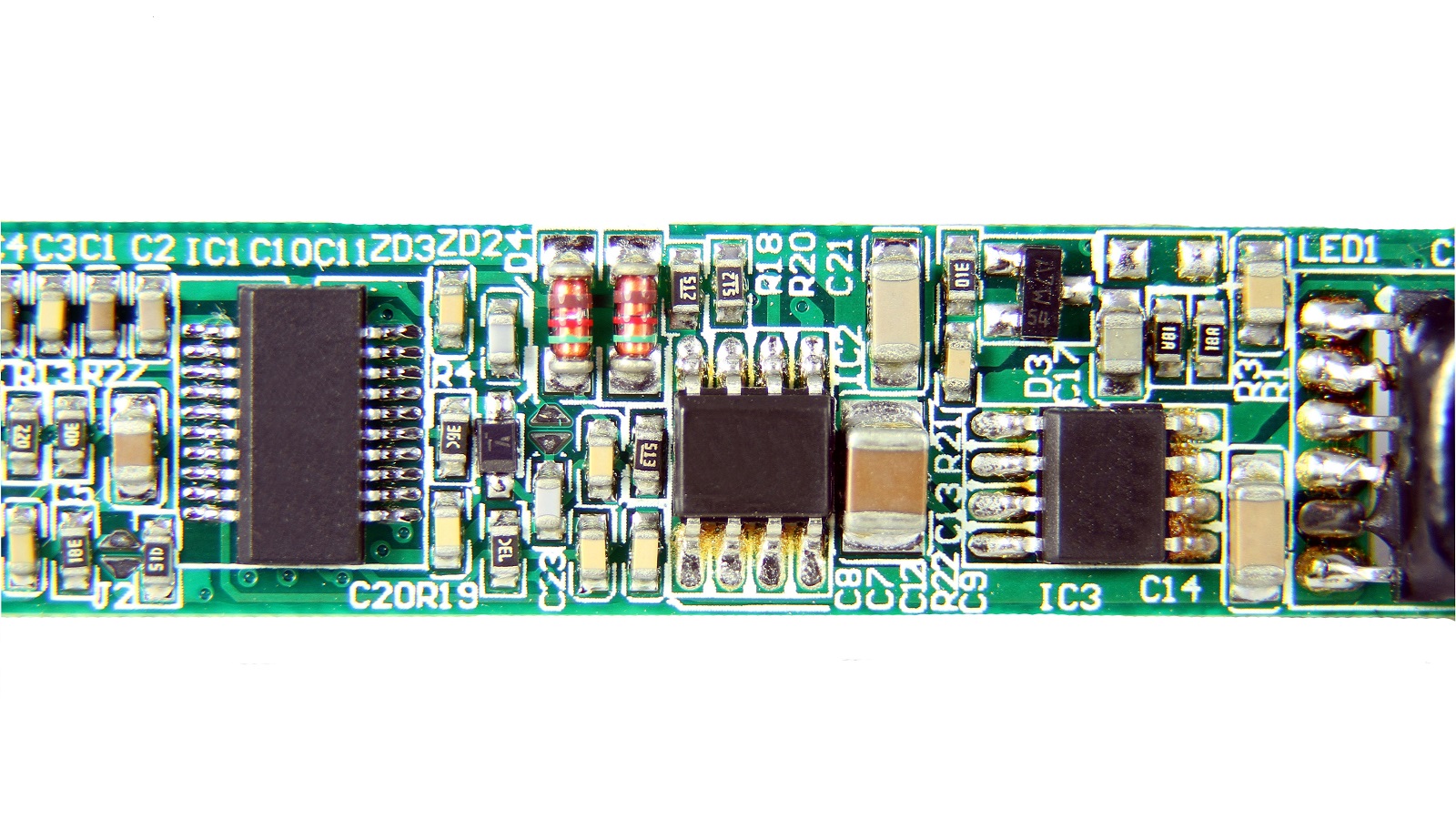
Key DFA and DFM Considerations:
Component Types:
Choose components, depending on their appropriateness for either SMT or THT.
Make use of the precision of SMT or strength of THT in the selection of components to get the most out of performance on the board.
Automated vs. Manual Placement:
Large-quantity production is not only faster with automated placement but also very consistent.
Manual placement, even though more labor-intensive, has the advantage of being slower and less uniform, hence can be more economical in smaller batches.
Component Placement Rules:
Wherever possible, place all components on the same side of the PCB.
Avoid placing heavy components near the board's edges to evade bending.
Leave some spacing between through-hole and BGA (Ball Grid Array) components to avoid problematic situations.
Applications of Mixed Assembly PCBs
The versatility and performance of Mixed Assembly PCBs enable them to find their application in quite a few high-level applications. They can find their usage in:
CPUs: They will handle tasks that require complex computation with high efficiency.
IoT Hardware: It is advantageous when small designs with reasonable reliability are needed.
Sensor Boards: Those applications that have a requirement for a mix of accurate and tough components.
Server Boards: Application requirement that needs to deal with a high velocity of data processing.
Video Processing Devices: They have a critical requirement for precision and performance.
LED Lighting Products: Requiring strong and durable circuit designs.
Communication Hardware: Where RF and digital are used.
Smartphone Accessories: Needing compact form factors with performance.
Industrial Controllers: Needing high reliability and stability.
Conclusion
The SMT and THT integration in Mixed Assembly PCBs brings out the best of both worlds by being robust, flexible, and efficient for modern electronics. With their enhanced reliability, broader range of components, wider flexibility, improved performance, and cost-effective manufacturing efficiencies, the Mixed Assembly PCBs are held in better esteem than several other applications across varied industries. There is no doubt that with increased demands for smaller, faster, and more reliable electronic gadgets, Mixed Assembly PCBs will play a very fundamental role in the development and production of such gadgets.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) revolutionized electronics, facilitating smaller, faster, and more reliable products. It mounts components directly on PCBs, enabling miniaturization and automation. Though SMT boosts space efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and reliability, it poses rework challenges and requires high initial investment.

Through-hole assembly is a key PCB manufacturing technique offering reliability and mechanical strength. This article details design elements, requirements, and standards, including thermal pads, IPC performance levels, component types, solder joint quality, hole sizes, and annular ring dimensions, ensuring robust and manufacturable PCBs for various applications.
Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) employs Through-Hole Technology (THT) and Surface Mount Technology (SMT). THT offers robust mechanical bonds, ideal for high-stress applications, whereas SMT supports efficient, high-density assemblies. Each method has unique advantages and limitations, impacting cost, manufacturing efficiency, and component compatibility. Understanding these differences is key for optimal PCB design.