RFID and IoT Integration
IoT and RFID integration revolutionizes device communication, improving data, asset, and operational management. PCBX supports these innovations amid challenges.
The integration of IoT and RFID brings another revolution in how devices can talk to each other. This marriage puts forward huge positive implications in regard to data acquisition, asset management, and operational efficiencies across a number of industries. As one of the leading PCB manufacturing and solution providers, PCBX is well set to support and extend the innovations of IoT. This article looks at how RFID acts as an enabler of IoT by explaining the principles, applications, and challenges of this synergy.
The Role of RFID in IoT
This concept was first proposed in 1999, underpinning the idea of using information-sensing devices like RFID and connecting ordinary things to enable identification and manage them based on intelligence. Fundamentally, IoT can be regarded as an enabled sensory network through RFID technology underpinning automatic identification and communication of devices over the internet.
IoT and RFID Core Functions
Automatic Identification: RFID can let objects "talk" by maintaining special information with them that could be conveniently and simultaneously propagated in networked layers, a sort of giving a "digital identity" to physical objects.
Information Interconnection: via RFID, devices communicate without human interference, making the data exchange convenient between inter-connected systems.
Architecture of RFID-based IoT
The Composition of the IoT System
RFID System: The radio-frequency identification system provides a package of RFID tags and RFID readers for information collection, processing, and connectivity to IoT.
Savant System: It plays the role of an arbitrator, gathering the data presented by RFID and sending it over the network. Here, the servers process and manage the application data.
Internet System: It consists of computers and other servers operating amongst themselves based on store-and-forward procedures for the data received by them from the IoT devices.
Basic Principle of Working
RFID Readers: transmit signals that interact with RFID tags. On receipt of a response, the readers decode the same and transmit the data to the Savant system for further processing and action.
Savant System: The system inputs data from RFID, processes and makes it available over the Internet on various nominated servers for access and actionability by the systems as required.
Working Principles of an RFID System
System Components
Tags and Readers: RFID System The system consists of tags, which are composed of a chip and antenna, and readers that send and receive RF signals.
Operational Mechanics
RFID tags, upon entering the signal field of a reader, power their circuits to emit stored information. Energy is provided in a passive system through the signal from the reader and actively via a fitted battery in an active setup.
RFID-Based IoT Applications
IoT based on RFID brings a revolution to many sectors, including:
Supply Chain Management: It enhances the efficiency of tracking; improves inventory management; and reduces human errors by automatically feeding data and allowing real-time views.
Retail Innovations: Product availability, correct information about customer behavior, automation of inventory processes-all these result in enhanced customer experience.
Healthcare Improvements: Equipment location is more easily tracked, medicine usage can be tracked, and even tag-enabled monitoring devices help better patient care.
Smart Cities: It enables intelligent infrastructure to be optimized and utilized to maximum availability in terms of energy consumption and traffic management in a city.

Future Developments and Challenges
Novel Development and Solution
Continuous development has enormous potential for higher connectivity across verticals of all scales in RFID, especially combined with the clearly defined framework of the Internet of Things.
Challenges to Address
Standardization: The fact that various criteria exist in different parts of the world prevents smooth integration of IoT; therefore, international cooperation should be sought toward establishing international standards.
Cost: Owing to the high cost of production of RFID components, there is an increased demand for strategic approaches so that ubiquitous deployment of IoT would be possible.
Security Concerns: Among other issues, ensuring the security of data and privacy of users remains of prime importance and requires an increased focus on encryption and data management solutions.
Data Management Platforms: Efficient data handling systems need to be developed to handle the huge amount of information coming from the IoT networks, ensuring secure and accessible data storage. How PCBX Supports IoT Development
Conclusion
The integration of IoT with RFID technology stands tall as a beacon that could allow improvements in automation, data management, and connectivity. Yet, to make full utilization of such potential of these technologies, one has to embark on a voyage that calls for recognition of the challenges encountered in such processes. Applications that are IoT-based hold much potential to be optimized by solving issues with standards, costs, security, and data management.
At PCBX, we believe in the facilitation of furtherance in IoT technologies with our complete range of PCB solutions. Our clients' needs are fulfilled promptly and efficiently. Companies intending to utilize IoT technologies can rely on the partnership with PCBX for all expertise and facilities that are required to place an advanced IoT solution in the market.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
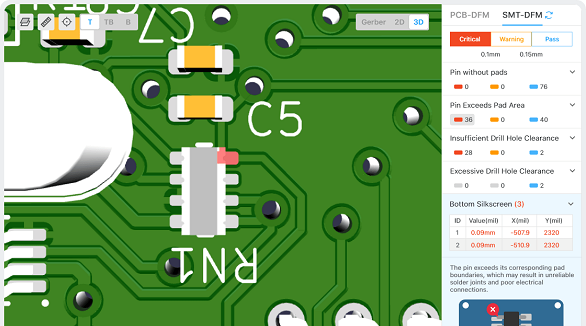
The article is developed concerning the breakthrough of integrated circuits and the need for custom PCBs in some electronic products. It enumerates ten golden rules in conducting PCB layout design and manufacturing: grid selection, routing, power layers, component placement, panel duplication, component value combination, frequent DRC, flexible silkscreen use, decoupling capacitors, and pre-production parameter checks. These rules provide for the optimum design and manufacturing of a PCB.
Most electronic circuits are mounted on PCBs, or Printed Circuit Boards, which provide mechanical support and electrical interconnection of electronic components. There are, however, special applications that involve the use of single and double-sided PCBs, multi-layer PCBs, or even rigid and flexible PCBs with aluminum backing, targeting medical, industrial, auto, and aerospace industries. They may use materials such as fiberglass, epoxy, aluminum, and others.

The article explains the current situation of Printed Circuit Boards and future development based on efficient production helped by advanced software and manufacturing processes. Future technological developments are in store for 3D Printed Electronics, flexible PCBs, eco-friendly biodegradable PCBs, and board cameras. It elaborates on other powerful automation tools that are going to make the entire PCB design process efficient in the near future. All of them will further improve and develop with the technological advances in PCBs, keeping up with the ever-increasing industry and consumer demands.