Solderable Breadboards
Solderable breadboards offer stable, permanent circuit solutions ideal for prototyping, education, and hobbies, balancing flexibility and long-term use in electronics.
In electronics prototyping, solderable breadboards have a vital role: a transitional phase between the flexibility of a traditional solderless breadboard and the permanence of a custom PCB. Such tools enable engineers and hobbyists to create stable, long-lasting prototypes that are both functional and cost-effective. This article discusses the unique properties, benefits, and applications of solderable breadboards, with an emphasis on their importance in modern electronics development.
A solderable breadboard, also known as a perfboard, is designed for constructing permanent electronic circuits. Unlike solderless breadboards, which hold the components temporarily using spring-loaded slots, solderable breadboards require that components be soldered directly onto the copper traces of the board. This creates robust and stable electrical connections, ideal for long-term projects.
Key Features and Connection Layout of Solderable Breadboards
Grid Arrangement: Solderable breadboards are made with a matrix of holes, usually spaced at 2.54 mm (0.1 inches), which matches the standard spacing for through-hole components. This allows orderly component placement.
Copper Traces: Each hole is surrounded by a copper pad or part of a continuous strip of copper that allows components to be securely soldered, forming permanent connections.
Component Placement: Components are inserted into the pre-drilled holes, and the leads are soldered onto the copper pads to create electrical connectivity. This technique is reliable and very suitable for holding components in place under mechanical stress conditions.
Jumper Wires: These are soldered between the pads to connect different circuit sections on the board. The process of soldering allows current to flow and integrates the whole circuit together. To avoid short circuits, it is better to use wires with plastic coating. The wire gauge for easy handling is 0.6 mm.
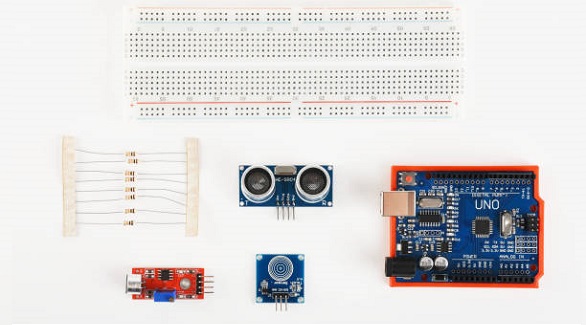
Advantages of Solderable Breadboards
Strong Connections: The components stay firmly in place, ensuring stability. They minimize the risk of losing any connection due to movement or vibration.
Customizability: The solderable breadboards make the prototypes look professional and custom-tailored to the desired type of circuit arrangement.
Time and Cost Efficiency: It saves time in retesting the connections and hence minimizes frequent adjustments. The solderable breadboards will be economical for projects in the long run.
Disadvantages of Solderable Breadboards
Limited Reusability: Once components are soldered onto the board, they cannot be reused for other projects, limiting the flexibility offered by solderless alternatives.
Difficult Repairs: Mistakes in assembling can be hard to fix. Desoldering can easily damage the board and the parts, which requires a great deal of planning and careful execution to avoid mistakes.
Application of Solderable Breadboards
Solderable breadboard finds their application in education as well as professional development based on their specifications:
Prototyping and Development: Good for first level circuit design testing in which an engineer can play around with various configurations before taking it to custom PCBs.
Education Settings: As learning tools, making students understand the practical process of soldering and assembling electronic circuits on them.
Hobby Projects: A great board for electronic hobbyists doing self-made projects and experiments, with the added advantage of a more durable board and ease of usage.
Small-Scale Production: For small-scale productions, they may serve as economical means for prototype building without the added cost of fabricating PCBs.
Tips for Working with Solderable Breadboards
Wire Selection: Use solid core or jumper wires instead of stranded wire to make it easier to manipulate the wire and to make a clean connection.
Merging Boards: For bigger projects, two boards may be merged to increase the workspace and to keep things neat and orderly.
Reusing Component Leads: If possible, use cut leads from components such as capacitors and resistors for jumpers to reduce material.
Solder Choice: Use either lead-tin or silver-tin solder for connections. Note that lead-free (silver-tin) solder requires higher heat, demanding a powerful soldering iron.
Solderable breadboards are indispensable in electronics, as they can provide permanent circuit solutions with stability and still maintain cost-effectiveness. Students, hobbyists, and professional prototype developers find a practical and reliable choice in these breadboards. Their permanence and ease of use make them ideal for anyone who wants to bring a project from concept to reality without the initial commitment to a custom PCB. For those negotiating which breadboard to use, solderable options really smooth out the development process, proving advantageous in both time and function.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Burn-in boards are vital for testing semiconductor reliability, simulating stress to reveal defects, ensuring high-quality devices before mass production.

Breadboards and protoboards are key prototyping tools in electronics. Breadboards allow for flexible, solderless circuit design, while protoboards provide durable, soldered connections for finalized designs.
High-speed PCBs (>1GHz) are crucial for advanced electronics like 5G and data processors. Key practices include ensuring signal integrity, controlling EMI, and maintaining power integrity for reliable performance.