Teflon PCBs
Teflon PCBs excel in high-frequency and extreme conditions; they're essential for aerospace and communication but costly and complex to manufacture.
Among such a variety of materials applied within manufacturing processes, Teflon (Polytetrafluoroethylene, abbreviated PTFE by the producing company DuPont Corporation) holds prime of place for its outstanding properties. Popular for great resistive values for frequency and temperature, PCBs made of Teflon material have been crucial for revolutionary changes in the modern field of electronics. The article deals with Teflon PCBs, focusing on their peculiar advantages, applications, and the challenges in manufacturing provided by them.
Teflon was first discovered by Roy Plunkett in 1938 and soon became recognized for its excellent dielectric properties. These properties made Teflon particularly interesting to the technology of PCBs, especially in high-demand applications related to high-performance electronics. From their original uses for mid-20th-century military equipment to their applications in sophisticated communications systems of the present, Teflon PCBs have been one of the most powerful evolutions driving electronic devices forward. It has redefined how electronics are developed and implemented to significantly enhance functionality and reliability.
Teflon PCBs, sometimes referred to as PTFE PCBs, are special, high-frequency printed circuit boards using the low dielectric constant and minimal energy dissipation of Teflon. These characteristics make the Teflon PCBs especially suitable for the transmission of signals at frequencies of 5GHz and above, thus making them very suitable for microwave and RF applications where precision and performance are critical.
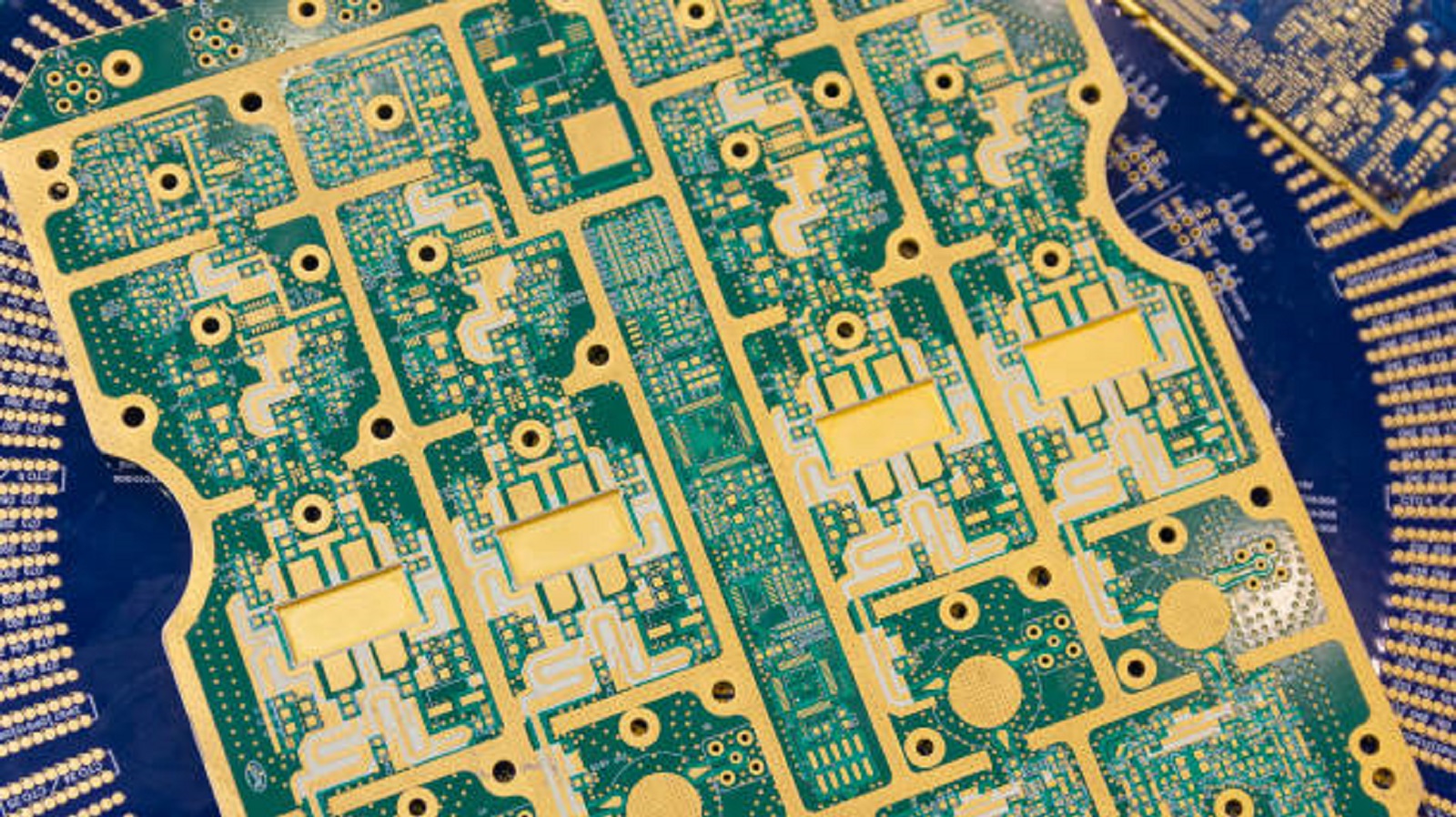
Key Properties of Teflon PCBs
Low-Temperature Durability: Teflon PCB maintains mechanical robustness down to -196 degrees Celsius; hence, they are super reliable in very cold conditions.
Chemical Resistance: With the chemical inertness in Teflon PCBs, the variety of corrosive substances applied does not cause any degradation with respect to its structural and functional abilities.
Weather Resilience: These PCBs will bear the different and worst environmental conditions; it enhances their reliability and adds to their service life.
Low Energy Dissipation: Teflon PCBs have a very low dissipation factor, hence presenting the best insulation properties for high-precision and high-performance systems that include radar and RF devices.
Thermal Stability: Capable of working at very high temperatures, Teflon PCBs also indicate their use in systems with higher heat generation.
Non-reactive Nature: Strong carbon-fluorine bonds in PTFE make Teflon PCBs non-adhesive and chemically inert; hence, there are no unwanted reactions.
Minimum Water Absorption: These PCBs are almost impervious to moisture; the low water absorption rate makes them suitable to work in high humidity conditions.
Electrical Excellence: Teflon PCBs have a consistent dielectric constant and low dielectric loss, which means they perform great at RF and microwave applications.
Advantages and Challenges of Teflon PCB
Advantages:
High Frequency Performance: With their very low dielectric constant, Teflon PCBs give very good high-frequency performances hence find applications in antennas and RF circuits.
Temperature Resistance: The ability of these boards to bear high temperatures makes them suitable for applications involving a lot of heat generation.
Chemical Resistance: These PCBs provide toughness and reliability in chemically aggressive environments, prolonging their service life.
Low Moisture Absorption: The hydrophobic nature of Teflon reduces moisture absorption, which further improves the durability and performance of Teflon PCBs.
Disadvantages:
Cost: Teflon is intrinsically costlier than most other PCB materials, which raises the cost of production by a great margin.
Manufacturing Complexity: The fact that it is non-adhesive presents challenges that require specialized equipment and expertise, possibly raising manufacturing time and costs.
Mechanical Strength: While the Teflon PCBs are chemically and thermally robust, their mechanical strength is restricted as compared to some other materials, which might affect their applicability.
When to Use Teflon PCB
Teflon PCBs are to be used when their properties become uniquely required for an application, such as:
High-Speed Digital Circuits
RF and Microwave Systems
Aerospace and Defense Electronics
Advanced Telecommunication
On the other hand, for projects that are tight on budget or do not have special requirements for high frequency, other materials like FR-4 or aluminum would be better since they are cheaper.
Applications of Teflon PCBs
Due to their properties, the Teflon PCB is vital in high-frequency fields where excellence and dependability are not compromised:
Military Applications: They are a must in missions and every military communication tool because they can withstand very extreme conditions.
Commercial Telecommunications: These are applied in WiFi antennas and power amplifiers; their excellent signal integrity really improves performance.
Automotive Safety Systems: Teflon PCBs make sure sensors work in active safety components, supportive of their dependable electrical properties.
Manufacturing Teflon PCBs
The manufacturing process of Teflon PCBs requires specialized and comprehensive measures to ensure the quality and functionality of:
Surface Preparation: This is the first step in preparing the substrate with much care to avoid any damage during the formation of layers. The usual bristle or scrubber tools will damage the laminate and hence sodium etchants or plasma gas treatments are used.
Copper Plating: PTFE has a high thermal expansion and hence copper plating needs to be done with much care to avoid the risk of pad lifts and barrel cracks.
Solder Mask Application: The solder mask needs to be applied in that tight 12-hour window after etching, ensuring moisture does not affect the completed board.
Drilling: Specialized techniques must be used to work with the specific consistency of PTFE. Ceramic-filled laminates are preferred due to their easier process during drilling.
Handling and Storage: PTFE laminates are soft and thus require extra precaution while handling to avoid tearing or gouging. Storage recommendations include keeping the boards at room temperature, avoiding direct sunlight.
Teflon PCBs possess some very impressive properties, which make them contribute a lot to industries such as aerospace, telecommunications, and high-speed computing. However, their higher costs and manufacturing complexities require thoughtful consideration before implementation. Knowing these factors helps the manufacturers and designers to make better use of the Teflon PCBs. As the field is constantly in development, with further advances in Teflon PCB manufacturing, the cost could decrease and efficiency increase, finding more applications and becoming more desirable. Companies dealing with Teflon PCBs, like PCBX, can increase their performance, reliability, and lifetime of electronic devices by making use of these special characteristics. This again underlines the fact that material selection is the backbone in the development of technology.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Carrier PCBs are crucial for data modulation, multiplexing, and network integration, supporting efficient and robust telecom infrastructures globally.
Amplifier PCBs enhance audio signals in devices like headphones and theater systems using components like transistors and capacitors for clear sound.

Flex PCBs fit into devices, saving space, while Rigid-Flex PCBs combine flexible and rigid parts, ideal for varied applications. PCBX offers custom designs, rapid prototyping, and high-quality manufacturing.