Understanding IPC Standards of Solder Masks on PCBs
IPC standards ensure PCB quality by guiding solder mask application, focusing on material properties, performance tests, classifications, and coverage criteria.
IPC standards are significant references for ensuring quality, consistency, and functionality within the electronic world. These specifications denote various facets of the design and building processes of PCBs; solder mask application is one such respect. The solder mask itself is an extremely important part of protecting and insulating the conductive traces on a printed circuit board from solder bridges and environmental resistance. Herein, we discuss the main IPC standards related to solder masks and point to why they are significant in achieving reliable processes in manufacturing PCBs.
IPC-SM-840: Qualification and Performance Specification of Permanent Solder Mask
IPC-SM-840 is the principal standard that governs properties, performance, and qualification of permanent solder masks in manufacturing PCBs. It helps ensure that solder masks are up to the necessary specifications to survive manufacturing, assembly, and application life. Key considerations of IPC-SM-840 include:
Material Characteristics: This document identifies the minimum properties that should be possessed by solder mask materials; for example, adhesion, flexibility, and resistance to environmental exposure. These characteristics ensure that throughout the life of the board, the solder mask will be resistant against kinds of chemical exposure, temperature variation, and mechanical stress.
Performance Tests: A lot of performance tests need to be performed for confirmation of durability, such as thermal shock, moisture and insulation resistance, solvent resistance, and flammability. These tests ensure that solder masks will maintain their protective qualities under extreme operational conditions.
Classification of Solder Masks: IPC-SM-840 classifies solder masks into Class T (Telecommunications), Class H (High reliability, like military applications), and Class C (Consumer electronics) depending upon the end-use environment. It is useful to help manufacturers identify the correct class of solder mask for the application in consideration.
IPC-6012: Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards
IPC-6012 is complementary to the solder mask standards since it focuses on the qualification and performance of the rigid PCB in totality. To this end, since solder masks are integral parts of the design of a PCB, this standard advises several issues:
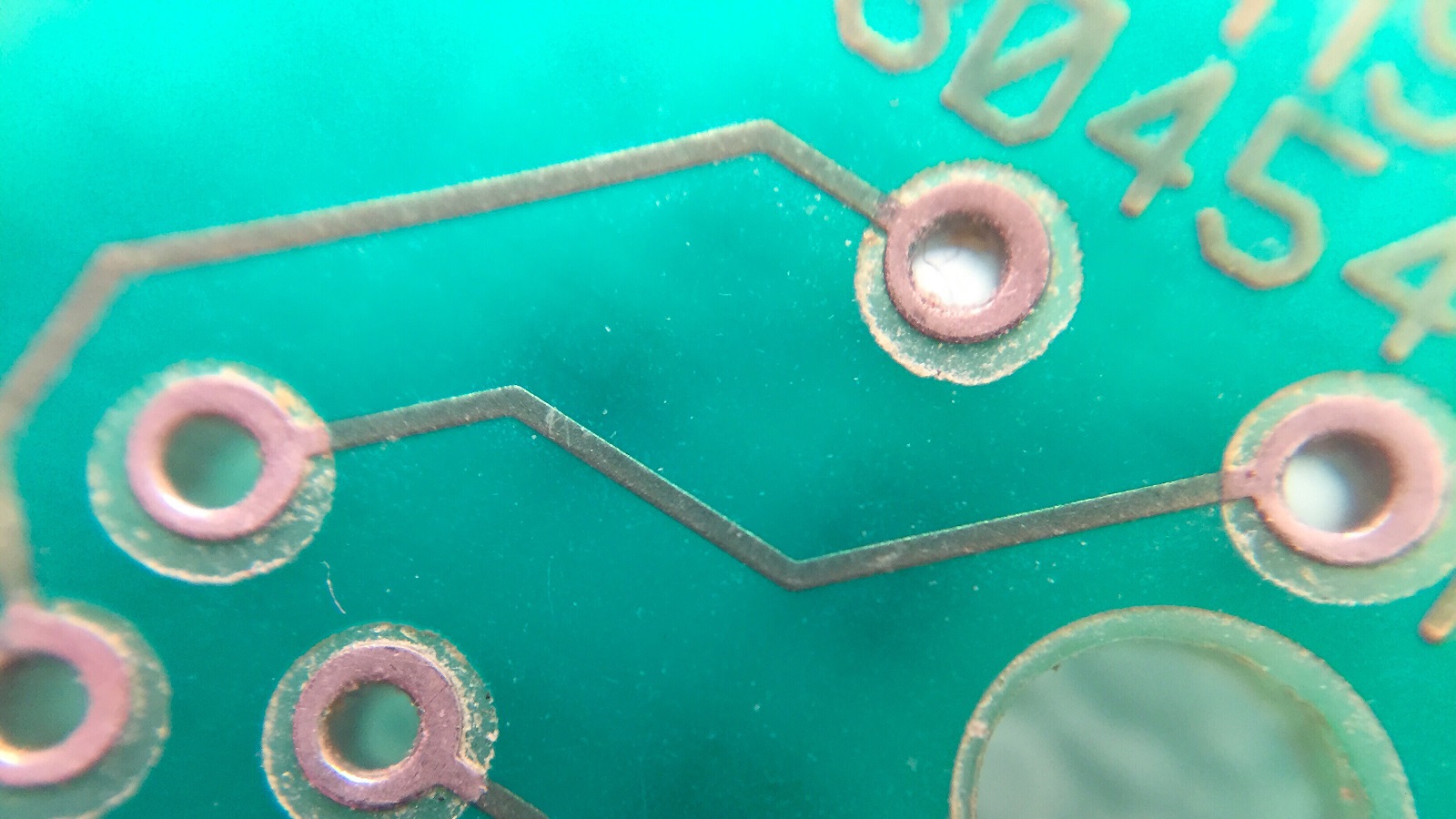
Solder Mask Coverage and Registration: These specify criteria to effect solder mask coverage-the masks must be properly positioned to mask the board, yet not interfere with access to the solder pads. The proper registration is necessary in order to avoid coverage over vias or pads that need subsequent soldering.
Dimensional Tolerances: It provides specifications to keep the dimensional tolerances of solder mask layers aligned with other features on a PCB. In fact, such alignment is highly critical in order to avoid exposure to environmental hazards due to conducting traces or pads.
IPC-A-600: Acceptability of Printed Boards
IPC-A-600 forms one of the major bases on which the visual quality and acceptability of the PCBs are founded, with special attention to solder masks.
Surface Quality: This specification outlines the limits for allowable imperfections, such as pinholes, scratches, and bubbles on the solder mask layer. A high-quality surface ensures that no imperfection in the surface compromises the functionality or appearance of the board.
Solder Mask Misregistration: This sets acceptable limits for misregistration of solder masks in relation to features on a PCB, such as pads and vias. Proper registration enables effective protection without obstructions to soldering processes.
Color and Coating Uniformity: The color and thickness of the solder mask layer should be consistent. This goes towards aesthetic and functional integrity. Consistent coatings are an indication of precision in manufacturing and adherence to quality standards.
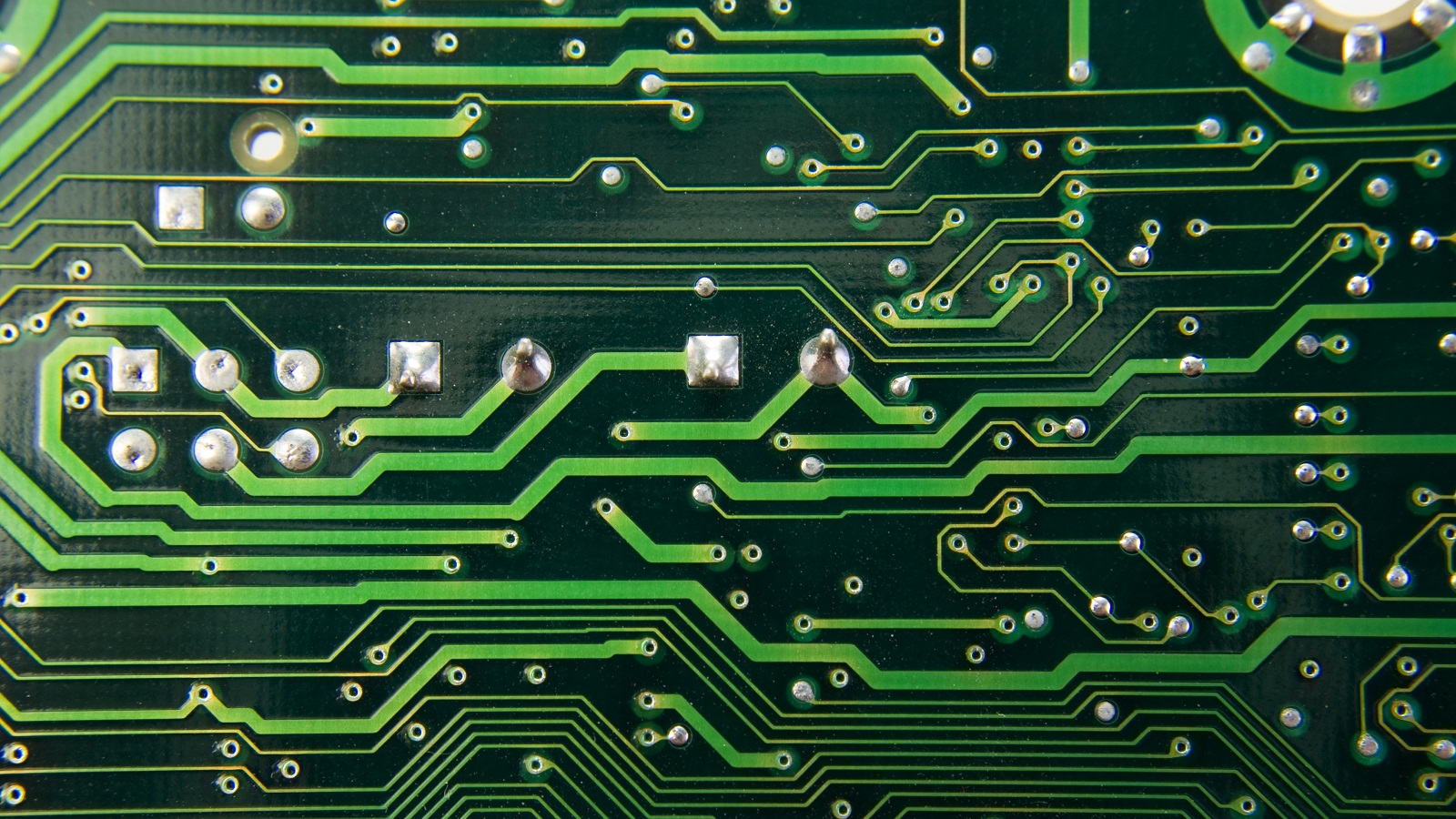

Additional Guidelines and Best Practices
Besides these particular IPC standards, general guidelines for the application of solder masks include:
Application Methods: Specifications recommend methods such as liquid photo-imaginable or dry film application methods. Each application technique offers certain advantages, the LPI being one of the prominent ones for fine-line boards owing to its accuracy.
Curing Processes: Proper curing is quite necessary to achieve the desired hardness and adhesion of the solder mask. Recommendations on thermal curing times and conditions are provided that will optimize these attributes.
Design Considerations: IPC provides design guidelines to enhance the efficiency and reliability of boards, such as the size of clearances and configurations of stack-up for the solder mask layer.
Resistance to Environment and Chemicals: Checking within IPC that materials utilized for making solder masks are capable of withstanding environmental and chemical exposure commonly occurring in their service is very important. It ensures durability and dependability.
Deployment and Industry Impact
The adaptation of IPC standards to PCB solder masks exceeds mere adherence to a guideline; it basically forms the backbone of the electronics manufacturing industry. Because the product quality and performance were already standardized under the IPC, the communication becomes better since there is better mutual understanding between the manufacturer and designer on what to expect regarding quality control.
Moreover, solder masks are very important in the prevention of problems like solder bridges and shorts. As complexity in electronic components continues to improve and miniaturization evolves further, meeting IPC standards not only means product reliability but strengthens the overall value proposition of electronic devices in competitive markets.
In short, all the above are important features of IPC standards for PCB solder masks. Ensuring strong manufacturing processes and quality final products is thus important. At PCBX, we follow such standards as we take customers through crucial processes in the solder mask application to ascertain that electronic designs meet both reliability and qualitative measures. We finally incorporate these standards into our manufacturing ethos for steady development in electronic technology and its applications.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
PCBs are essential for organizing information and power flow in electronic devices, benefiting from flexibility, durability, safety, efficiency, and heat management.
Creating PCB prototypes before full production avoids potential failures, saves costs, and ensures quality. PCBX offers rapid, accurate prototyping for efficient testing and design validation.

Choose between single-layer or multi-layer PCBs based on your project's needs. Single-layer is simpler and cost-effective; multi-layer offers complex functionality and durability. Evaluate based on functionality, size, durability, budget, and turnaround time.
