Universal PCB
Universal PCBs provide flexible, cost-effective solutions for prototyping, enabling efficient development in electronics with diverse applications and easy adaptability.
The fast-growing electronics world requires every day flexible, cost-effective, and efficient solutions for prototyping devices and system design. Universal PCBs have been an essential link in this chain. These circuit boards are designed to provide flexibility and ease of use, making them very helpful in developing new gadgets and machines that could integrate the PCB technology seamlessly. This article looks at what makes Universal PCBs great, their unique advantages, their varied applications, and their crucial role in shaping the future of electronic design.
Universal PCBs mostly work during the design phase to try out an idea and/or approve a system concept. These are printed circuit boards that easily adapt to different electronic applications. Such boards are essential in saving time and cost by allowing manufacturers the opportunity to perfect functionality before high-volume production starts. They are essentially made from glass fiber, an inexpensive and durable alternative to less durable, brown-colored, phenolic paper boards.
They are sold in various shapes, sizes, and designs that range from large boards of several dozens of centimeters to the compact, postage stamp-sized board. They are also made in single-sided and double-sided versions with materials ranging from paper laminates to glass-epoxy laminates with thicknesses from 0.7 to 1.6 mm. All these options make Universal PCBs a very versatile platform for many purposes.
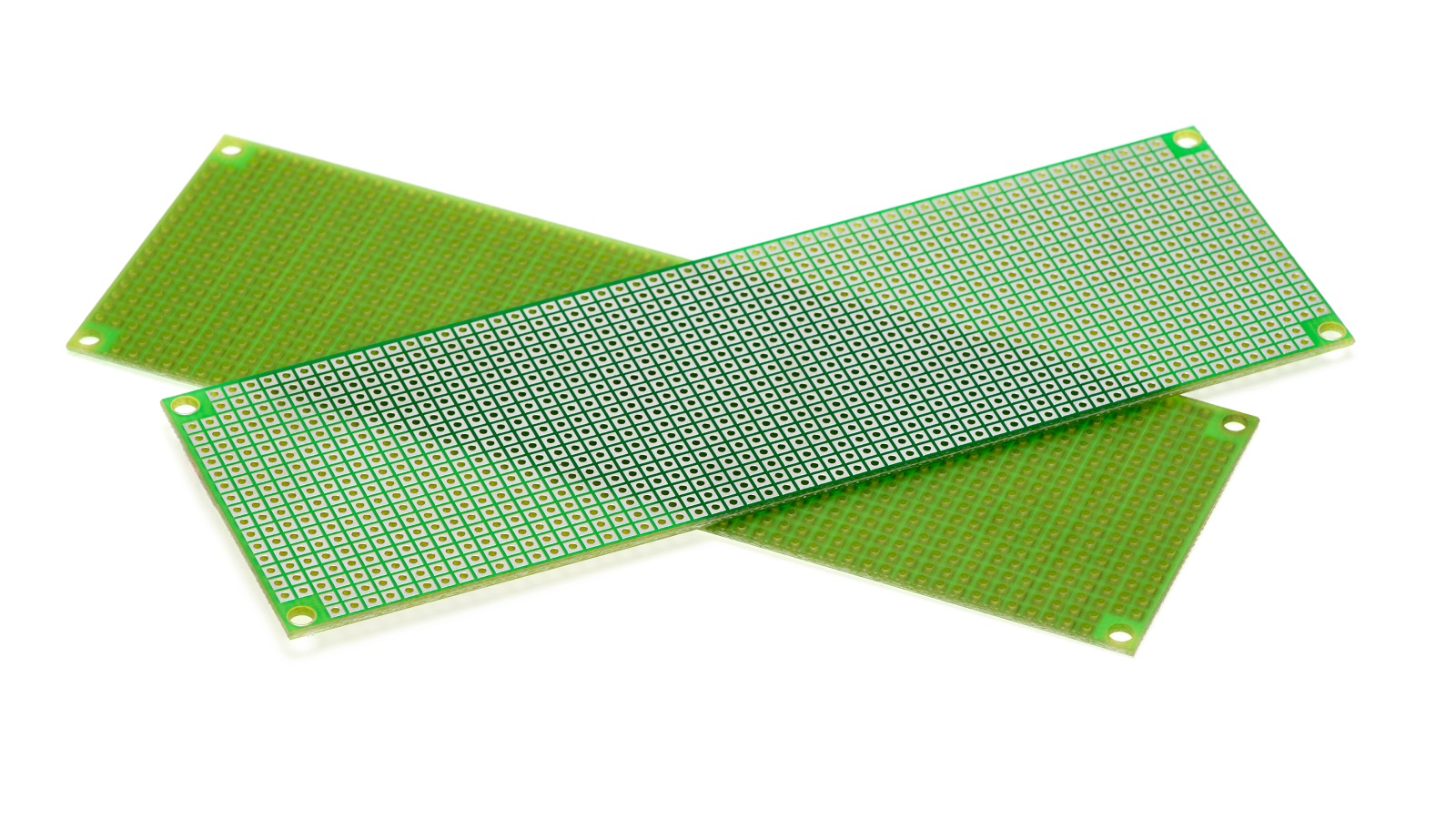
Key Characteristics of Universal PCBs
Soldering Flexibility: Most of the universal PCBs are provided with soldering pads to connect the components. Some types of variants have spring terminals, which are used for simpler and hobbyist projects.
Durability: Made primarily from glass fiber, these boards are resistant to wear and moisture, therefore useful in both temporary and robust long-term uses.
Different Display Options: Boards come in various shapes, according to industrial standards of measurement and configurations, for seamless continuity on other devices and systems.
Advantages of Universal PCB
Cost-Effective: Universal PCBs are cheaper compared to custom PCBs. For small projects or first prototypes, this is often a welcome option. Their mass production and general application enable them to be relatively cheaper since the production costs have been minimized, thus making them affordable to many people.
Universality and Flexibility: Universal PCBs can hold various components and circuit configurations since the layouts are standardized. This makes them very useful during the prototypic stages of a design because changes in designs and components can be made very fast.
Ease of Use: They provide a simplified platform for assembling circuits, making them very user-friendly for beginners and experienced engineers when constructing and modifying circuits.
Time Efficiency: Without the need for a custom PCB for each project, Universal PCBs save enormous development time, which is of prime importance in rapid markets where the timing of products plays a key role.
Applications of Universal PCBs
Educational Tool: An ideal platform to educate principles of electronics, circuit design, and soldering skills. Universal PCBs offer the learners hands-on experience without any complications.
Consumer Electronics Prototyping: The universal PCB plays an important role in the development and testing of new consumer electronics. It facilitates rapid iterations in the effort to refine designs and functionalities before full-scale production.
Industrial Equipment: These universal PCBs will be applied within industries, such as manufacturing facilities, where control systems and sensors are put into place for functionality and process optimization.
Medical Devices: The increased utilization of technology-based medical equipment has made Universal PCBs useful for prototyping devices intended for diagnostics, monitoring, and therapy that are subjected to strict testing under healthcare regulations.
Automotive Electronics: As the number of electronic parts increases in vehicles, Universal PCBs make prototyping easier for developing advanced safety and convenience features. The manufacturers have to choose materials that can bear high temperatures and vibrations typical in automotive applications.
Universal PCB Manufacturing and Techniques
The production of Universal PCBs varies based on etching methods and material choices. Common manufacturing processes include:
Acid Etching: This traditional method is slow and requires safety measures due to chemical use, ideal for circuits of low to medium complexity.
Routing: Equipment mechanically removes excess copper from the board to create circuit paths. While this process can be costly, it’s beneficial for producing high-quality, repeatable PCBs efficiently.
These may range from as simple as a photo-sensitive circuit board and its corresponding UV light source to even more complex elements like chemicals to undertake etching processes. Selection of methods affects the quality and applicability of PCBs for intended use.
Universal PCBs have remained handy tools within the realm of electronic designs for accomplishing crucial tasks of fast prototyping and validation of designs. In all these uses, from consumer electronics to automotive and industrial systems, the cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and usability make them quite indispensable. In conclusion, Universal PCBs will continue to play an important role in promoting innovation and efficiency, whereby manufacturers, educators, and hobbyists will be able to explore and realize their electronic vision with continued advancement in technology. Through ongoing innovation, these boards are set to keep pace with the increasingly diverse and evolving demands within the industry.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Amplifier PCBs enhance audio signals in devices like headphones and theater systems using components like transistors and capacitors for clear sound.

Breadboards and protoboards are key prototyping tools in electronics. Breadboards allow for flexible, solderless circuit design, while protoboards provide durable, soldered connections for finalized designs.

Prototyping PCBs is crucial for all designers and costs vary based on factors like board size, material, complexity, and urgency. Prices range from a few dollars to hundreds. Smaller batches cost more per unit.
