Voltage Regulator PCB Design
Voltage regulator PCBs ensure stable electronic device operation, offering solutions like linear and switching regulators for efficiency and reliability in designs.
Voltage stability in the rapidly changing world of electronics is essential for proper functionality and good lifespan. In power management, the role of voltage regulators provides solutions with constant voltage output, irrespective of fluctuations in load and input conditions. The following article describes the intricacies of voltage regulator Printed Circuit Board designs, their types, selection criteria, and the indispensable role in power engineering and electronic applications.
Voltage regulators are designed to supply a constant output voltage independent of variations in load current or input voltage. They protect voltage-sensitive electronic components that need a specific voltage value to operate properly. Voltage regulators increase the reliability and performance of a system by maintaining a constant voltage supply.
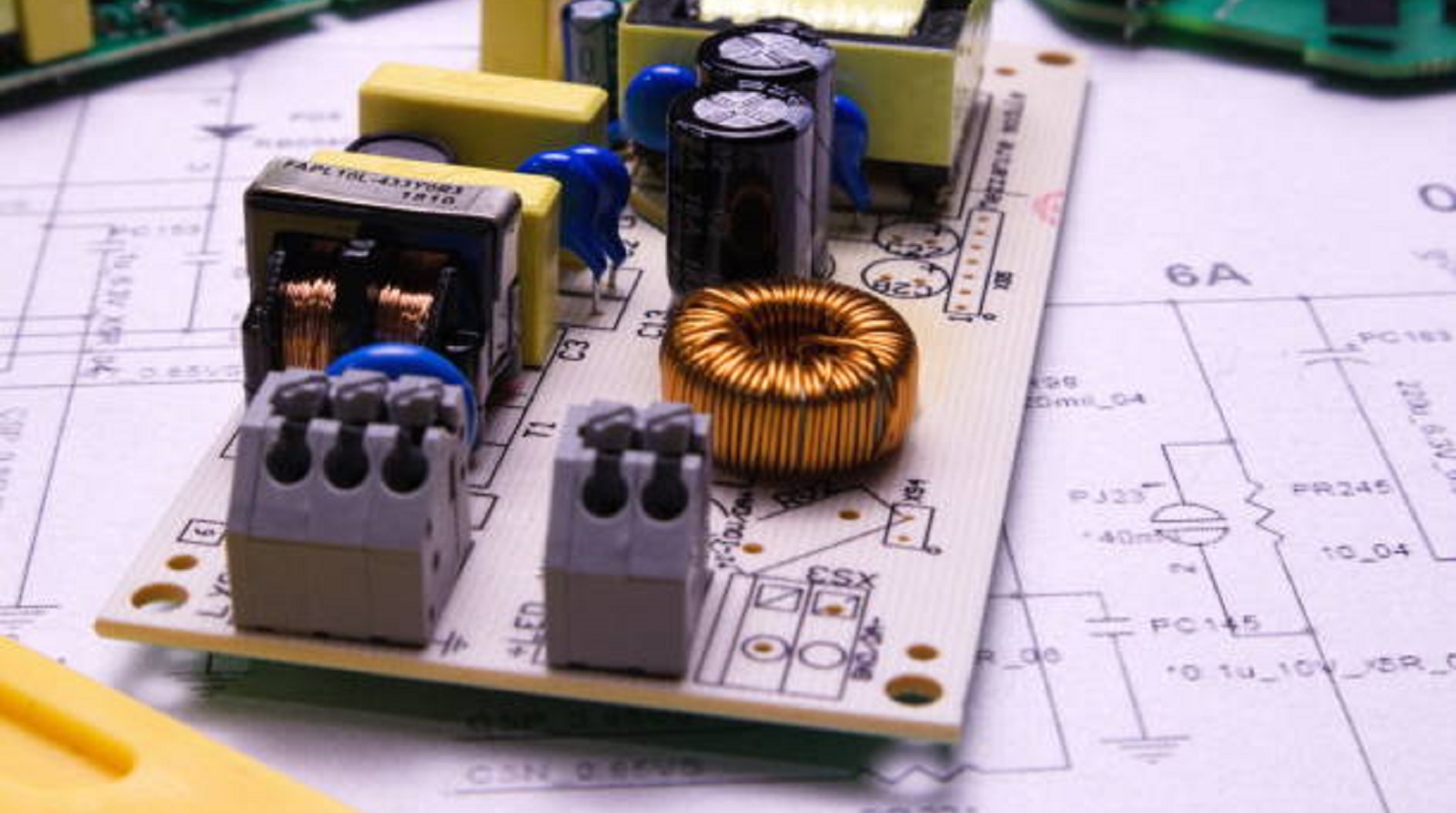
Types of Voltage Regulators
The voltage regulators can be classified into two major categories, each serving a different purpose, as follows:
Linear Voltage Regulators:
Operation: It uses active elements like BJT or FET that dissipate the excess input voltage as heat. These regulators maintain a constant output voltage by comparing the output voltage with a reference voltage.
Applications: Ideally suited to applications requiring low noise and low ripple, such as audio equipment and sensitive analog circuits. In general, they are less efficient, especially in cases involving a substantial difference between input and output voltages, and they usually require heat management arrangements.
Switching Voltage Regulators:
Principle of Operation: Switching regulators utilize active power switches (BJTs or MOSFETs), inductors, and capacitors to accomplish the conversion of the input voltage. Boost (stepping up), buck (stepping down), or both-if necessary-can be provided.
Applications: More efficient and, therefore, very suitable for applications requiring high power conversion, such as battery-powered devices and portable electronics.
Voltage Regulator PCB Design Considerations
The design of the voltage regulator PCB is a very critical task because it needs a great deal of planning regarding its performance and reliability:
Component Selection
Selection of appropriate components in a voltage regulator PCB is paramount.
Output Voltage and Current: The application pre-determines the voltage and current. This will ensure that the regulator selected can provide the required output with maximum efficiency.
Efficiency Requirements: For applications where there is a large difference in input and output voltages, a switching regulator is normally more efficient. Where low noise is imperative, the solution is to use a linear regulator.
Thermal Considerations: Assess the amount of heat that will be dissipated carefully. The Linear regulators sometimes use heat sinks, and there are designs where switching regulators manage heat internally.
PCB Layout Considerations
A thoughtful PCB layout can minimize EMI, optimize thermal performance, and ensure greater electrical reliability:
Placement: Place the voltage regulator near the load to reduce voltage drop and to stabilize it easily.
Trace Design: Wider traces are used for high-current paths to reduce resistive losses, ensuring robust performance.
Ground Planes: Continuous ground planes reduce EMI and provide low-impedance paths for return currents.
Thermal Challenges Management
Thermal management is very critical, especially for linear regulators:
Heatsinks and Thermal Pads: Shall be applied whenever needed. Their correct mounting would facilitate heat sinks to efficiently dissipate excessive amounts of heat outside with no overheating.
Optimized Trace Design: Design traces that assist in dissipating heat, possibly using thicker copper layers in high-power areas.
Choosing a Voltage Regulator: Important Considerations
Selection of appropriate voltage regulator includes the tradeoff among various factors such as efficiency, noise, power dissipation and transient response:
Noise vs. Efficiency: While linear regulators are quieter, they are less efficient than switching regulators. When noise-sensitive components are at risk, low-noise solutions are important. When the priorities are for power efficiency and compactness, the use of switching regulators is better.
Transient Response: The transient response describes how well the output voltage of the regulator can be kept within specification during fast changes in load.
Space and Power Limitations: Consider the space limitations of the PCB design. Further, linear regulators may require additional space due to heat dissipation, whereas switching regulators are compact and power-effective.
Applications and Challenges
Voltage regulator PCBs find their usage in many industries as a cornerstone to make sure that the electronic component works within its specified voltage range:
Applications
Consumer Electronics: From smartphones to appliances, voltage regulators are in every device that operates consistently, and their reliability comes from the power supplies.
Automotive and Aerospace: This is very important in regulating power to the electronic control units, entertainment, and safety gadgets that generally require precise voltage levels.
Industrial Equipment: Keep power stable in control systems; this is important in industries where the conditions of power supply always change.
Communication Devices: Networking equipment and radios require consistent power to perform at high levels on communication platforms.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite their utility, voltage regulators do come with some challenges:
Efficiency Concerns: Linear regulators can be inefficient when there is a large difference between the input and output voltages. This calls for careful thermal management.
Design Complexity: The sophistication in layout required to reduce radiation and noise in switching regulators complicates the design process.
Thermal Management: In most of the cases, heat dissipation is necessary to prevent overheating and component damage.
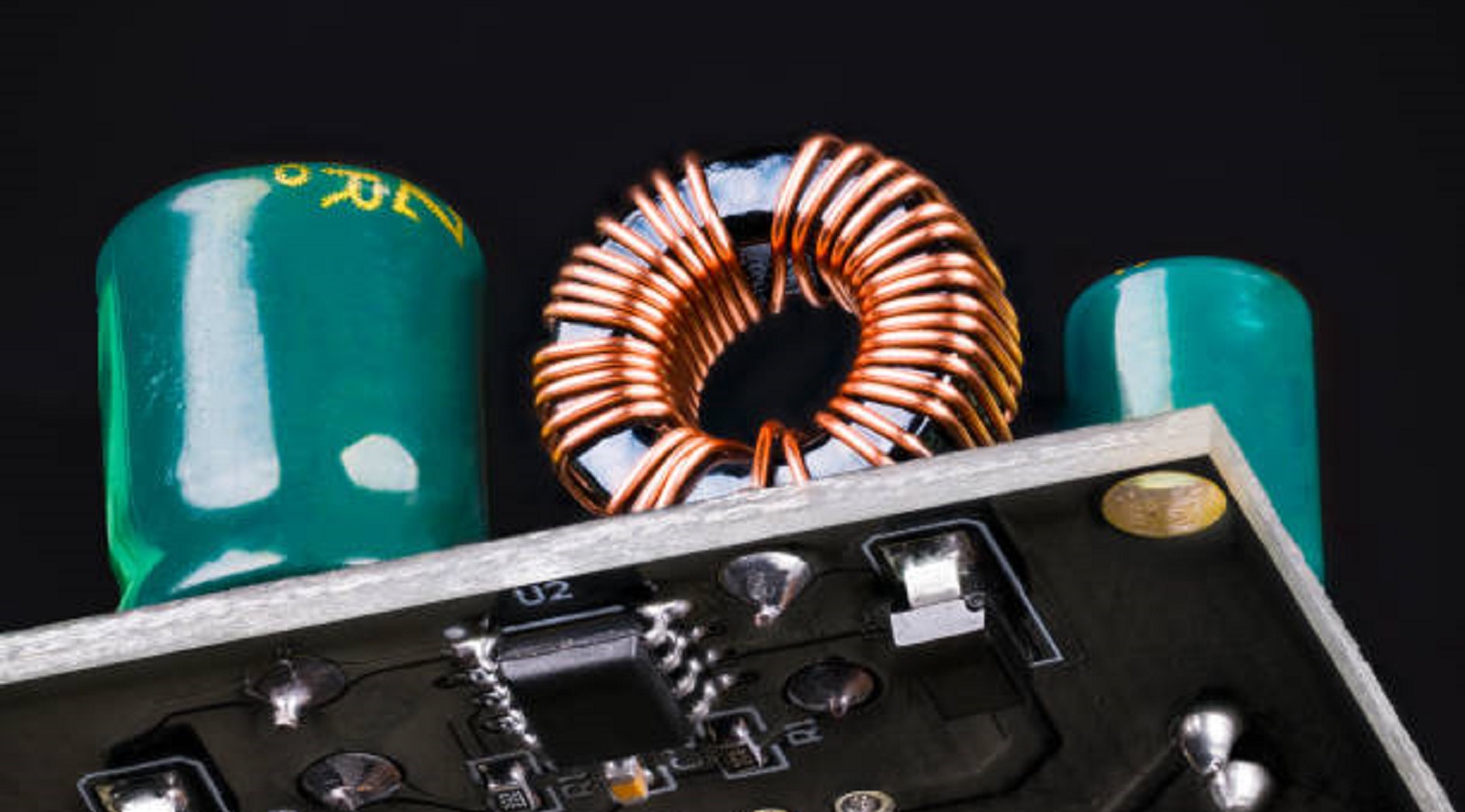
Voltage regulator PCB designs play a critical role in making sure electronic devices work stably in a wide array of applications. A proper type of voltage regulator selected with close attention to such design elements as layout, thermal management, and component selection will enable engineers to ensure their PCBs meet demanding standards of modern electronics. It helps in pushing the boundaries of efficiency and reliability in electronic design by insightful design and rigorous testing to drive innovation but still guarantees performance optimization in real conditions. Understanding Voltage Regulation Complexity It thus helps the engineers fabricate state-of-the-art durable electronic products that satisfy the changing requirements of different fields.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article

Capacitors are crucial in PCB design for filtering and timing. Correct polarity in electrolytic and tantalum types prevents malfunctions and ensures reliability.
High-speed PCBs (>1GHz) are crucial for advanced electronics like 5G and data processors. Key practices include ensuring signal integrity, controlling EMI, and maintaining power integrity for reliable performance.
The article compares Ball Grid Array (BGA) and Land Grid Array (LGA) packaging technologies for mounting microprocessors on PCBs. It details their pros and cons, applications, and factors to consider for optimal design choices.
