What is FR4 Thickness Tolerance?
FR4 is a favored PCB material for its cost-effectiveness and versatility. However, its thickness tolerance impacts mechanical strength, thermal performance, and electrical efficiency, affecting overall PCB reliability and performance.
FR4 is one of the most popular base materials used in manufacturing a PCB due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility. FR4 thickness affects many aspects of performance in a PCB, including mechanical strength, thermal performance, and electrical efficiency. This article will discuss how the FR4 thickness tolerance leaves room for error during the manufacturing of PCBs, which subsequently affects board performance and overall device reliability.
Introduction to FR4 Material
FR4 was manufactured by using a woven fiberglass cloth embedded in an epoxy resin, which provided great mechanical strength, electrical insulation, and fire resistance. The typical thickness for FR4 varies from 0.8mm to 1.6mm, though it may be specified well in millimeters and inches. Due to the huge variability in the thickness of the board, the PCB designer should be very aware of issues regarding component compatibility and space availability.
Importance of Thickness Tolerance in FR4 PCBs
The thickness tolerance is the acceptable deviation in the thickness of a PCB within its manufacturing. Such a characteristic factor will influence the mechanical stability, electrical performance, and compatibility of the PCB with electronic components. The tolerance normally depends on the type of PCB, material, and manufacturing process involved in its fabrication.
For example, a PCB can have a nominal thickness of 1.6mm with a tolerance of ±10% by the manufacturer. This would put the allowable range in any direction between 1.44mm and 1.76mm; thus, the board performance within these limits would determine its fit for the purpose of meeting the specifications and functionality.
Manufacturer Specification: Tolerances can be different for different suppliers based on the particular quality control.
Type of FR4 Laminate: Variants like high-Tg FR4 can be allowed to have a different standard tolerance.
Copper Cladding: Presence or absence, and thickness of copper layers can add to the overall tolerance during manufacture.
Manufacturing Processes: The accuracy and manner in which the lamination and drilling are carried out become important.
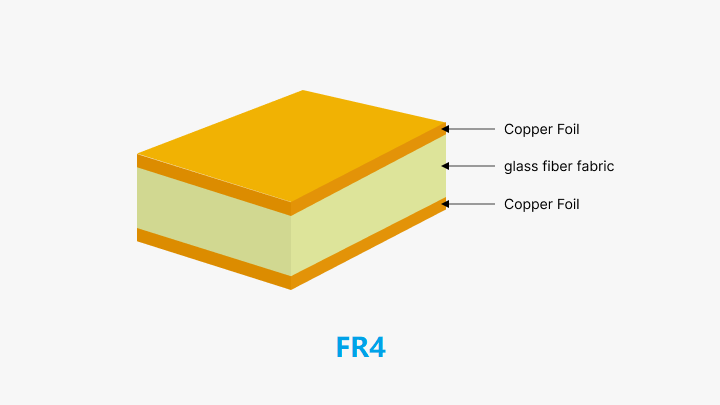
How Thickness Tolerance Affects PCB Performance
Mechanical Strength
Thickness of FR4 substrate has a very vital influence on the mechanical strength of the PCB. Thicker substrates will resist bending and twisting forces much better, making the PCB more robust, in particular in mechanically stressed conditions such as those encountered in portable electronic equipment. On the other hand, substrates with big thickness are prone to crack when excessive stress is applied and may make the PCB heavier, which is a negative point for portable applications.
Thermal Performance
The FR4 substrate in the PCB serves as a heat sink; therefore, it assists in thermal management. Thicker substrates usually have lower thermal conductivity and may be less capable of dispersing heat away from sources. Consequently, temperatures could rise and result in degraded performances and lower reliability of electronic components. Therefore, the adjustment of FR4 thickness in regard to specific heat dissipation requirements will be essential for maintaining optimum thermal performance.
Power Distribution
FR4 thickness dependence of low resistance of copper traces and planes has a significant effect on the power distribution network on a PCB. Thicker substrates raise the resistance, which will also increase voltage drop across traces and planes, hence poor power distribution efficiency.
Impedance Control
Impedance control is one of the critical aspects that need to be considered in high-speed PCB design. The impedance on traces in a PCB is inversely proportional to the thickness of FR4 material. Thicker FR4 materials make higher impedances, which may affect signal integrity via signal reflections and distortions. The thickness of FR4 needs to be attended to with importance in order to retain accurate impedance control.
Signal Integrity
Signal integrity, regarding the PCB, is the capability of electronic signals to retain their quality as they propagate through the PCB. In this perspective, the substrate thickness affects dielectric loss in FR4. This has an effect on the speed at which the signals are transmitted and therefore may cause signal loss or distortion. Thick substrates have a higher dielectric constant, Dk; this normally results in increased signal attenuation, especially for signals operating at high frequencies. The substrate thickness shall vary according to the frequency range of the signals, which will ensure minimal distortion and loss within the signal.
Key Factors to Consider when Choosing FR4 Thickness
While choosing FR4 thickness, the following are the key considerations:
Compatibility of Component: This is important for the types of components used, especially in THT, which sometimes requires a thinner PCB.
Space Efficiency: Space-saving is very crucial in compact designs such as USB connectors and Bluetooth devices.
Mechanical and Thermal Stresses: The operating environment determines the choice of thickness because of the trade-off between mechanical strength and thermal stress.
Impedance Control: Impedance is a function of thickness as it directly affects signal integrity.
Connection Requirements: The kind of connection used might be a function of FR4 thickness.
Conclusion
Amongst the most important manufacturing parameters in PCB manufacturing is the FR4 thickness tolerance, as it usually affects the mechanical stability, electrical performance, and, finally, overall reliability. The variation normally occurs in terms of nominal thickness with specified tolerance ranges. By understanding such specification, it allows the designer to include their requirements; hence leading companies like PCBX are able to ensure that all its design consideration has its best fit. It also guarantees that accurate consideration has been taken into designing the phase for the effects of operating conditions which the PCB will be subjected to in its case of application, ensuring efficacy and durability.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article

Understanding core and prepreg materials is crucial for PCB performance and manufacturability. Core provides stability and dielectric properties, while prepreg binds layers. Both affect signal integrity, mechanical stability, and thermal performance.
Designing a PCB involves ten detailed steps: schematic capture, creating a blank PCB layout, syncing designs, defining stackup, setting design rules, placing components, adding drill holes, routing traces, labeling, and generating output files. These steps ensure an organized, error-free process from concept to manufacturing.
Most electronic circuits are mounted on PCBs, or Printed Circuit Boards, which provide mechanical support and electrical interconnection of electronic components. There are, however, special applications that involve the use of single and double-sided PCBs, multi-layer PCBs, or even rigid and flexible PCBs with aluminum backing, targeting medical, industrial, auto, and aerospace industries. They may use materials such as fiberglass, epoxy, aluminum, and others.