What is PCB Panelization?
Panelization combines multiple PCBs on one panel, boosting efficiency and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing by optimizing space and enabling automation.
Panelization is one of the most important techniques in modern electronics manufacturing for effective and efficient PCBs. The technique allows several individual PCBs to be combined on to one larger panel that enables smooth and efficient handling and assembling, raising the production rate considerably. The explanation in detail of the process, benefits, and ways of successful integration of a PCB panelization into the processes of automated manufacturing are outlined below.
Panelization is made by placing one or several, identical or different from each other, circuit board designs on one single and bigger panel, often called a circuit board panel. The process is of great help for the automation of PCB assembly, for example, in deals of surface mount technology, where equipment like pick-and-place machines, stencil printers, and reflow ovens are used. Here, a manufacturer can overcome the disadvantage of dealing with small or irregularly shaped PCBs by introducing panelization to achieve efficiency in general manufacturing.
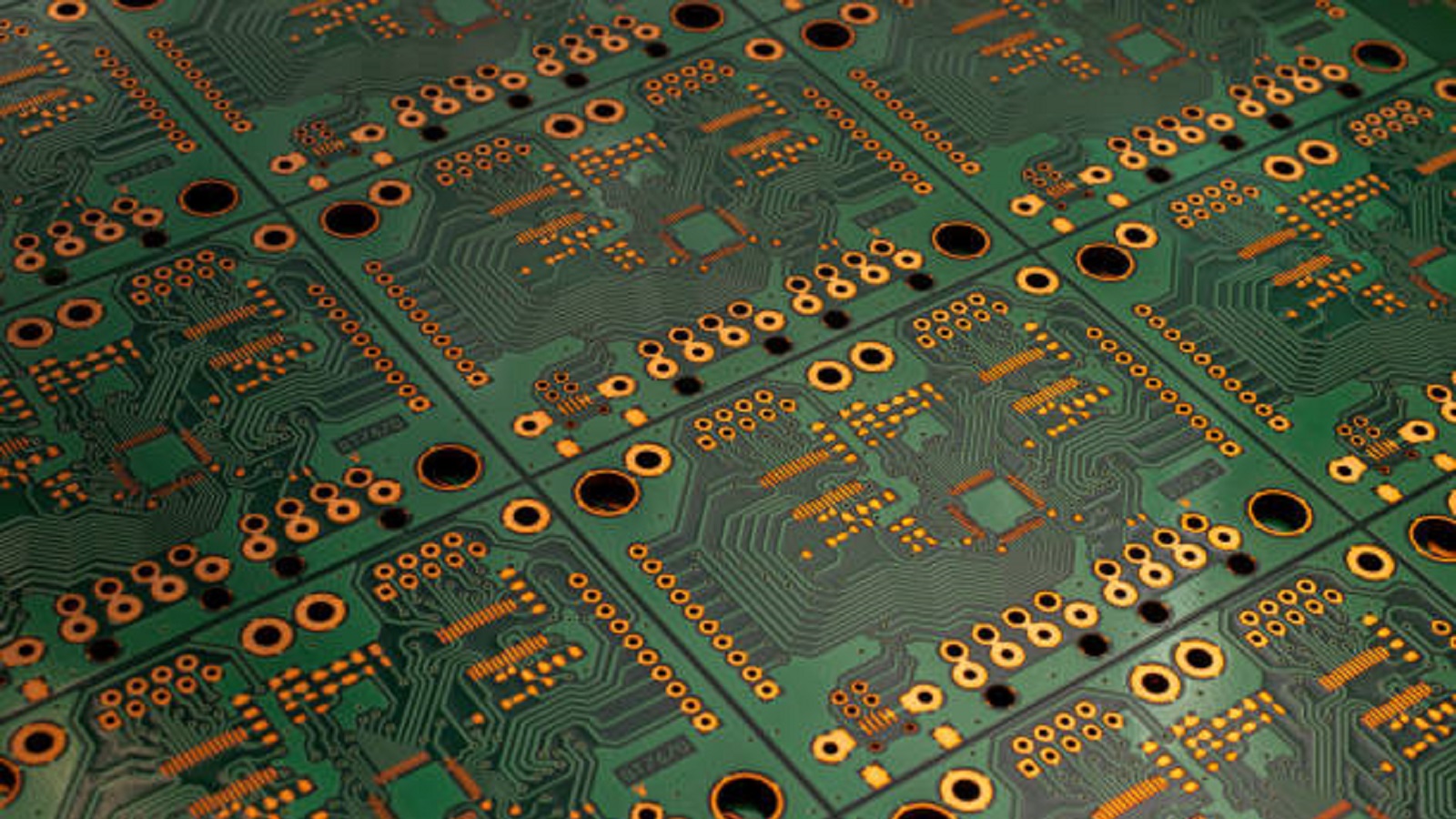
When and Why to Use PCB Panels
PCB panels are helpful in the following situations:
Small Board Sizes
Some pieces of automated assembly equipment have minimum size specifications; panelizing small boards into a PCB panel will meet these requirements, making handling easier and increasing efficiency on the line.
High Production Volumes
This saves time and reduces the cost of preparing several PCBs at the same time in a panel circuit board for large-scale production. A consolidated approach means that economies of scale can be achieved, streamlining the overall assembly process.
Component Proximity
Panelization provides further protection where the components are at the edges of the board. Panel rails, thin strips enclosing the array of boards, serve to provide structural integrity, allowing safe conveyance on conveyor systems without damage during assembly.
Depanelization Methods
After the assembly, individual PCBs shall be separated from the panel. The separation process is called depanelization and it can be performed in several ways:
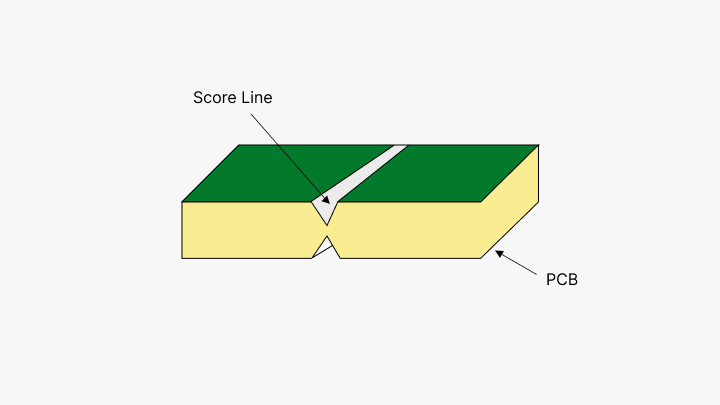
V-Scoring
V-scoring involves grooves that go in a 'V' shape down the line where boards will be demarcated. The groove would typically take out about two-thirds of the material of the board, which leaves you with thin pieces that then easily can be separated using any tool used like a pizza cutter. This process is less expensive and leaves very small spacing between boards, hence suitable for rectangular shapes. It is not very usable for complex geometries or boards with overhanging components, which could easily get damaged in this case when trying to separate them.
Tab Routing
The tab routing method uses the CNC machinery to rout slots between the PCBs so that each is connected to others through perforated tabs, also called "mouse-bites." These tabs allow a very flexible method since they support irregularly shaped boards and those with overhang beyond the edge. These tabs can be easily broken away post-assembly but slight spacing between the boards necessitates larger panel size and greater fabrication cost.
Breakaway Rails
Breakaway rails are temporary support structures added to the edges of a panel that improve stability during manufacturing. These are typically 5-8 mm wide and can easily be detached after assembly so that clean edges are provided in the final boards with more protection during production.
Key Design Considerations for PCB Panel
There are a few key considerations in effective PCB panel design:
Rail Design
Rails should not be wider than necessary to provide panel strength, yet not so wide as to waste material and increase costs. In general, it has to be based upon a general estimation of handling and mechanical stability requirements.
Tooling Holes
Three or four unplated tooling holes in the rail are helpful in providing alignment or handling during the assembly process. They are typically made to a diameter of about 0.12 inches to accommodate the majority of equipment used.
Fiducial Marks
These are reference points used by automatic assembly equipment for alignment purposes. The addition of at least two fiducial marks enables the placing of components with high accuracy by pick-and-place machines.
Panelization is an important strategy to help your production become more efficient and cost-effective. This process will optimize space, enable automation, and consequently improve handling in order to take the manufacturing process to the next level. Panelization is indispensable when it deals with high volume production environments, be that by working directly with a surface mount device distributor or taking into account the design of the panel circuit board layout. Understanding these principles will make the big difference in your manufacturing process.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Tab routing in PCB manufacturing boosts efficiency and quality, ideal for non-linear shapes, offering flexibility, support, and cost-effectiveness in production.
Tab routing enhances PCB production efficiency and quality, ideal for complex shapes. It offers cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and protection, crucial for high-precision designs and panelization.

PCB testing ensures quality and reliability by assessing key components like lamination, copper plating, and conductivity. Methods include ICT, FPT, Burn-in, and AOI. Testing reduces bugs, time, cost, and enhances safety.
