What is Solder Flux?
Solder flux ensures strong PCB joints by cleaning oxidation. Types include rosin, no-clean, and water-soluble, crucial for reliable electronics assembly.
Now, solder flux has a very important role in the modern PCB manufacturing process and technology of electronics assembly. This is not just related to being an auxiliary tool in this regard; instead, it is very important in acquiring reliable and strong solder joints.
In its most reduced form, flux is a chemical cleaner which assists in joining solder to the metal surface in which a soldering operation takes place. The prime task of flux is to clean the metal surfaces from oxidation and other contamination, allowing the smooth flow of solder and hence realizing a good bond. Without any flux, this oxidation could create a barrier and joints formed would be weak and unreliable.
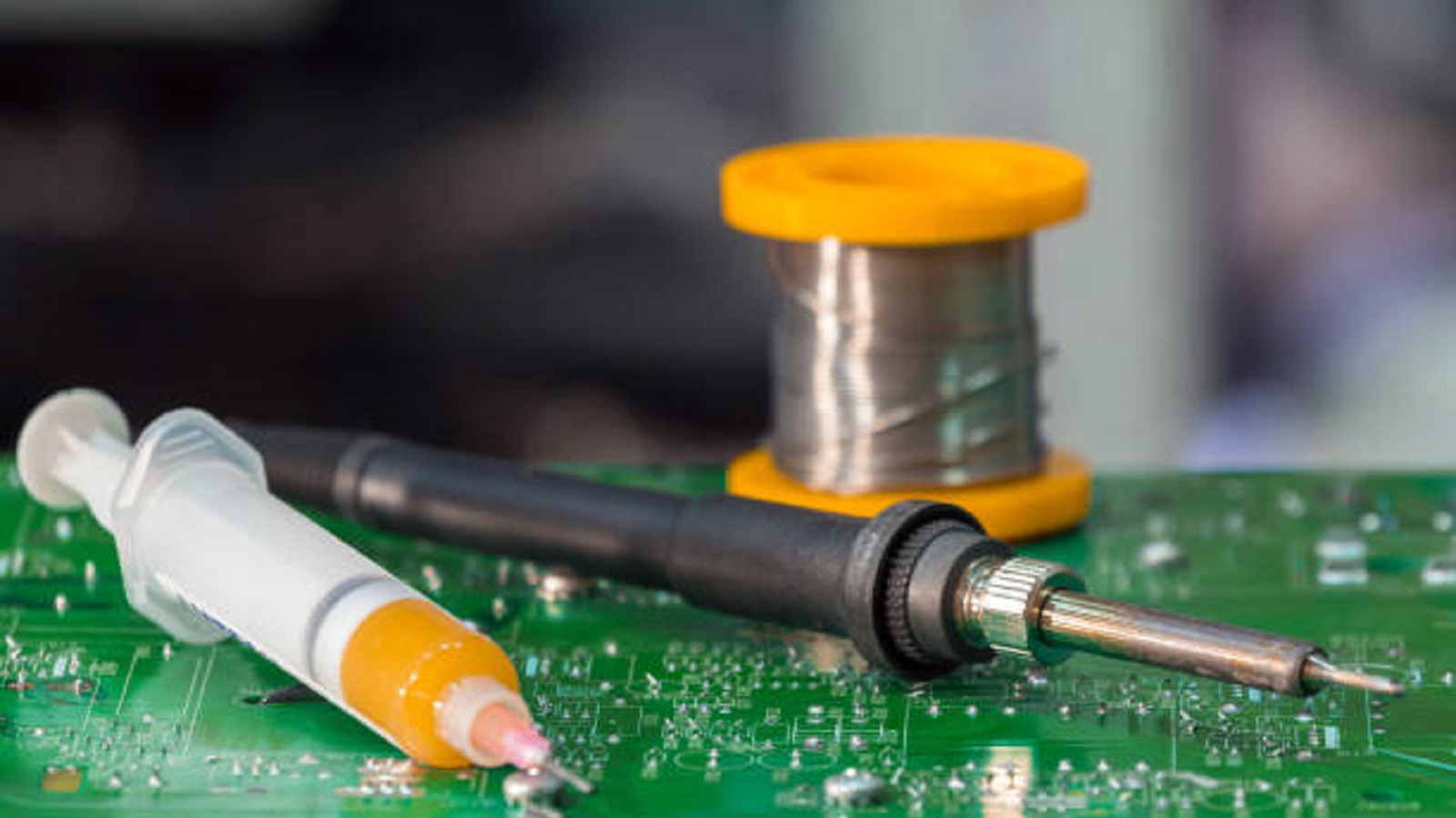

Types of Solder Flux
Choosing the right type of flux is of vital significance because it relates to application-specific and requirement-based operations. Some of them are listed as follows:
Rosin Flux:
Usual application in electronics, because it is nontoxic.
Highly excellent performance in the soldering temperature, with minimal chances of poisonous residue left on the PCB.
Application in general electronics jobs where post solder cleaning is allowed.
No-Clean Flux
Designed to minimize cleaning of flux residue in case it is impractical to clean.
Leaves minimum, harmless residues, essential when large quantities of production are involved.
Those applications which require minimum or no cleaning process.
Water-Soluble Flux
In its most common form, a glycol-based type finds very wide application in automated PCB assembly where the production rates are high.
Are readily removed with a light water wash following soldering, thus efficiently stripping possible corrosive residues.
Effective Soldering with Solder Flux
Solder flux has two crucial considerations: compatibility and activity level.
Compatibility: The flux shall be compatible with the materials to be joined so as not to cause any corrosion or damage; poor compatibility, especially while working with copper, results in joint failure.
Activity Level: The flux should be active enough to remove oxidation or contaminants while being mild during its operation so that it may not damage the components or joints. There has to be the right balance for effective soldering.
Clean Flux Residue
Flux residues can be controlled by a variety of methods including solvent, isopropyl alcohol or cleaning solution. The technique for cleaning depends upon flux type and cleaning equipment available.
When Can Soldering Be Done Without Flux
Solder flux is generally advisable, but not in all cases, such as pre-tinned pads or solder paste with enough flux. In the case of very small components, like surface mounts, it depends entirely on the flux inside the solder paste for a good bond. The need for applying any flux is according to specific needs of materials, surface conditions, solder type, and strength of joint required.
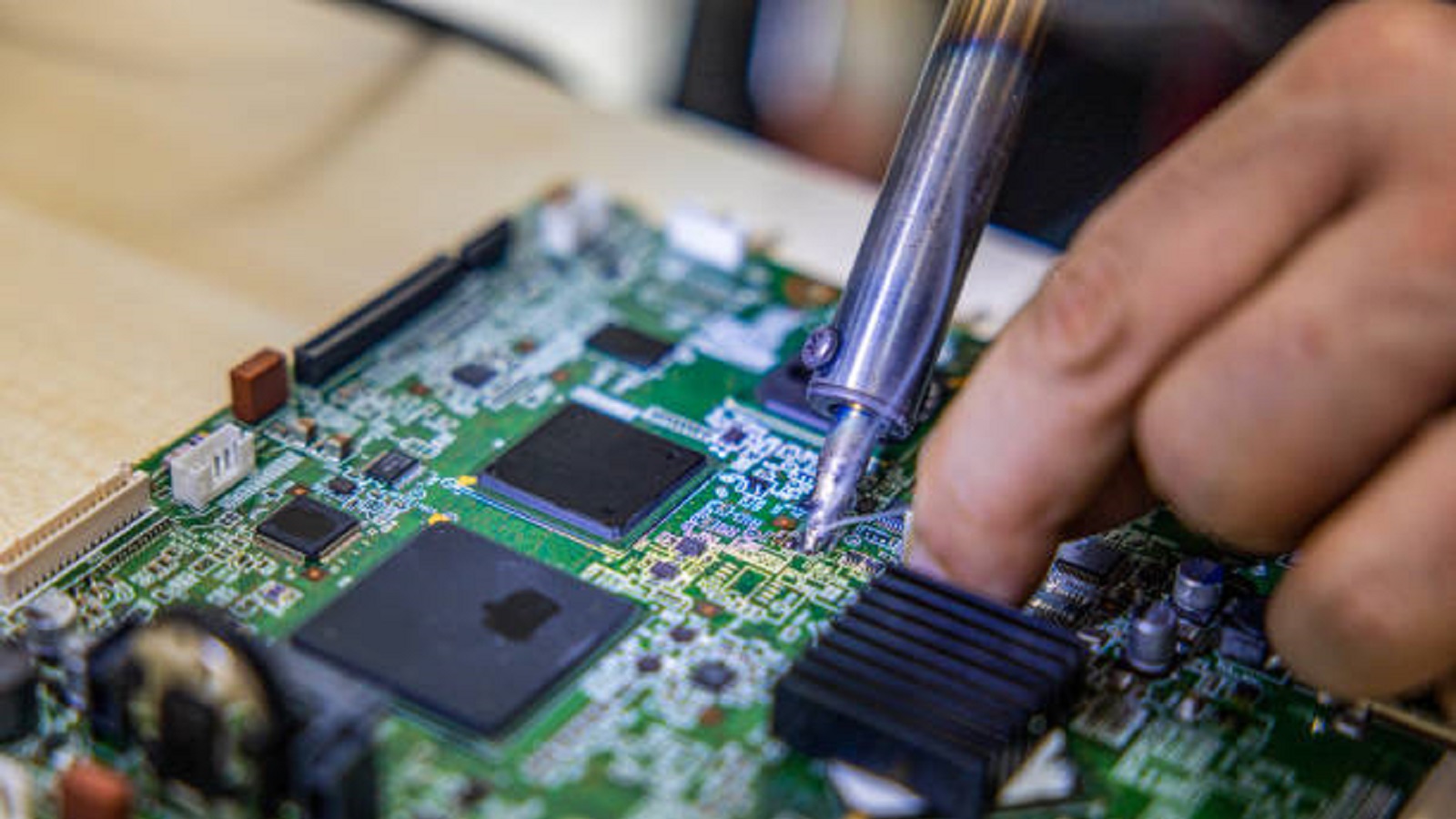

Solder flux is hence a very important ingredient in electronics and PCB assembly regarding the solder joints' durability and reliability. At PCBX, we recognize the critical role of solder flux and strive to provide insights and solutions that enhance manufacturing efficiency and product reliability. Whether in high-tech electronics or large-scale manufacturing, mastering the application of solder flux is essential for achieving excellence in soldered assemblies.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
The article provides a step-by-step guide to soldering a PCB, covering workspace setup, essential tools, and safety measures. It explains heating the soldering iron, applying flux, tinning the iron tip, placing components, heating joints, applying solder, cooling, inspecting, and cleaning. Emphasis is on practice and safety for successful soldering.
Wave soldering is a PCB assembly process that moves the board over a molten solder wave to create reliable connections. Evolving from dip and drag soldering, it offers consistent, high-quality solder joints. Despite its complexities, it remains essential for through-hole components and complex PCB assemblies.

Ensuring BGA soldering quality involves defect prevention, pre-soldering measures, and precise control during SMT assembly and reflow soldering.