What is Heavy Copper PCB?
Heavy copper PCBs enhance current capacity and thermal performance, essential for high-power applications in military, automotive, and energy sectors, offering strength and heat dissipation.
Printed circuit boards carry current through the etched copper tracks. Increasing the width can improve the current-carrying capability of a copper trace, but this is not practical. The other methods of improving the carrying capacity without variation of the width of the copper traces involve the use of heavy or thick copper. It carries more current and improves efficiency with better heat management.
In the fabrication of heavy copper boards, there are no definite rules that specify the amount of copper to be used. However, the PCB industry normally considers 3 or more ounces of copper on any circuit board layer as heavy copper.
Why are Heavy Copper PCBs used?
Some PCB designs require higher current levels in the way of wider traces. However, as higher levels of power are required, it needs thicker copper to transmit the signals across the board. That is why heavy copper PCBs are used in high current designs. Benefits of Heavy Copper PCB
The main advantage of Heavy Copper PCB is the capability to support frequency to excessive current, high temperatures, and repetitive thermal cycling that could destroy a regular circuit board in a matter of seconds. Besides, heavy copper PCBs are in great demand within computer, automotive, military, and some industrial controls.
Moreover, the board of heavy copper PCB is also applied in the following other areas:
Compact product size due to several copper weights on the same layer of circuitry;
Onboard high-power-density planar transformers;
Heavy copper-plated vias that pass elevated current through the PCB are good for transferring heat to an outer heat sink.
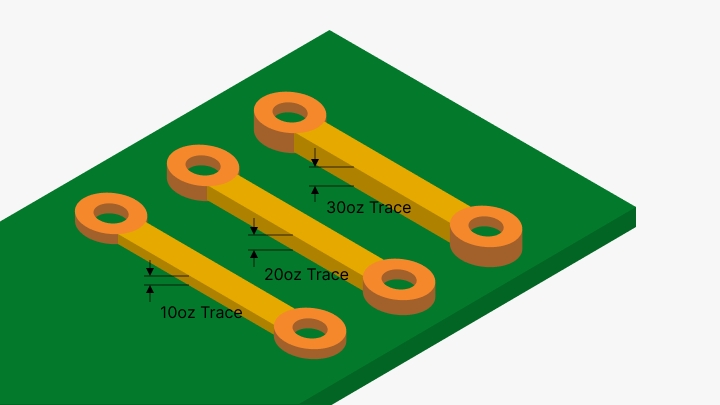
Advantages of Heavy Copper PCB
Improved thermal performance: Heavy copper PCBs can withstand repeated thermal cycles during manufacture and assembly processes.
Improved current carrying capacity: Heavy copper PCBs provide improved electrical conductivity and support higher current loads due to the extra thickness of copper. The current carrying capacity can be improved by increasing the width of copper traces; even higher loads of current can be supported with copper trace thickness.
Improved mechanical strength: Heavy copper PCBs provide greater mechanical strength at connectors and plated-through holes, maintaining the structural integrity of the board and making the electrical system at the model more robust and resistant to voltage.
Best dissipation factor: Heavy copper PCBs find huge applications in large power-loss components. These PCBs don't allow the electrical systems to get overheated and dissipate the heat effectively.
Good conductor: Heavy copper PCBs are good conductors. They find extensive use in manufacturing electronic products. These boards connect with several other boards that can transmit currents.
Applications of Heavy Copper PCB
Heavy copper PCBs have been in increasing demand these days due to their wide application in the following fields:
Military: Weapons control, radar, monitoring systems.
Automotive industries: The rail track system and the signal transmission system.
Power distribution: Excitation systems for the power regulator, the power grid switching system, high power rectifiers, overload relays.
Transportation: Power converters for railway systems, power line monitors, traction converters.
Industrial Controls: Safety and signal systems, welding equipment, protection relays, surge protectors.
Renewable Systems: Power converters, energy storage, power grid backup, hydroelectric power plants control panels.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Copper thickness in PCBs, crucial for functionality, influences operation, thermal management, and reliability. IPC standards guide its choice, balancing performance and cost for optimal design.
PCB copper plating is key for creating conductive traces that drive electronic circuits, offering benefits like conductivity, anti-corrosion, and cost-effectiveness. Plating methods include electroless and electrolytic.

Aluminum PCBs are widely used electronic boards with comparatively better heat dissipation properties. The aluminum core cools down the components of the product, thereby improving its performance. These are eco-friendly, light, and strong PCBs and hence appropriate to be used in audio equipment, power supplies, and lighting products such as LED lighting.
