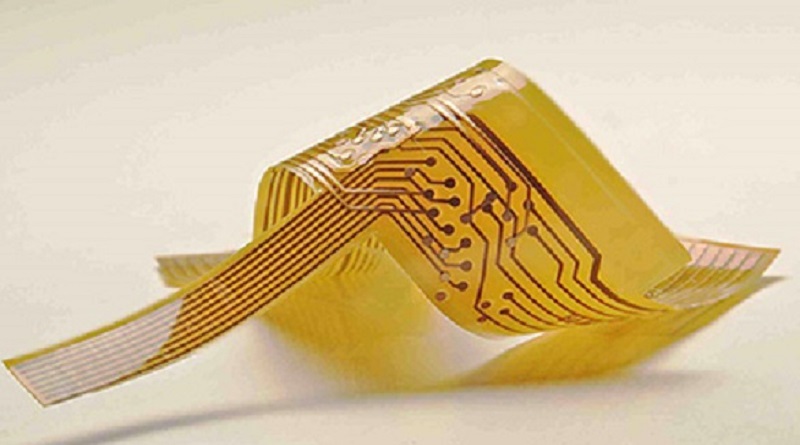
What is the Construction of Flex PCB?
Flex PCBs are bendable circuit boards ideal for space and weight-sensitive applications. Key elements include polyimide or PET substrates, copper traces, adhesives, coverlays, protective finishes, and component mounting areas.
Flexible Printed Circuit Boards, Flex PCBs, are a class of electronic circuit boards designed to be more flexible and bendable than the traditional rigid PCBs. The flexibility extends the usability of the boards in applications where space and weight are at a premium, and the circuit has to assume complicated shapes. The following is a detailed look into the construction of a Flex PCB:
1. Base Material (Substrate)
The base material for a Flex PCB usually consists of flexible polymer film. The two most usable materials are as follows:
Polyimide (PI): It is the most popular substrate material owing to its excellent thermal stability, flexibility, and chemical inertness.
Polyester (PET): Used in less demanding applications due to low-cost compared to polyimide but it has low thermal stability.
2. Conductive Layer
The conducive traces in Flex PCBs are normally made of copper, as this is a very good electrical conductor. These copper layers may be applied by the following methods:
Electroplating: Deposits a layer of copper by electroplating onto the substrate.
Laminating Copper Foil: Pre-manufactured copper foil is attached to the substrate with adhesive.
3. Adhesive Layer
Most of the time the copper foil is bonded to the substrate using an adhesive layer. There are two major types of adhesives:
Acrylate Adhesive: High flexibility, good thermal performance
Epoxy Adhesive: Strong adhesion, excellent thermal properties, less flexible than acrylate
4. Coverlay Cover Film
The coverlay protects copper traces from environmental damage, such as moisture, dust, and handling. It assists in supplying electrical insulation. The coverlay generally is made of:
Polyimide Film: Used most due to its flexibility and thermal stability.
Adhesive Layer: This is just like the adhesive for bonding copper and is very helpful in attaching the polyimide film to the copper layer.
5. Protective Finish
This step protects exposed copper areas, pads and traces from oxidation and maintains good solderability. The common finishes include:
HASL: A layer of solder is applied for giving the protective coating.
ENIG: Gives a smooth surface and excellent resistance to oxidation.
OSP: Water-based coating applied for protecting the copper till soldering.
6. Component Mounting Areas
In the design of a flex PCB, areas are usually left for mounting the components. And these may be provided with stiffeners, or rigid sections, to enhance strength and rigidity for easy mounting of components during operation. The used stiffeners can be fabricated from:
FR-4 Epoxy Glassing: Commonly used material for PCB
Polyimide: Compatible with the substrate material with increased rigidity.
Layer Construction
Single-Sided Flex PCB: This has a conductive layer of copper on one side over a flexible dielectric film; it is covered on one side with coverlay.
Double-Sided Flex PCB: It contains two conductive layers separated by a flexible dielectric layer, both sides protected by coverlays.
Multilayer Flex PCB: These include three or more layers of conductive material separated by flexible insulating layers that are laminated together in one structure. The through-hole vias provide electrical interconnections between layers.
Important Considerations in Flex PCB Construction
Bend Radius: It defines the minimum radius the flex PCB is permitted to bend without damage. This parameter is quite necessary in such applications where frequent flexing is expected.
Heat Management: Material selected should be able to handle or dissipate heat properly with consideration for proper design.
Mechanical Stability: Flexibility and mechanical strength of the PCB to withstand operating environments specific to its application.
Electrical Performance: Good trace design with appropriate shielding to ensure electrical signal integrity.
Conclusion
Material selection and process integration must be chosen with care for arriving at a specific final product in consideration of flexibility and durability. The different components that come into play, along with their interaction, must be understood well for solid and dependable flex PCB designs to come up for many applications.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article

Flex PCBs fit into devices, saving space, while Rigid-Flex PCBs combine flexible and rigid parts, ideal for varied applications. PCBX offers custom designs, rapid prototyping, and high-quality manufacturing.

Choose between single-layer or multi-layer PCBs based on your project's needs. Single-layer is simpler and cost-effective; multi-layer offers complex functionality and durability. Evaluate based on functionality, size, durability, budget, and turnaround time.
Most electronic circuits are mounted on PCBs, or Printed Circuit Boards, which provide mechanical support and electrical interconnection of electronic components. There are, however, special applications that involve the use of single and double-sided PCBs, multi-layer PCBs, or even rigid and flexible PCBs with aluminum backing, targeting medical, industrial, auto, and aerospace industries. They may use materials such as fiberglass, epoxy, aluminum, and others.
