White PCB
White PCBs offer modern aesthetics and enhanced LED efficiency but pose cleaning and inspection challenges, ideal for visually appealing electronics.
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) in the realm of electronics form a basic framework on which components are mounted and interconnected. Conventionally, green in color, the range has diversified into several colors, one of them being white, especially when a specific application requires this particular hue. This article describes white PCBs by elaborating on aesthetic appeal, practical use, and possible challenges.
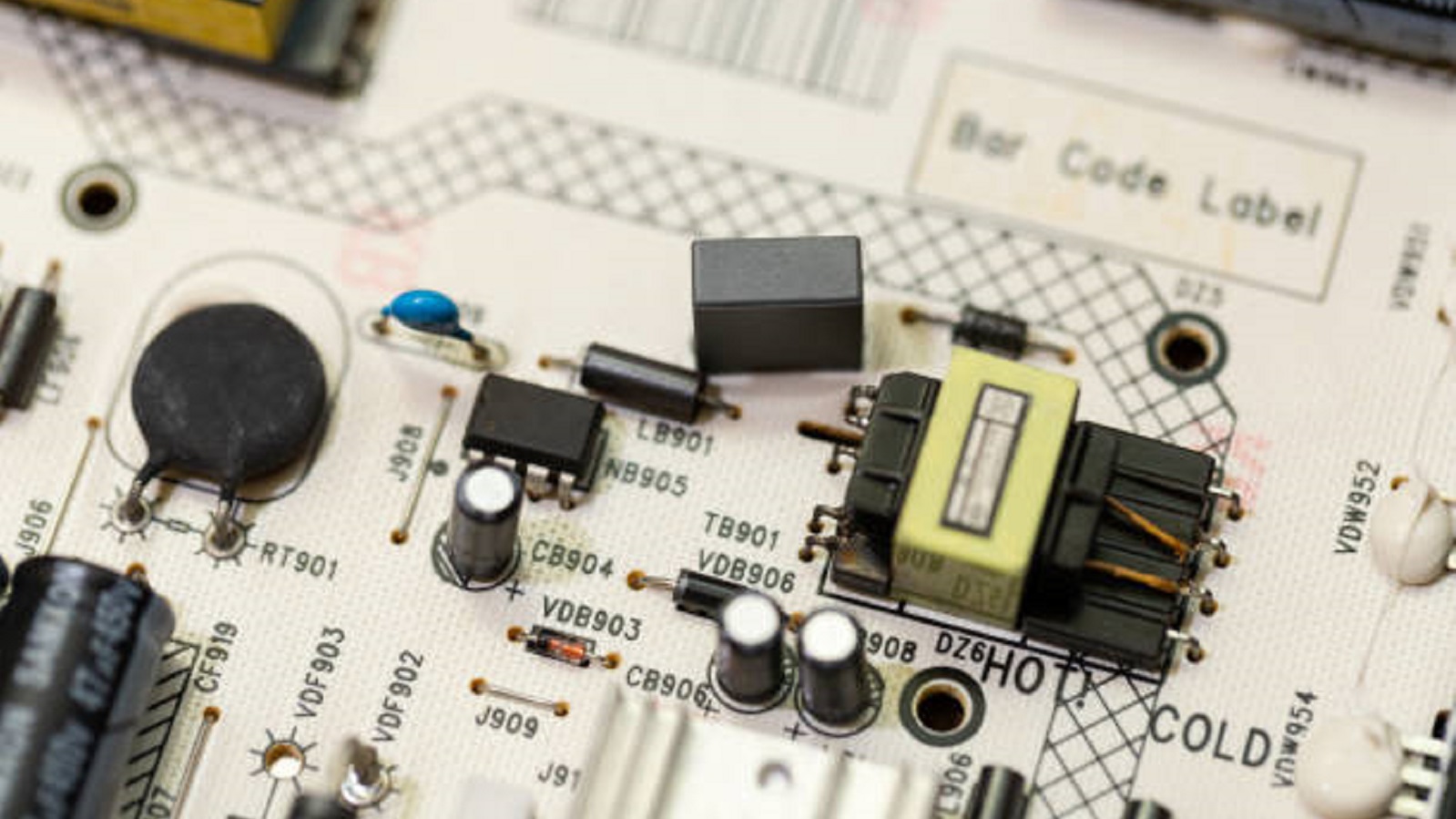
A White PCB is differentiated by its white solder mask, which is a layer applied atop the board for protection against environmental damage and to avoid any accidental solder bridging while assembling. The bright white color is attained with a composition of the solder mask in such a way that the white pigment concentration is high enough to make it durable and resistant to substantial fading.
The Advantages of White PCBs
Aesthetic Appeal
Modern Design: White PCBs have a clean, modern look and are hence quite in demand for consumer electronics to add an attraction factor to the product. Devices like smart home gadgets or highly advanced audio equipment leverage this stylish look.
Component Visibility: The high-contrast background of a white PCB makes the components stand out, which is very useful in products whose casings are made of clear or semi-transparent material to show the internal components.
Ideal for LED Applications
Improved Light Reflection: White PCBs are very valued in LED systems as they have great reflective capabilities that increase light output, providing uniform brightness.
Less Light Absorption: White masks absorb less light compared to darker masks, hence maximizing the efficiency of LED devices by enhancing luminosity.
Branding and Customization
Customization Flexibility: White boards facilitate brand customization, allowing logos and graphics to appear more vibrant and eye-catching.
Design Consistency: White PCBs easily fit into a line of products for companies seeking consistency in the aesthetic message or specific color theme being promoted.
Considerations and Challenges with White PCBs
Despite the listed advantages of white PCBs, these are specific challenges associated with their use, which shall be considered:
Cleaning and Visibility: A white solder mask shows every bit of even a minor imperfection and may take rigorous cleaning to appear decent. Residuals and dust also seem far more evident than with other colors.
Inspection Issues: This reflective nature can make white PCBs challenging to inspect visually, requiring advanced inspection techniques or special lighting arrangements to correctly identify defects.
Heat Management Issues: Although color can affect heat dissipation, this is usually a minimal concern in applications for which white PCBs are used, such as low-power or LED applications.
Application of White PCBs
White PCBs find usage in several application areas:
Consumer Electronics: White PCBs contribute to the sleek design of modern consumer electronics, from smart speakers to stylish home appliances.
LED Lighting Systems: Their white color enhances reflection, making them ideal for LEDs and architectural lighting applications.
Wearable Technology: In wearables, where both form and function matter, white PCBs provide a visually appealing and compact solution.
White PCB vs. Black PCB
While white and black PCBs are less common than the traditional green, each color has a different purpose for which it is used:
Aesthetic Appeal: White PCBs are considered polished and modern, while black PCBs offer sleek elegance, more suitable for high-end electronics.
Light Management: white is good for reflecting light, hence suitable for LED applications, while black often fits premium aesthetics for non-light-emitting products.
Ease of Inspection: Black may mask circuit traces, while white is highly reflective, making the process of visual inspection for either color difficult to conduct.
Tips for Designing with White PCBs
The following are some designing considerations with white PCBs. When using white PCBs, the following design tips can help maximize their potential:
Keep Clean: Ensure strict cleaning processes during manufacturing to avoid any visible marks.
Optimize Inspection: Use newer inspection methods that are suitable for reflective white PCBs.
Leverage Lighting Efficiency: In applications involving LEDs, designers can utilize the reflecting characteristics of white PCBs and create circuitries that increase light output.
Explore Branding Opportunities: The ability to customize the surface brings out the brand elements or instructions on the surface remarkably well.
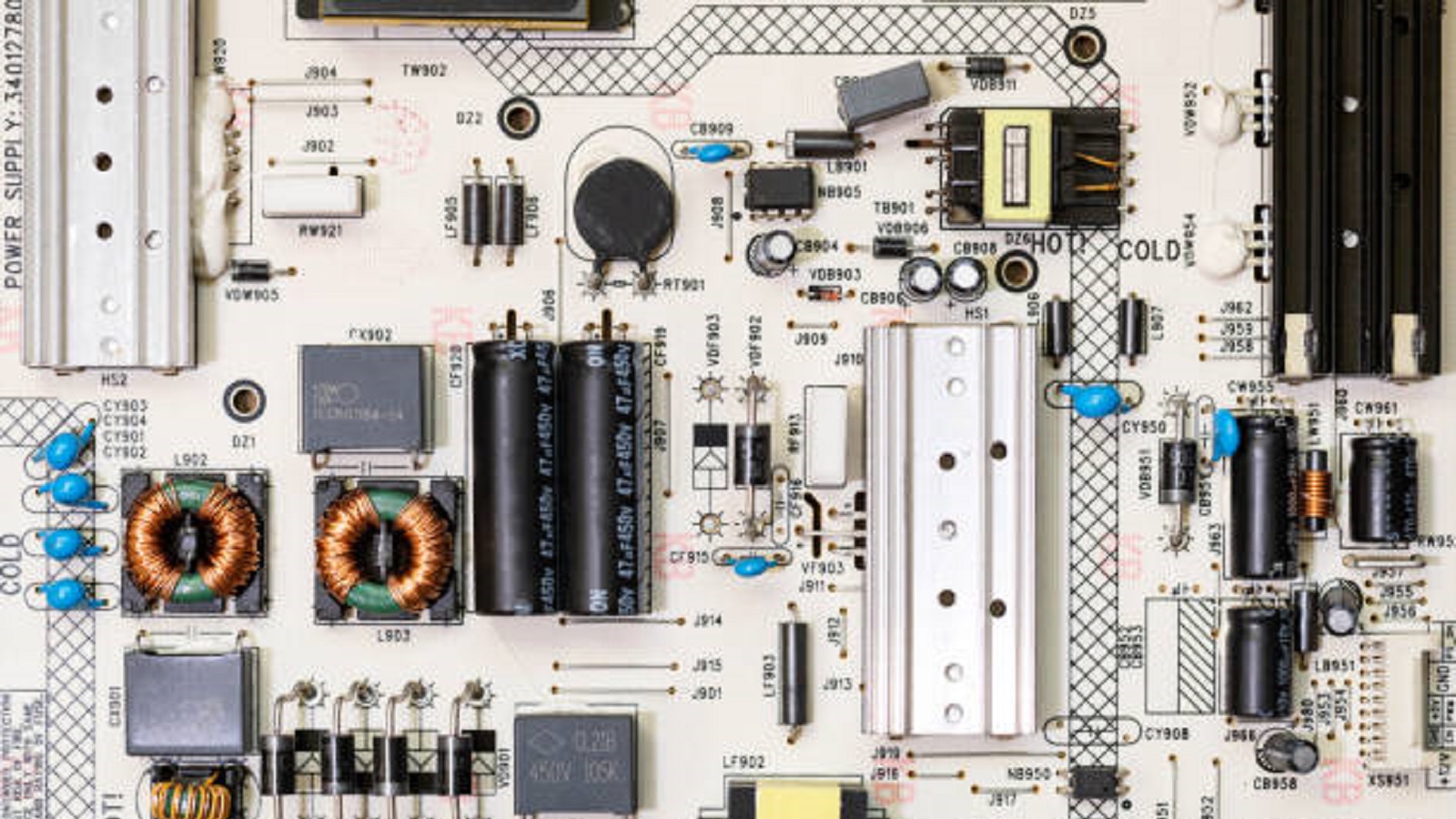
White PCBs hold an important place in electronics, serving remarkable aesthetic and functional benefits, most especially when it comes to applications dealing with lighting. While they do present certain manufacturing and inspection challenges, advantages in their use make them a very attractive option for targeted applications where design and light efficiency are key. In the evolution of PCB technology, selecting the solder mask color, including white, has become an integral part of the design process. Whether it be visually appealing consumer electronics or high-efficiency lighting systems, white PCBs represent a great option for anyone seeking to innovate and leave a mark on their electronic designs. In general, understanding the distinctiveness of white PCBs can lead to more informed decisions, yielding products that are both aesthetically pleasing and functionally superior.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Blue PCBs enhance electronics with aesthetic appeal, improved inspection, temperature resistance, and brand identity, offering unique advantages over traditional options.
Purple PCBs offer aesthetic and technical benefits, enhancing contrast and performance. Ideal for various industries, they require careful manufacturing for best results.
Black FR4 PCBs offer aesthetic and functional benefits, including light blocking, heat dissipation, and enhanced signal performance, suitable for electronics.