General Knowledge of PCB OSP Surface Finish
The article insinuates the need for Organic Solderability Preservatives on printed circuit boards. OSP can adsorb onto the copper surface to prevent oxidation and moisture and can easily get washed out by soldering. It is easy to manufacture an OSP, which is environmentally friendly and not expensive, thus becoming one of the most popular surface finishes today.
The electric connection on a PCB depends on the conductivity of copper. As an active chemical substance, however, copper tends to be oxidized upon exposure to atmospheric humidity, which may cause subsequent problems during high-temperature soldering and seriously threaten the solid fixation of parts on PCBs, influencing the reliability of the end product. Thus, surface finish has two main duties regarding the performance of PCB: protecting copper from getting oxidized and providing a surface to yield high solderability when the component is ready to be assembled on the PCB.
Board finishes can be categorized into different classes, depending on various technologies and involved chemical substances: HASL, Immersion Tin/Silver, OSP, ENIG, and ENEPIG. Of all the finishes, OSP is becoming increasingly prevalent due to its low cost and environment-friendly nature, which adds to the need for a better understanding of it. That is why this article gives a detailed introduction to OSP.

Brief Introduction
OSP stands for "organic solderability preservatives", and it is also known as anti-tarnish. The organic finish on clean and bare copper is created through adsorption, preventing copper from oxidation, thermal shock, or moisture. On the other hand, it has to be easily eliminated by flux in the later process of soldering so that the exposed clean copper can be joined with the melting solder for solder joints to be generated within an extremely short period.
The applied water-based chemical compound belongs to the azole family which includes benzotriazoles, imidazoles, and benzimidazoles, all of which get adsorbed on the copper surface with coordination formed between them and copper atoms that lead to film production. On film thickness, the film made through benzotriazoles is thin while that through imidazoles is relatively thick. Here, the thickness differentiation will bring a distinct impact on the effect of the board finish, which is to be discussed later in the article.
Manufacturing Process
OSP has a history of a decade, longer than that of SMT. The process flow of OSP is as shown below.

cleaning functions to remove organic contaminants such as oil, fingerprints, and oxidation films to keep the copper foil surface clean and bright, and this may be regarded as the most basic requirement, which plays quite a critical role in building up preservatives of high quality, as bad cleansing often results in flash thickness non-uniformity. First of all, ensuring that the finished OSP film is high quality, on the one hand, it is necessary to control the concentration of cleaning solution within the standard range by chemical laboratory analysis. On the other hand, the cleaning effect is suggested to be checked as frequently as possible, and once that effect doesn't reach the standard, the cleaning solution shall be instantly replaced.
In topography enhancement, micro-etching is usually applied to eliminate enormously the oxidation generated on copper foil to improve the bonding forces between copper foil and OSP solution. The speed of micro etching is going to directly influence the film build-up rate. Hence, for smooth and even film thickness, keeping the stability of micro etching speed seems quite critical. Generally speaking, the micro-etching speed shall be controlled within the scope of 1.0~1.5μm per minute.
DI rinse should be utilized before preservatives build in case the OSP solution might get polluted by other ions, which can be the cause of tarnish happening after reflow soldering. It's also best to use DI rinse after preservatives build with a PH value between 4.0 and 7.0 in order not to destroy the preservatives as a result of pollution.
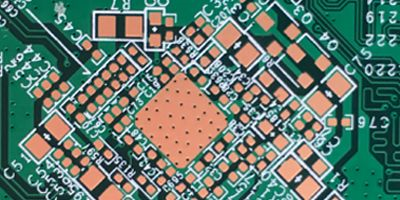
Advantages
As mentioned, OSP has been the most popular surface finish in recent years because of the following advantages:
• Simple manufacturing process and Reworkable: The circuit boards coated with OSP can be easily reprocessed by the PCB fabricators, allowing PCB assemblers to replace damaged coatings.
• Good wettability: OSP-coated boards perform better in solder wetting if flux touches with vias and pads.
• Eco-friendly: Water-based compound is applied during OSP generation, environmentally friendly and falling into people's expectations for a green world. As a result, OSP is an optimal selection for electronic products catering to green regulations like RoHS.
• Low cost: Due to the simple chemical compounds applied in OSP creation and the easy production process, OSP gives less cost, which eventually contributes to a reduced cost of PCB.
• Ideal for reflow soldering in double-side SMT assembly: Combined with the ever-changing and improving OSP, it has been approved from single-sided SMT assembly to double-sided SMT assembly, greatly extending its application areas.
• Can be used with minimum demand for solder mask ink
• Long storage life
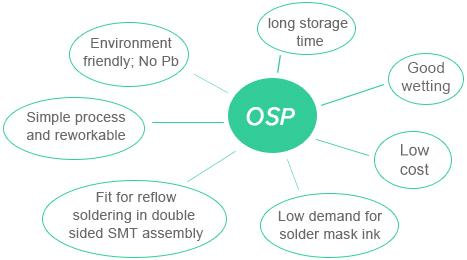
Storage Requirements for OSP-Coated PCBs
Since the OSP technology-generated preservative is thin and easily cut, much care should be taken during operation and transportation. OSP surface-finished PCBs are exposed to such a high temperature and humidity for a long time that oxidation could be generated on the surface thereafter, leading to low solderability. Therefore, storing methods must stick to these principles:
a. Vacuum package shall be used with desiccant and humidity display card. Insert release paper between PCBs to prevent friction damage to the PCB surface.
b. These PCBs cannot directly be exposed to sunlight. The optimum storage environment requirements involve relative humidity 30-70%RH, temperature 15-30°C, and storage time, which should be fewer than 12 months.
Possible OSP problem after soldering
Sometimes, the color of OSP boards changes after soldering, which has something to do with preservative thickness, micro etching quantity, soldering times, or even abnormal contaminants. Luckily, this problem can be observed just from the appearance. Normally, there are two conditions:

For Circumstance#1, during the soldering process, flux is capable of helping to eliminate oxidations so that the soldering performance will not be influenced. Accordingly, no more measurements have to be taken. On the contrary, Circumstance#2 occurs because OSP integrity has been destroyed so that flux is not capable of eliminating oxidations, which would greatly decrease the soldering performance.
The following improvements and measurements to the thickness of OSP and micro-etching amount, therefore, should be taken to ensure the appearance and performance of organic solderability preservatives surface finish:
a. OSP thickness is to be controlled within a certain range;
b. Micro-etching amount is to be controlled within a certain scope;
c. Contaminants such as gel residue, ink, etc., should be 100% eliminated in PCB fabrication to avoid part abnormity or bad performance on solderability.
PCBX Provides You with the Best
PCBX offers standard IPC1 for quick-turn prototype PCBs and standard quality with standard IPC2 at a short turn time, high quality but competitive price, which has been the core of our business since its inception 20 years ago. Up to now, we have won a customer satisfaction rate as high as 99% from more than 10,000 customers around the world. And, you will be one of them.
Hot Tags:
Contact us

If you can't find what you're looking for, please contact us.
Article
Selecting the right PCB surface finish, from options like HASL, ENIG, ENEPIG, and OSP, is crucial for preventing oxidation, ensuring solderability, and meeting reliability standards.
Dive into our PCB glossary to master the key terms and definitions essential for efficient design and production, ensuring your projects run smoothly and effectively.
In the late 1980s, when electronics began to shrink, BGA packaging was developed to integrate more connections within a given area. Today, BGA is widely used with high-connection chips—processors being a good example. BGA uses solder balls at the bottom of the chip to connect it to the circuit board. It provides high density along with good heat dissipation and fast signal transmission, one of the main reasons it is ideal for modern electronics. However, it requires precise techniques of soldering in BGA manufacturing.
