PCBX.com Resources
Your source for industry knowledge, news, and expert insights
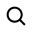
Latest Posts
Article
Preheating PCBs enhances soldering by reducing thermal shock, improving wetting, and activating flux, using methods like conduction, convection, and IR.
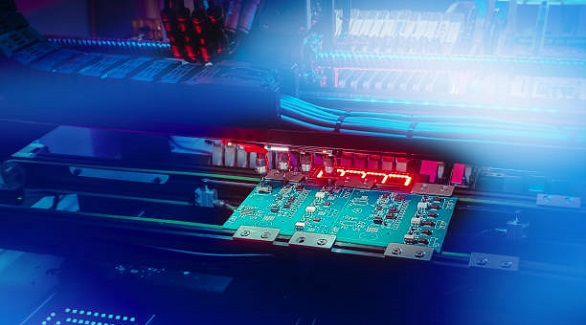
FPGAs with Arduino, like MKR Vidor 4000, enhance electronics prototyping with high flexibility, real-time processing, and customization for diverse applications.
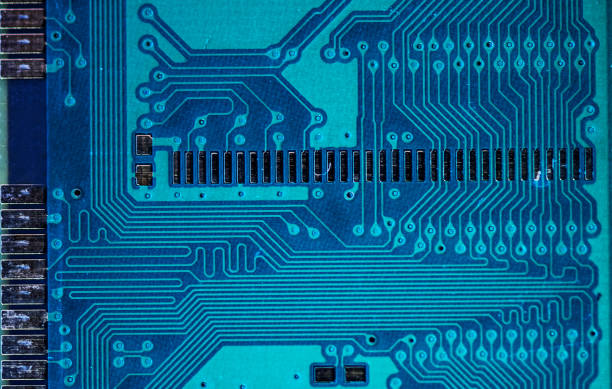
PCB aspect ratio, relating board thickness to via diameter, is key for quality, cost, and reliability in manufacturing, impacting plating and design.
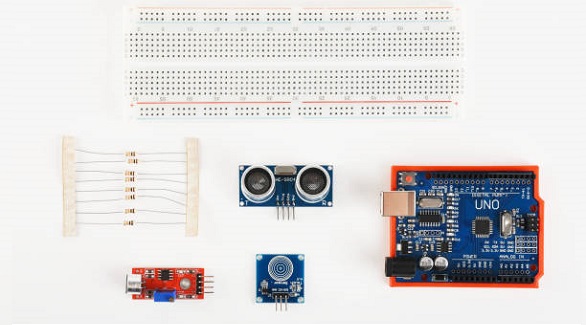
Solderable breadboards offer stable, permanent circuit solutions ideal for prototyping, education, and hobbies, balancing flexibility and long-term use in electronics.
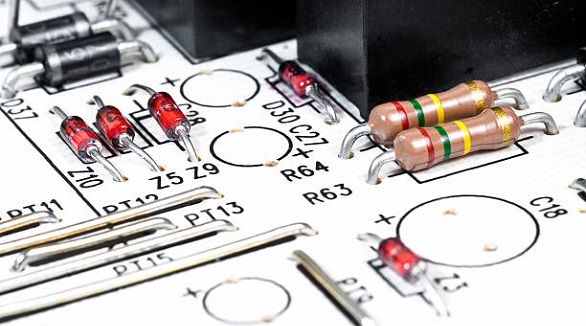
Fuses protect electrical systems from overcurrent, preventing damage and fires. Various types suit different applications, requiring careful selection for safety.
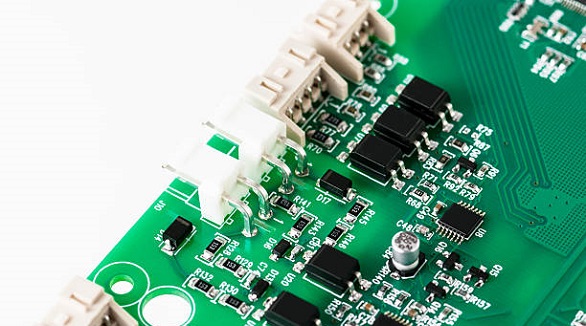
PCB pins enable connectivity in electronics, coming in types like through-hole and surface-mount, for signal transfer, power distribution, and modularity.
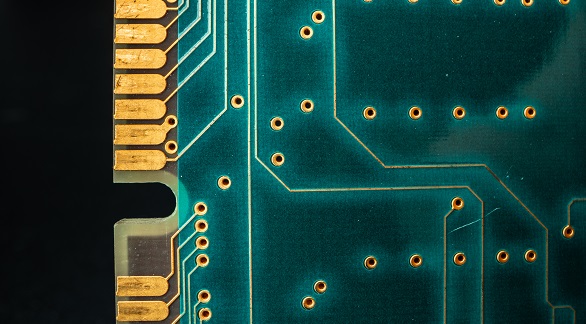
Vias in PCBs connect multiple layers and come in types like through-hole, microvias, blind, and buried. Proper sizing and design optimize PCB performance and reliability, aiding advanced device development.
PCBs are central to electronic devices, featuring holes and vias critical for functionality. Holes, like through-holes and mounting holes, serve electrical or mechanical purposes, while vias ensure electrical connections across PCB layers. Understanding their differences is key for optimal performance, reliability, and manufacturability in PCB design.
