PCBX.com Resources
Your source for industry knowledge, news, and expert insights
Latest Posts
Article

Dry solder joints in PCBs cause unreliable connections, leading to device failure. Prevent with proper heat, cleaning, quality solder, and skilled techniques.
Aluminum PCBs excel in thermal management and mechanical strength for high-performance uses, but FR4 offers better electrical insulation and lower cost.

Reduce PCB noise for reliable analog signals with organized design, strategic layout, component selection, and targeted noise management techniques to enhance performance.
Flex PCB thickness affects performance, offering flexibility, compact design, and durability but demands careful material selection and precise engineering.
The dielectric constant in PCBs affects signal speed, integrity, and impedance, crucial for optimizing high-frequency circuit performance.
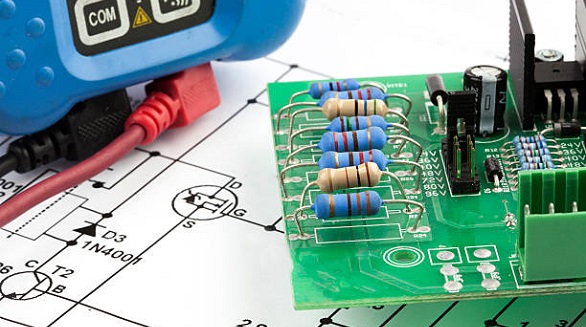
Current limit control circuits safeguard electronics by regulating excess current, ensuring device safety and reliability across various applications and industries.
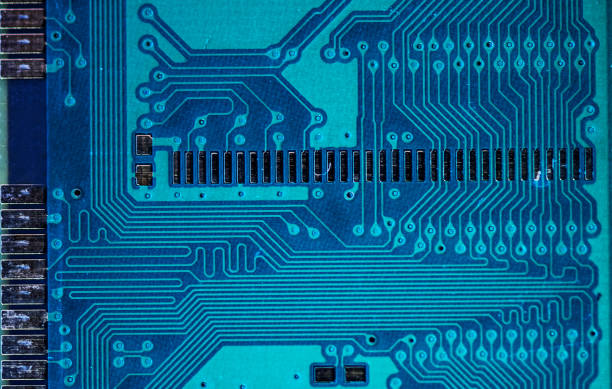
PCB aspect ratio, relating board thickness to via diameter, is key for quality, cost, and reliability in manufacturing, impacting plating and design.
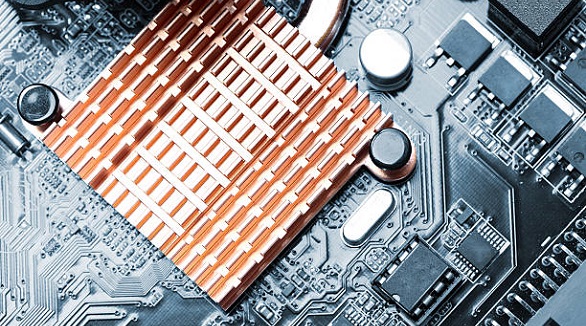
Aluminum PCBs offer cost-effective thermal management for moderate applications, while copper PCBs excel in high-performance electrical and thermal tasks.
