PCBX.com Resources
Your source for industry knowledge, news, and expert insights
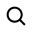
Latest Posts
Article
Wave soldering, crucial for assembling PCBs with through-hole components, remains vital for producing strong joints efficiently, despite SMT advances, by optimizing key parameters.
Selective soldering offers precision and efficiency for complex PCB assemblies, targeting specific areas with improved quality, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility, overcoming limitations of wave soldering.
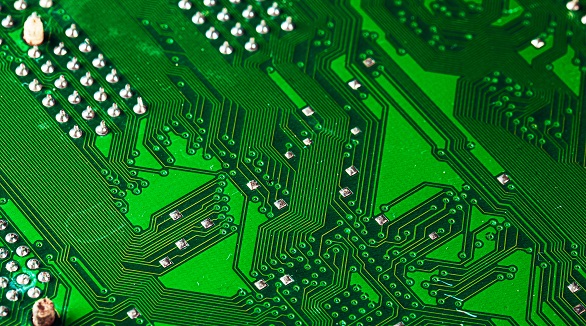
SMD soldering mounts small components on the PCB surface for compact, automated designs but has high setup costs and repair challenges. DIP soldering uses through-hole components for robust, easily repairable, lower-volume applications.
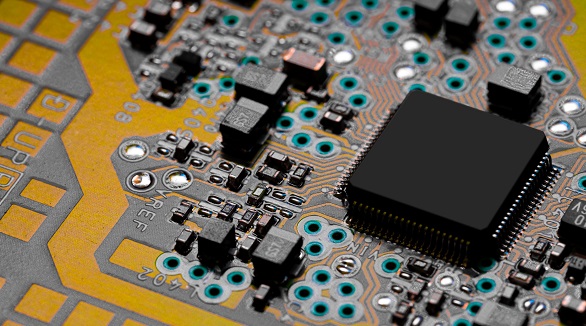
The article introduces the SMT (Surface Mount Technology) assembly process and future trends. Key steps include solder paste printing, chip mounting, reflow soldering, cleaning, inspection, and rework. Future trends highlight fast, flexible systems, green practices, and high-efficiency, intelligent systems. SMT's potential revolutionizes electronics manufacturing with wide industrial applications.

Soldering forms a very important part in the assembly of a PCB. Wave soldering is ideally applied in Through-Hole Technology, while reflow soldering in Surface Mount Technology. Wave soldering involves flux spraying, pre-heating, soldering, and cooling, while in the case of reflow soldering, pre-heating, thermal soak, soldering, and cooling steps are applied. Temperature and time control are the two most critical parameters in the above-mentioned techniques for ensuring soldering reliability.